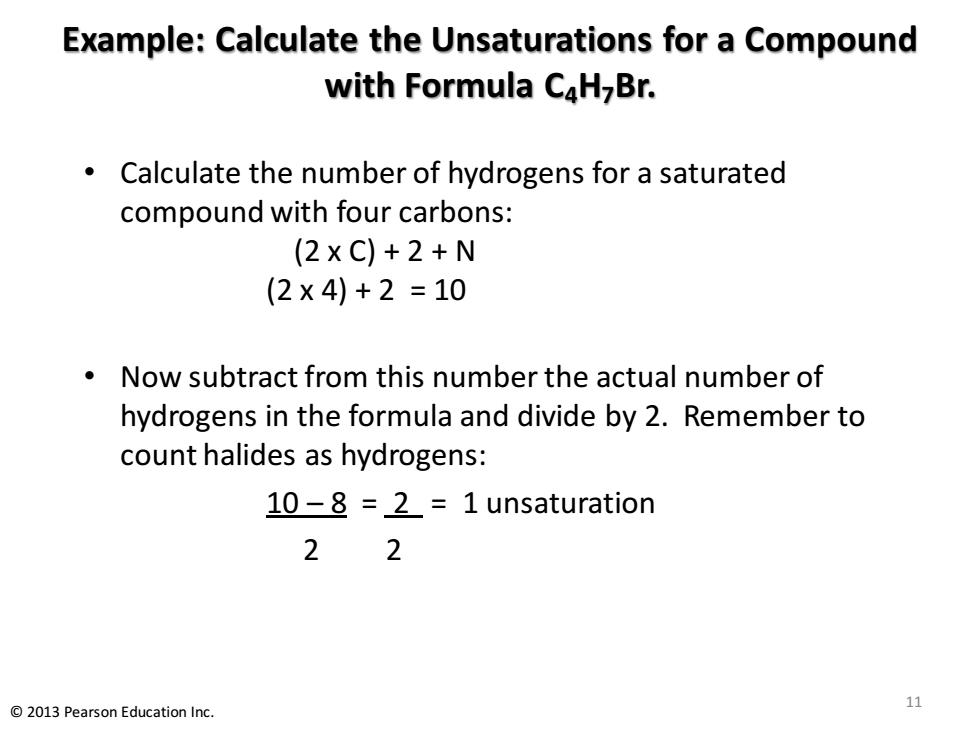
Example:Calculate the Unsaturations for a Compound with Formula C4H-Br. Calculate the number of hydrogens for a saturated compound with four carbons: (2xC)+2+N (2×4)+2=10 Now subtract from this number the actual number of hydrogens in the formula and divide by 2.Remember to count halides as hydrogens: 10-8 =2=1 unsaturation 22 2013 Pearson Education Inc. 11
Example: Calculate the Unsaturations for a Compound with Formula C4H7Br. • Calculate the number of hydrogens for a saturated compound with four carbons: (2 x C) + 2 + N (2 x 4) + 2 = 10 • Now subtract from this number the actual number of hydrogens in the formula and divide by 2. Remember to count halides as hydrogens: 10 – 8 = 2 = 1 unsaturation 2 2 11 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc

Example:Calculate the Unsaturations for a Compound with Formula CH-N. First calculate the number of hydrogens for a saturated compound with six carbons.Add the number of nitrogens: (2XC)+2+N (2×6)+2+1=15 Now subtract from this number the actual number of hydrogens in the formula and divide by 2: 15-7 =8=4 unsaturations 22 12 2013 Pearson Education Inc
Example: Calculate the Unsaturations for a Compound with Formula C6H7N. • First calculate the number of hydrogens for a saturated compound with six carbons. Add the number of nitrogens: (2 x C) + 2 + N (2 x 6) + 2 + 1 = 15 • Now subtract from this number the actual number of hydrogens in the formula and divide by 2: 15 – 7 = 8 = 4 unsaturations 2 2 12 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc

IUPAC Rules for Naming Alkenes 1.Name the longest chain that contains the double bond or double bonds.The name of the chain will end in -ene. 2.Number longest chain so C=C bond or bonds has/have lowest number. 3.The first C of the C=C bond (for C=C bond to have lowest number)identifies the positional location of the double bond. 4.Name the attached functional groups. 5.Combine the names of the attached groups and longest chain, the same as you would with alkanes. 6.For multiple double bonds,indicate the locations of all multiple bonds,use numeric prefixes indicating number of double bonds (-diene,-triene). 7.In a ring,the double bond is assumed to be between carbon 1 and carbon 2. Seager SL,Slabaugh MR,Chemistry for Today:General,Organic and Biochemistry,7th Edition,2011
IUPAC Rules for Naming Alkenes 1. Name the longest chain that contains the double bond or double bonds. The name of the chain will end in –ene. 2. Number longest chain so C=C bond or bonds has/have lowest number. 3. The first C of the C=C bond (for C=C bond to have lowest number) identifies the positional location of the double bond. 4. Name the attached functional groups. 5. Combine the names of the attached groups and longest chain, the same as you would with alkanes. 6. For multiple double bonds, indicate the locations of all multiple bonds, use numeric prefixes indicating number of double bonds (-diene, -triene). 7. In a ring, the double bond is assumed to be between carbon 1 and carbon 2. Seager SL, Slabaugh MR, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic and Biochemistry, 7th Edition, 2011
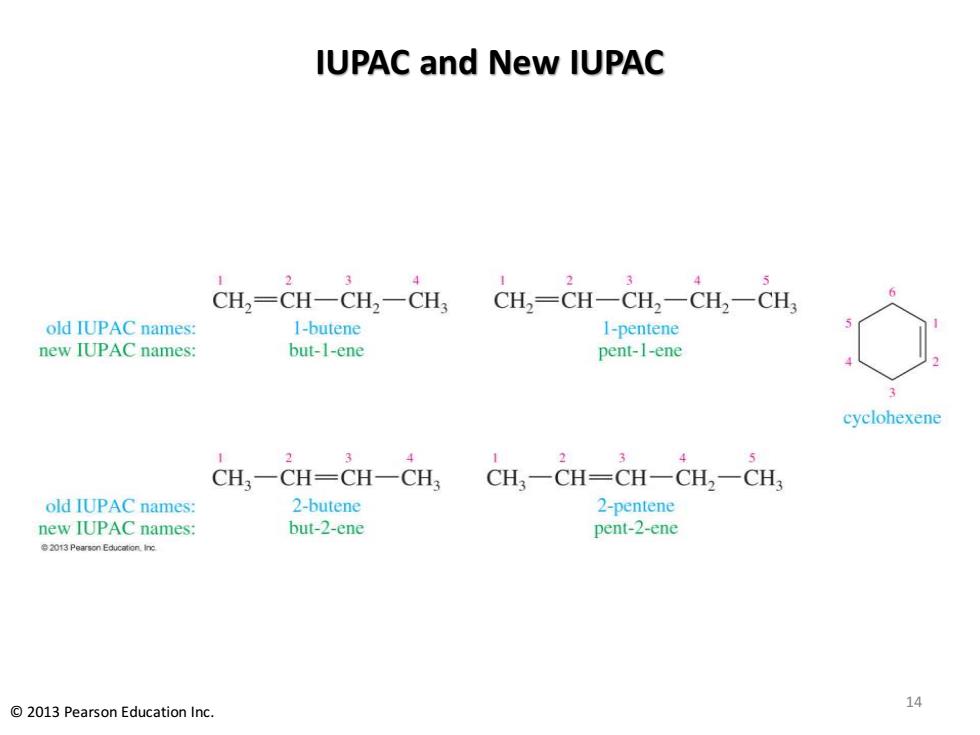
IUPAC and New IUPAC CH,=CH一CH2-CH CH2=CH一CH2一CH2一CH old IUPAC names: 1-butene 1-pentene new IUPAC names: but-1-ene pent-1-ene cyclohexene CH,-CH-CH-CH, CH一CH=CH一CH2-CH old IUPAC names: 2-butene 2-pentene new IUPAC names: but-2-ene pent-2-ene 2013 Pearson Education.nc 2013 Pearson Education Inc. 14
IUPAC and New IUPAC 14 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc

Ring Nomenclature In a ring,the double bond is assumed to be between carbon 1 and carbon 2. CH3 3 CH3 1-methylcyclopentene 3-methylcyclopentene 2013 Pearson Education Inc. 15
Ring Nomenclature 1-methylcyclopentene In a ring, the double bond is assumed to be between carbon 1 and carbon 2. CH3 CH3 1 2 1 2 3 3-methylcyclopentene 15 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc