
Chapter 13 Matrix Displacement Method(矩阵位移法) 月大学 土工程学院 11 TONGI UNIVERSITY COLLGE OF CVIENGINEERING 13.1 introduction Displacement method + Matrix + Computer 月济大学 土工程学院 2 TONGJI UNIVERSITY COVEGINRNG
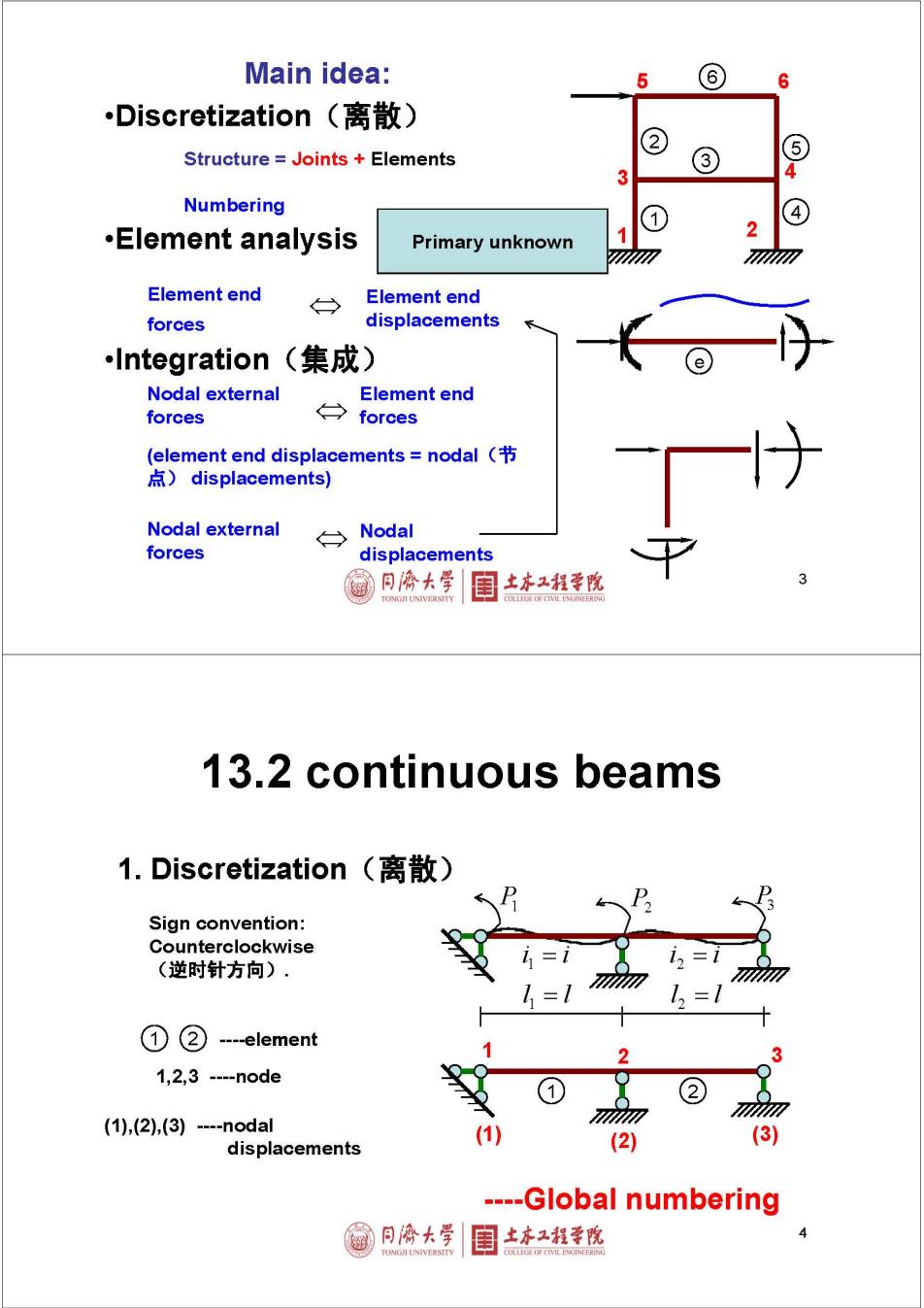
Main idea: 5 6 6 Discretization(离散) Structure Joints Elements 5 3 Numbering ·Element analysis Primary unknown Element end → Element end forces displacements .Integration (集成) Nodal external Element end forces → forces (element end displacements nodal 点)displacements) Nodal external Nodal forces displacements 同海大学 土本工程学院 TONGI UNIVERSITY 13.2 continuous beams 1.Discretization(离散) Sign convention: Counterclockwise i,= (逆时针方向), i= ,= ①② --element 2 1,2,3--node 2 (1),(2),(3)-nodal (3) displacements (2) ----Global numbering 同©大学 闺土本红程学院

2.Element analysis 1,2----local numbering FY= E --element end F forces (2 8 69 --element end (1) (2) (3) 8: displacements Sign convention: Counterclockwise (逆时针方向). 同©大学 土亦工程学院 Force-deformation relations E=4i.6+2i.δ9 41 2i, F=2i6+4i.6号 2i。41 62 Fy=k{δ --element stiffness equation [ --element stiffness matrix [- 始 「4i。2 2i K货 2i。41。 Symmetric (对称). 同像大学 土亦工程学院
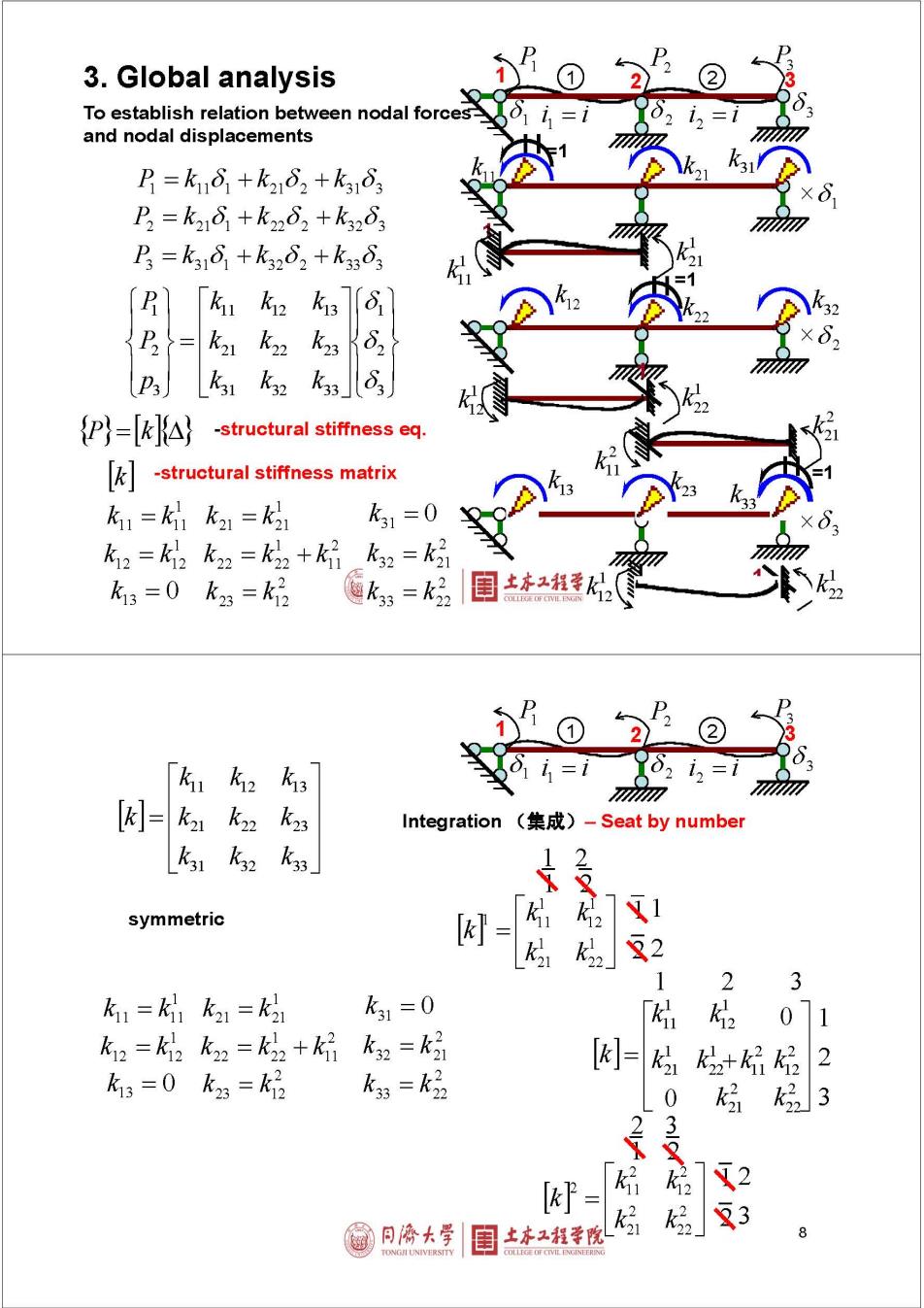
3.Global analysis To establish relation between nodal forces=i and nodal displacements B=k16+k162+k1⊙ D2=k216+k2n62+k263 =k318+k3262+k3⊙3 kat 芝31 3 飞31 P)=kIA -structural stiffness eq. [ -structural stiffness matrix k1=飞21=K21 k31=0 k2=2飞2=k32+k品k2=经 k:=0k3=k号 题k=k经 [ku δ21 =i kat k2 飞3 Integration (集成)-Seat by number ka k32 K3」 及冠 symmetric K KG」 14 2 3 k1=1k21=k21 k1=0 071 k2=2飞2=2+ k2=k号 [= k3=0 k3=品 k朗=k品 保品 2 3 [= 2 3 同降大学 土本工程学院
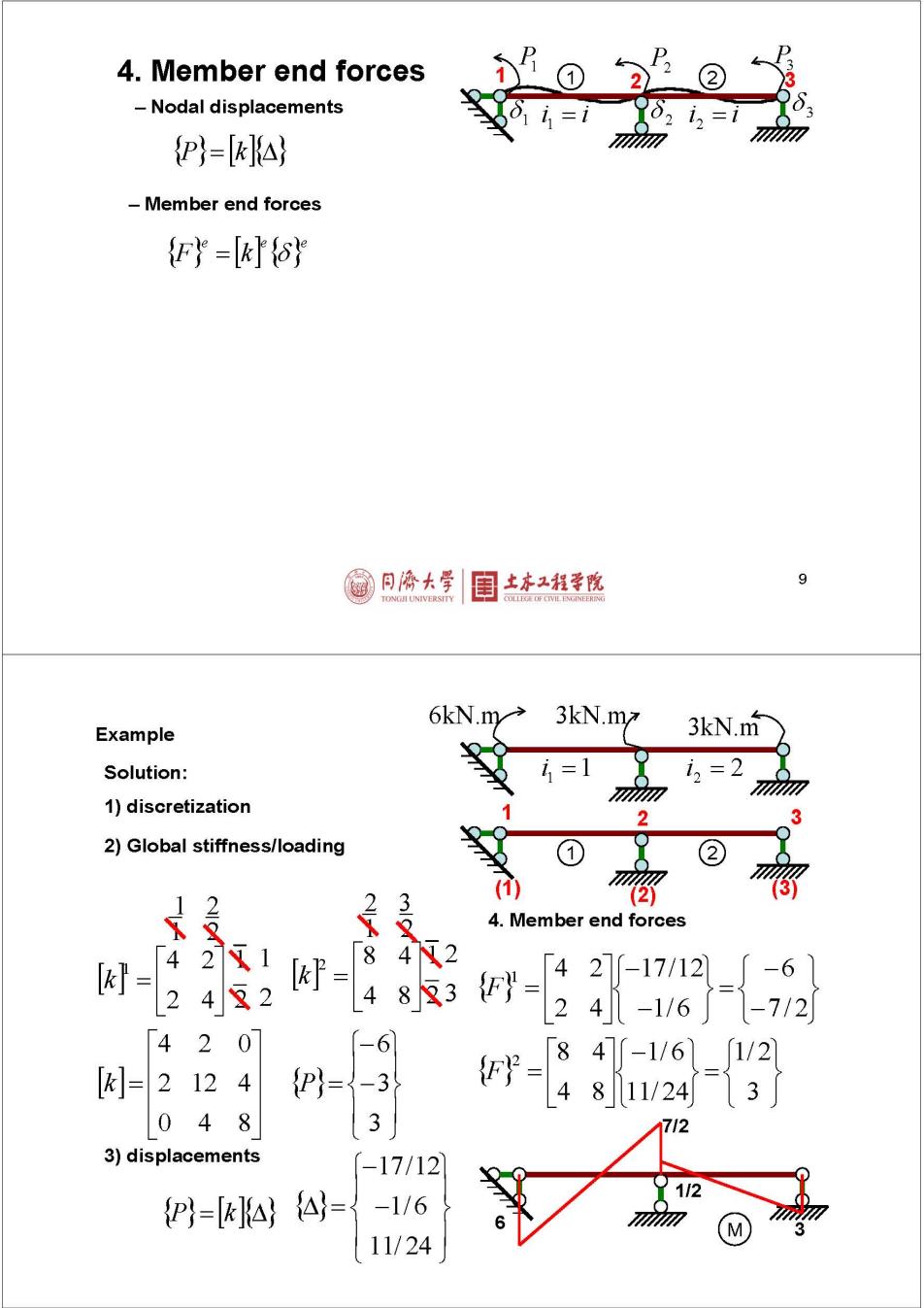
4.Member end forces -Nodal displacements P)=IklA) -Member end forces {Fy=[kδ 同源大学 土本工程学院 6kN.m> 3kN.m Example 3kN.m Solution: 1=1 i2=2 1)discretization 2 2)Global stiffness/loading ② 1 4.Member end forces = 42 1 「84N2 242 k9 区3 -%-{2 4-116j1-712 42 0 -6 [= 212 4 P)= 3 811/24 0 48 3 712 3)displacements -17/12 P)=kHA) A= -1/6 6 11/24