
4 Introduction Some Facts in the Case 5 even name the age-twenty-at which she expects to get married. were not involved.Earlier this year Rae leant that Delia was in There are some feminist teachers at her school who have different a group that smoked and got drunk at weekends;she exerted notions of what women might aim for.But as their ideas centre herself,successfully,to separate Delia from them.Yet Fred and on'careers'for women and advancement through higher education, Rae are not opposed to Delia having an active social life.The they only make much sense to the girls in the 'A'stream-who boyfriend is not only approved of,but,astonishingly,he seems to are the only ones,in a working-class school,likely to have any have been chosen by the parents.At least they introduced him to chance of going to college or university.Delia is not one of them. Delia. Yet Delia's future is not being constructed in a closed system. Behind this constant management of the children is a structure There are changes going on,even in small details.Her mother of authority that makes Fred,very definitely,the 'head of the Rae,for instance,has taught Delia's brother,as well as the two household'and Rae the second-in-command.He is self-confident girls,to cook.On larger issues there is significant tension,even in public,she is not.He contrasts his own behaviour with that of contradiction.Rae herself had done well at school and was obliged his father,'a hard man'(read:violent)who would belt even an to leave before she wanted to,to help her widowed mother.She eighteen year old for bad manners at table.Fred reports with had wanted to become a nurse but her boyfriend(Fred)did not some complacency that he has thrashed each of his children once, like the idea,so she gave it up.Her mild comment,'it's my only hard,and never needed to again.Now he is able to control them regret now',is the nearest she gets in the interview to expressing by 'applied psychology'.We did not ask if Rae was included in anger against Fred. the thrashings.(Statistics on domestic violence suggest that at Even more striking is the fact that Rae kept a job when the least a quarter of all wives have been assaulted by their husbands children were young.This was for a 'good'reason,to pay for the at some time.)Fred puts a lot of energy into coaching local junior house,but still violated an almost universal Australian doctrine football teams and is president of their club;Rae is the treasurer. that mothers should stay home with their pre-school children-a He takes,as a right,a couple of nights out for beers with the boys doctrine duly recited and endorsed by Delia.Rae was defensive each week.Rae,even if she felt it the thing to do,does not have and 'guilty'(her word)about this and has probably come in for the time. a lot of criticism from relatives.She seems to have tried to Clearly this is only the beginning of an analysis of Delia's compensate by being the perfect wife-and-mother ever since.One circumstances.It is perhaps enough to show that what lies behind result is overload,doing a full-time job at home and a nearly full- her relationship with school and intentions about leaving,the time job at work.At thirty-eight she already looks worn and her original question in our research,is a very complex interplay of manner is a little stressed and abrupt.Even Delia,with perception personal and social forces.Much of this has to do with her family's unusual in a fifteen year old,thinks that the job is good for Rae class situation,as educational sociology has long insisted.But as but that she is working too hard. much has to do with the fact that she is a young woman,growing Both Rae and Fred have a clear idea of what a good family is. up in a setting where relations between women and men work in Both have sacrificed something in their own lives to make it a particular way. possible and both have invested a lot of emotion and energy in We cannot understand Delia's life without having a way of trying to produce it.Delia,the youngest child,is now the focus understanding the division of labour between women and men in of that process.Where Rae's mother had never spoken of sex,Rae her houschold,in other families she encounters,in Rae's and and Fred have organized 'round-table sex talks'with their children. Fred's workplaces and in the school.We need to understand the They have tried to be more humane than their own parents power relations between husbands and wives,between men without losing control of the kids.They closely monitor what is and women in trade unions and companies and in voluntary going on in the teenage peer groups.Fred heard rumours of'sex, organizations like the football club.We need to understand how drugs,playing up in toilets'at the school,so he went and challenged Rae's femininity and Fred's masculinity are constructed,how the teachers about it,to be reassured that Delia and her sister Delia's sexual awakening is being managed,how images of

6 Introduction Some Facts in the Case femininity are conveyed to her.We cannot understand Delia women is 45 per cent of the average income of all men. without having some grasp of the tensions and contradictions in Statistics on wealth are harder to come by,as wealth is better these processes and the ways they change between generations. concealed.But there is no doubt at all that men control the major These are not independent issues.They interact;indeed they concentrations of wealth in the Australian economy.The magazine define a sphere of social life that is strongly patterned.As soon as Business Revie Weekly compiles,from a miscellany of sources,an this is recognized,it is obvious that the pattern is not peculiar to annual list of the 200 richest people in the country.In the 1985 Delia,Rae and Fred.What happens in their milieu is part of a list just four of the listed names were women. much wider set of social processes,which must be analyzed to Australia has a reputation for putting women down;are these understand what is happening in Delia's life.Let us turn,therefore, figures exceptional?There are no systematic statistics on men's to evidence about these patterns on the larger scale. and women's incomes on a world scale.But there are many pointers to the state of affairs in individual countries.A recent International Labor Office study of manufacturing industries in The Public World:Wages,Education,Jobs twenty countries,for instance,shows that women's wages are less than men's wages in every country studied.As examples: The division of labour in Delia's household and the kinds of jobs Women's wages as her mother and father hold outside,have roots in the conventional images of man-as-breadwinner and woman-as-home-maker.They of men's also have a hard material base.We do not have Fred and Rae West Germany 73 Japan 43 Prince's tax returns but the general position is known.In 1978, 63 the year of these interviews,the average wages for adult full-time Egypt El Salvador employees in Australia were $239 a week if they were men,$183 81 if they were women.That is to say,a decade after the Equal Pay Figures for Eastern European economies show much the same Case that established a notional policy of sex equality in pay rates, pattern as in Western Europe: women got 77 per cent of what men got.By 1985 this had moved Women's median full- up to 82 per cent. time earnings as of These figures greatly overstate the general level of equality.In the mid-1980s more women than men earn less than a full wage men'了 because they are less than full-time workers.About 36 per cent Czechoslovakia 67 Poland 67 of employed women in Australia are part-timers(Rae Prince being 73 one),compared with 6 per cent of employed men.Taking all Hungary employed people,women's average earnings are 66 per cent of A comparison of Latin American countries uses a different measure, men's (1985 figures).Further,a higher proportion of women setting cut-off points and showing what percentages of women and workers earn no wage because they areare unemployed,and many men fall above and below them.These figures show the percentages more women than men have very low incomes because they are falling in the lowest income category in each country: dependent on a pension or welfare benefit.Figures for 1981/2 Women Men show that 1.97 million women have social security as their main source of income compared with 0.78 million men.The result is Colombia (all employees) 47% 38% 27% 7% that the average income of women who have any income at all is Chile(non-agricultural) Panama(non-agricultural) 34% 6% 48 per cent of the men's average(1981/2).And even that overstates the degree of equality,since a higher proportion of women have Clearly the pattern of unequal income is international,though the no income at all.Adjusting for that,the average income of all level of inequality varies from place to place
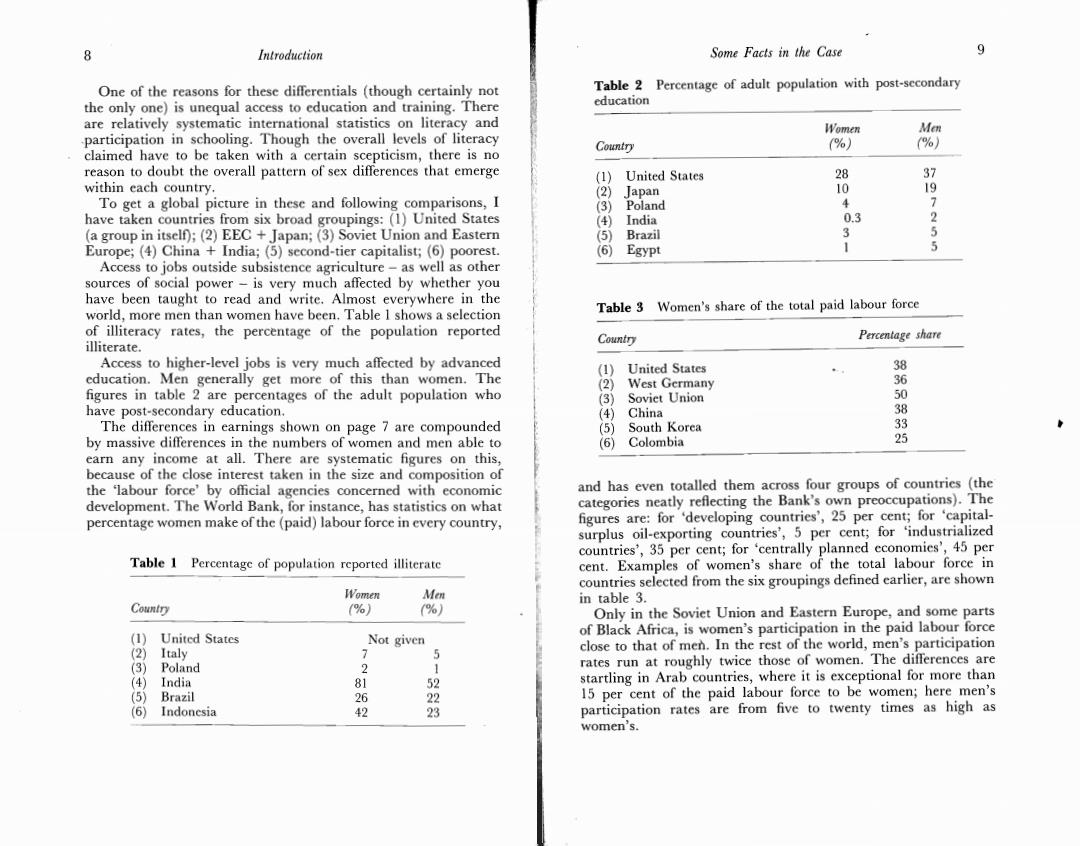
8 Introduction Some Facts in the Case 9 One of the reasons for these differentials (though certainly not Table 2 Percentage of adult population with post-secondary the only one)is unequal access to education and training.There education are relatively systematic international statistics on literacy and Women Men participation in schooling.Though the overall levels of literacy Country %) (%) claimed have to be taken with a certain scepticism,there is no reason to doubt the overall pattern of sex differences that emerge (1) United States 28 37 within each country. (2) apan 10 1 To get a global picture in these and following comparisons,I (3) Poland 7 have taken countries from six broad groupings:(1)United States (4) India 0.3 (a group in itself);(2)EEC Japan;(3)Soviet Union and Eastern (5) Brazil 5 Europe;(4)China India;(5)second-tier capitalist;(6)poorest. (6) Egypt 5 Access to jobs outside subsistence agriculture-as well as other sources of social power-is very much affected by whether you have been taught to read and write.Almost everywhere in the world,more men than women have been.Table I shows a selection Table 3 Women's share of the total paid labour force of illiteracy rates,the percentage of the population reported Percentage share illiterate. Country Access to higher-level jobs is very much affected by advanced (1) United States 38 education.Men generally get more of this than women.The figures in table 2 are percentages of the adult population who West Germany 36 (3) Soviet Union 0 have post-secondary education. (4) China 8 The differences in earnings shown on page 7 are compounded (5) South Korea 33 by massive differences in the numbers of women and men able to (6) Colombia 5 earn any income at all.There are systematic figures on this, because of the close interest taken in the size and composition of the 'labour force'by official agencies concerned with economic and has even totalled them across four groups of countries (the development.The World Bank,for instance,has statistics on what categories neatly reflecting the Bank's own preoccupations).The percentage women make of the(paid)labour force in every country, figures are:for 'developing countries',25 per cent;for 'capital- surplus oil-exporting countries',5 per cent;for 'industrialized countries',35 per cent;for 'centrally planned economies',45 per Table 1 Percentage of population reported illiterate cent.Examples of women's share of the total labour force in countries selected from the six groupings defined earlier,are shown Women Men in table 3. Country (%) %) Only in the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe,and some parts (1) United States Not given of Black Africa,is women's participation in the paid labour force (2) Italy 》 5 close to that of men.In the rest of the world,men's participation (3) Poland 2 1 rates run at roughly twice those of women.The differences are (4) India 81 5 startling in Arab countries,where it is exceptional for more than (5) Brazil 26 22 15 per cent of the paid labour force to be women;here men's (6) Indonesia 42 3 participation rates are from five to twenty times as high as women's

10 Introduction Some Facts in the Case 11 A low labour-force participation rate certainly does not mean given credit at all consist mainly of women.This includes people that large numbers of women do no work.What it means is that dependent on welfare payments and those with no current cash their work is not paid.They work mainly outside the cash economy, income.The difficulties this situation creates for women in getting in housework,childrearing,subsistence agriculture,or labour for finance to buy a house are familiar in the experience of women's a husband or father who markets the product. refuges. This is one aspect of an economic segregation between women and men that also runs through the money economy.In Australia, for instance,men hold 86 per cent of the jobs as administrators, Violence,Prejudice,the State executives and managers,but only 28 per cent of clerical jobs;88 per cent of jobs in trades,process work,labouring and mining The lack of alternative housing is one of the reasons women may and 47 per cent of jobs in sales (1983 figures).A study by stay in,or return to,a violent marriage.Domestic violence is a the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development very large part of all violence.It is difficult to get reliable statistics, (OECD),covering the richer capitalist countries,shows that this but a good many pointers exist.A study of four police stations in pattern is international:"The coefficient of female representation different suburbs of Sydney in 1977-8 showed that calls to shows that women are most under-represented in administrative domestic assaults exceeded calls to other assaults-in some areas and managerial occupations in all countries...Women are over- by a factor of three.(The notorious reluctance of police to intervene represented in clerical occupations in all countries ..They are in domestic violence has some basis in the risk to the police also over-represented in service occupations in all countries.'When themselves:in the United States about 20 per cent of police deaths the broad groupings are broken down,as the OECD study also in the course of duty occur in such cases:)A widely quoted study notes,the degree of concentration can be even more striking:For in Scotland found that 25 per cent of violent crimes reported to example,in the United States in 1978,97 per cent of registered the police were assaults against wives and girlfriends.A national nurses and 94 per cent of elementary teachers within this group sample survey in the United States in the mid-1970s reported were women,while 91 per cent of industrial engineers and 99 per that 28 per cent of couples acknowledged at least one violent cent of airplane pilots were men.' incident and estimated that the true figure was closer to 50 or 60 One reason why women rarely appear near the top of the per cent.In a recent phone-in in Victoria 22 per cent of women economic tree is that in a capitalist economy the ability to had experienced domestic violence but did not report it.While accumulate wealth is very much dependent on one's ability to violence by women against men is far from negligible,the majority command credit.There is reason to think that lenders -banks of serious domestic assaults are by men against women. and other financial institutions -do not extend the credit to This is part of a larger pattern of violence against women.Rapes women that they do to men.The New South Wales (NSW)Anti- reported to the police in Australia rose from around 600 a year Discrimination Board,currently studying this issue,cites cases in 1972-3 to over 1,200 in 1981-2.In the United States the such as this in the early 1980s:'A married couple...had a joint figure rose from 47,000 in 1972 to 79,000 in 1983.There is cheque account with the same suburban bank.They separated reason to think that these figures are still very much understated and then took out individual accounts with the same bank.They and that most rapes are not reported to the police.An alternative both overdrew.The man's cheques were honoured though he approach is to conduct a survey of the general population asking overdrew by $1500.The woman's cheques were bounced although people if they have been victims of various crimes.One such she overdrew by only $300.' survey,done on a very large scale by the Australian Bureau of Direct discrimination in terms of sex,marital status and the Statistics in 1983,estimated 26,700 sexual assaults on adult assumption that a husband is necessarily 'head of the household' women during a year,including 8,600 rapes or attempted rapes. and therefore a wife is not an independent agent,is compounded (Attacks on teenagers would have to be added to this figure.)This by the fact that several categories of people who are usually not gives a rate of five sexual assaults for every 1,000 adult women

12 Introduction Some Facts in the Case 13 which may not seem very many until it is seen in its context of prosecutions a year in the 1940s,rising to 400 to 500 prosecutions very widespread intimidation at a lower level,from wolf-whistles a year from the mid-1950s to the late 1960s.Great peaks and and shouted jokes to sexual harassment in workplaces.A number troughs (117 cases in 1966,1,204 in 1968,a lull in the early of the mothers we interviewed in Delia Prince's suburb will not 1970s)reflect changes in the intensity of policing.In the mid- let their daughters go out on the neighbourhood streets at night 1970s,when Sydney was well on the way to recognition as one because of the fear these assaults generate. of the 'gay capitals'of the world,the rate was rising again.In Homosexual men also have reason to fear assault in public 1975 NSW courts processed 300 homosexual prosecutions under places-and one of the main groups they have to fear are the the Crimes Act and Summary Offences Act (plus others,their police.There are no official statistics on these matters,but police number uncertain,under the Child Welfare Act). violence on a considerable scale has been carefully documented Police surveillance in pursuit of these laws merges into police for New York from 1960 through a twenty-year period in which harassment.'Decoy'squads on homosexual beats produce a stream the growing political strength of gays led to a decline in the of individual prosecutions;there were said to be two such squads attacks.The murder of Dr George Duncan in Adelaide in 1972 operating in Sydney in the mid-1980s,one in Adelaide.Much was almost certainly the result of an entertainment for off-duty more publicity is gained by large-scale police raids on homosexual police which consisted of bashing homosexual men and throwing bars and baths,such as the 1977 raid on the Truxx bar in them in the River Torrens;Dr Duncan could not swim. Montreal(146 arrested),the 1981 raid on bath houses in Toronto Other groups also are involved in attacks on homosexuals.A (304 arrested),or the 1983 raids on Club 80 in Sydney (over 100 1985 phone-in conducted by Gay Hotline in Sydney (sponsored arrested,though few charged).These patterns of intervention in jointly by the police)over two days received calls describing fifty- turn merge into the violence already discussed. three episodes of assault on homosexual men.In almost all these While there are clear patterns of domestic assault and sexual cases the attackers were groups of teenage boys or very young assault against women and of violence against gays,there are men,a fact that raises disturbing questions about the role of other patterns of violence which affect men more drastically than violence and homophobia in the construction of masculinity. women and heterosexual men as well as gays.The 1983 Australian These attacks occur in a context of general hostility towards national survey already mentioned estimated 113,000 assaults in homosexuals that ranges from discrimination in housing to legal a year against women and 278,000 assaults against men.In the danger.Antagonism to lesbians is less explicit than to gay men- same year there were 294 reported homicides in Australia:41 per there is a tendency to make lesbians socially invisible.Nevertheless cent of the victims were women and 59 per cent were men.In it becomes very clear in such cases as a lesbian mother fighting a the United States the 1978 rate of assaults per 1,000 people was custody battle in the courts.Lesbianism itself is liable to be offered 12 for women and 22 for men.In 1981 the United States had as evidence that a woman is unfit to have custody of a child.Gay 23,600 homicides:21 per cent were of women and 79 per cent men face the criminal law because of their sexuality.In most of were of men.In that year the rate of death by homicide per Australia it is still illegal for adult men to commit 'the abominable 100,000 people was 3 for white women,13 for black women,10 crime of buggery'or 'indecent assault upon a male person'.In for white men and 65 for black men. 1985 the state of Queensland even legislated to prevent hotels Those charged with or convicted of violent crime are overwhelm- from serving beer to 'sexual deviants or perverts',meaning gays, ingly men.For instance,in NSW in 1983 some 519 people were along with 'drug dealers'and 'child molesters'.This degree of convicted in the higher criminal courts of homicides,assaults and legislative stigmatization is exceptional;the attitudes underlying like crimes;93 per cent of them were men.A study of homicide it are not. in NSW over a 50-year period found that between 80 per cent Statistics on the operation of these laws are patchy but an and 85 per cent of those charged were men.In the United States indication is given by a study of Sydney court cases by the NSW in 1983,87 per cent of the people arrested for murder were men. Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.This showed 100 to 200 In the same year men were 87 per cent of those arrested for