
Two problems for catabolizing organic compounds in energy-yielding metabolism:产能代谢中有机物分解代谢 1.Conserving some of the energy released as ATP; By substrate-level phosphorylation 2.Disposing of electrons removed from the electron donor. Solved by the production and excretion of fermentation products Chen Feng,Microbiology,SJTU
Chen Feng, Microbiology, SJTU Two problems for catabolizing organic compounds in energy-yielding metabolism:产能代谢中有机物分解代谢 1. Conserving some of the energy released as ATP; By substrate-level phosphorylation 2. Disposing of electrons removed from the electron donor. Solved by the production and excretion of fermentation products
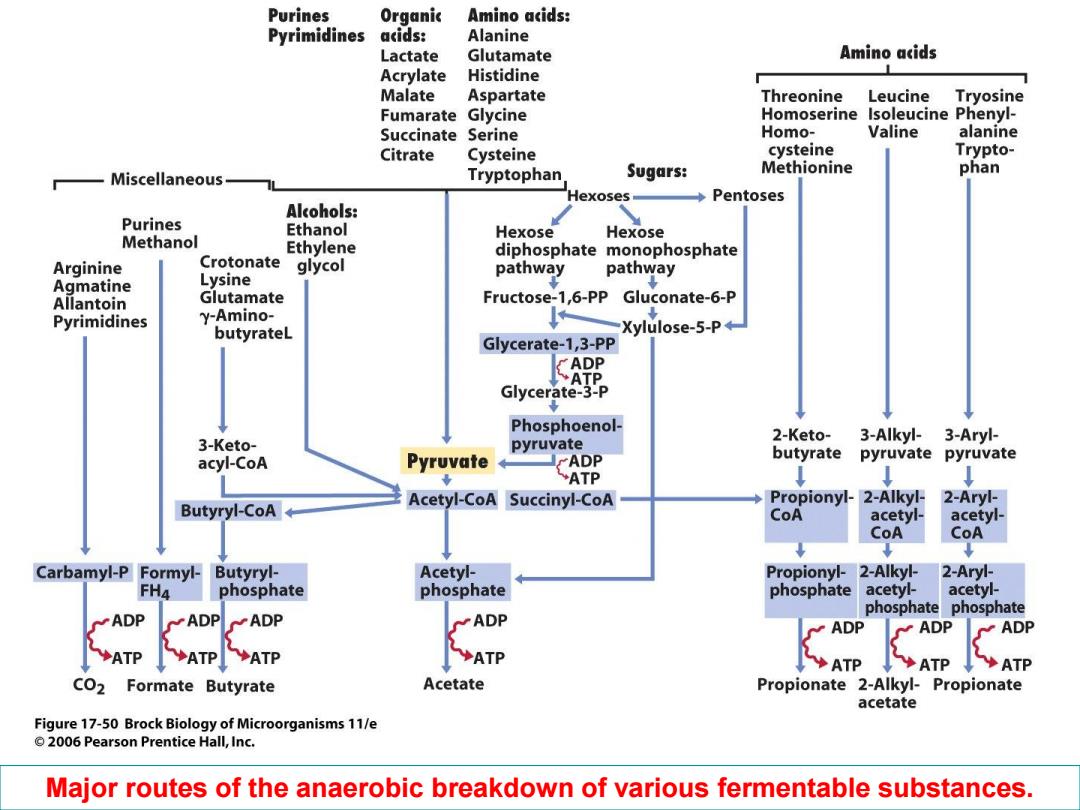
Purines Organic Amino acids: Pyrimidines acids: Alanine Lactate Glutamate Amino acids Acrylate Histidine Malate Aspartate Threonine Leucine Tryosine Fumarate Glycine Homoserine Isoleucine Phenyl- Succinate Serine Homo- Valine alanine Citrate Cysteine cysteine Trypto- Tryptophan Sugars: Methionine phan Miscellaneous- Hexoses- Pentoses Alcohols: Purines Ethanol Hexose Hexose Methanol Ethylene diphosphate monophosphate Arginine Crotonate glycol pathway pathway Agmatine Lysine Allantoin Glutamate Fructose-1,6-PP Gluconate-6-P Pyrimidines y-Amino- butyrateL Xylulose-5-P+ Glycerate-1,3-PP ADP ATP Glycerate-3-P Phosphoenol- 2-Keto- 3-Keto- pyruvate 3-Alkyl- 3-Aryl- acyl-CoA Pyruvate ADP butyrate pyruvate pyruvate ATP Acetyl-CoA Succinyl-CoA Propionyl-2-Alkyl- 2-Aryl- Butyryl-CoA CoA acetyl- acetyl- CoA CoA Carbamyl-P Formyl- Butyryl- Acetyl- Propionyl-2-Alkyl- 2-Aryl- FH4 phosphate phosphate phosphate acetyl- acetyl- phosphate phosphate ADP ADP ADP ADP ◆ATP ◆ATP ◆ATP ◆ATP C02 Formate Butyrate Acetate Propionate 2-Alkyl-Propionate acetate Figure 17-50 Brock Biology of Microorganisms 11/e 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Major routes of the anaerobic breakdown of various fermentable substances
Major routes of the anaerobic breakdown of various fermentable substances

13.16 Fermentative Diversity Some of the main types of fermentations are classified on the basis of products formed.基于 产物的分类 Some fermentations are classified on the basis of the substrate fermented.基于发酵底物的分类 Chen Feng,Microbiology,SJTU
Chen Feng, Microbiology, SJTU 13.16 Fermentative Diversity Some of the main types of fermentations are classified on the basis of products formed.基于 产物的分类 Some fermentations are classified on the basis of the substrate fermented.基于发酵底物的分类
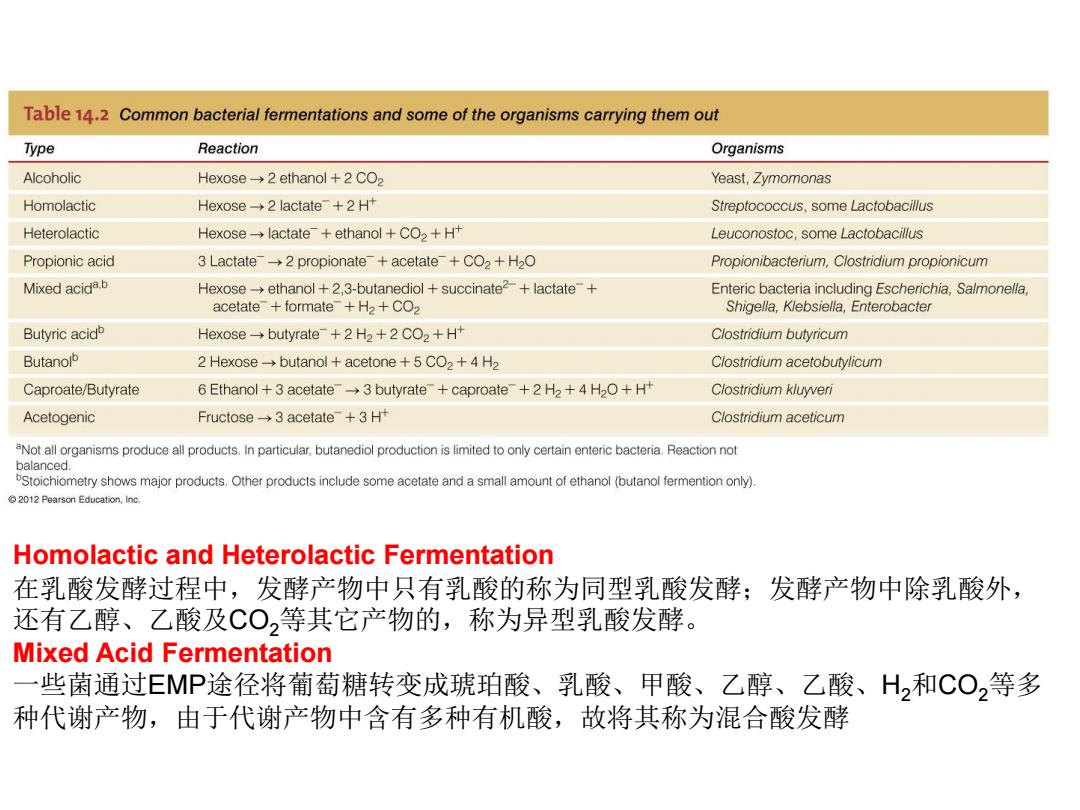
Table 14.2 Common bacterial fermentations and some of the organisms carrying them out Type Reaction Organisms Alcoholic Hexose-2 ethanol +2 CO2 Yeast,Zymomonas Homolactic Hexose-2 lactate+2 H+ Streptococcus,some Lactobacillus Heterolactic Hexose lactate+ethanol +CO2+H+ Leuconostoc,some Lactobacillus Propionic acid 3 Lactate-2 propionate+acetate+CO2+H2O Propionibacterium,Clostridium propionicum Mixed acida.b Hexose-ethanol +2,3-butanediol succinate2-+lactate+ Enteric bacteria including Escherichia,Salmonella, acetate formate+H2+CO2 Shigella,Klebsiella,Enterobacter Butyric acidb Hexose-butyrate+2 H2+2 CO2+H+ Clostridium butyricum Butanolb 2 Hexose-butanol acetone +5 CO2+4 H2 Clostridium acetobutylicum Caproate/Butyrate 6 Ethanol +3 acetate-3 butyrate+caproate+2 H2+4 H2O+H Clostridium kluyveri Acetogenic Fructose3 acetate+3H Clostridium aceticum aNot all organisms produce all products.In particular.butanediol production is limited to only certain enteric bacteria.Reaction not balanced. bStoichiometry shows major products.Other products include some acetate and a small amount of ethanol (butanol fermention only). 2012 Pearson Education,Inc Homolactic and Heterolactic Fermentation 在乳酸发酵过程中,发酵产物中只有乳酸的称为同型乳酸发酵;发酵产物中除乳酸外, 还有乙醇、乙酸及CO,等其它产物的,称为异型乳酸发酵。 Mixed Acid Fermentation 一些菌通过EMP途径将葡萄糖转变成琥珀酸、乳酸、甲酸、乙醇、乙酸、H2和CO,等多 种代谢产物,由于代谢产物中含有多种有机酸,故将其称为混合酸发酵
Homolactic and Heterolactic Fermentation 在乳酸发酵过程中,发酵产物中只有乳酸的称为同型乳酸发酵;发酵产物中除乳酸外, 还有乙醇、乙酸及CO2等其它产物的,称为异型乳酸发酵。 Mixed Acid Fermentation 一些菌通过EMP途径将葡萄糖转变成琥珀酸、乳酸、甲酸、乙醇、乙酸、H2和CO2等多 种代谢产物,由于代谢产物中含有多种有机酸,故将其称为混合酸发酵

Table 14.3 Some unusual bacterial fermentations Type Reaction Organisms Acetylene 2 C2H2+3 H2O-ethanol acetate+H+ Pelobacter acetylenicus Glycerol 4 Glycerol +2 HCO37 acetate+5H++4H2O Acetobacterium spp Resorcinol (aromatic) 2 CeHa(OH)2+6 H2O4 acetate+butyrate+H+ Clostridium spp. Phloroglucinol(aromatic) C6H6O3+3 H2O3 acetate+3 H+ Pelobacter massiliensis Pelobacter acidigallici Putrescine 10 CaH12N2+26 H2O-6 acetate+7 butyrate+20 NH4+ Unclassified gram-positive nonsporulating anaerobes +16H2+13H Citrate Citrate3+2 H2O-formate+2 acetate+HCO+H+ Bacteroides spp. Aconitate Aconitate3-+H++2 H2O-2 CO2+2 acetate +H2 Acidaminococcus fermentans Glyoxylate 4 Glyoxylate+3 H++3 H2O6 CO2+5 H2+glycolate Unclassified gram-negative bacterium Benzoate 2 Benzoate-cyclohexane carboxylate+3 acetate Syntrophus aciditrophicus +HCO3+3H+ 2012 Pearson Education,Inc. Many unusual fermentations are carried out by a very restricted group of anaerobes. 乙炔,甘油,间苯二酚,间苯三酚,腐胺,柠檬酸,乌头酸,乙醛酸,苯甲酸
Many unusual fermentations are carried out by a very restricted group of anaerobes. 乙炔,甘油,间苯二酚,间苯三酚,腐胺,柠檬酸,乌头酸,乙醛酸,苯甲酸