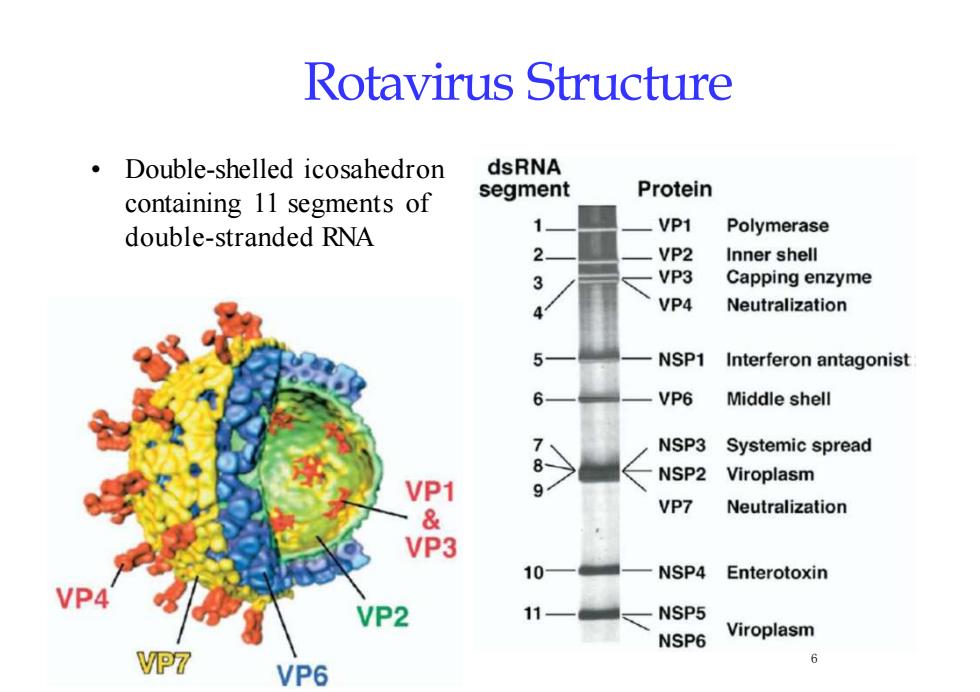
Rotavirus StructuredsRNADouble-shelledicosahedronProteinsegmentcontaining 11 segments of1VP1Polymerasedouble-stranded RNA2VP2InnershellVP3Capping enzyme3VP4Neutralization8-5NSP1Interferonantagonist6VP6Middleshell>NSP3Systemic spread8NSP2ViroplasmVP19VP7Neutralization&VP310NSP4EnterotoxinVP411NSP5VP2ViroplasmNSP66VP7VP6
Rotavirus Structure • Double-shelled icosahedron containing 11 segments of double-stranded RNA 6
Rotavirus ClassificationGroups: A, B, C,D,E, F, G.According to inner protein VP6: Most human illness is caused by group A, afew by groupsBand C. Group Bis reported in China and India onlySerotypes: G1-23, P1-31Defined by two outer-capsid protein VP7 (Gprotein) andVP4 (P protein): Only 10 Gtypes and 11 Ptypes found in human isolates
7 Rotavirus Classification Groups: A, B, C, D, E, F, G • According to inner proteinVP6 • Most human illness is caused by group A, a few by groups B and C. Group B is reported in China and India only. Serotypes: G1-23, P1-31 • Defined by two outer-capsid protein VP7 (G protein) and VP4 (P protein) • Only 10 G types and 11 P types found in human isolates

RotavirusDiseaseBurdenGlobally,estimated to cause 125million casesofdiarrhea.Ofthese, 18 million cases are considered at leastmoderately severe, with approximately 600,000 deathsper year.In china, estimated to cause more than 10 million casesofdiarrhea per year.:In U.S., estimated 3 million cases of diarrhea, 50,000hospitalizations, and 20-40 deaths annually in U.S
8 Rotavirus Disease Burden • Globally, estimated to cause 125 million cases of diarrhea. Of these, 18 million cases are considered at least moderately severe, with approximately 600,000 deaths per year. • In china, estimated to cause more than 10 million cases of diarrhea per year. • In U.S., estimated 3 million cases of diarrhea, 50,000 hospitalizations, and 20-40 deaths annually in U.S

Pathogens for acute gastroenteritis inchildrenFrequencyof enteropathogensinEuropeanchildren(O-5y)PathogenFrequency,%Rotavirus10-35Norovirus2-204-13Campylobacter2-10Adenovirus5-8Salmonella14.5EPECYersinia0.4-30.9-3Giardia0-3Cryptosporidium0-2EAggECShigella0.31.4STEC0-3ETEC0-0.50-4Entamoeba45-60No agent detectedEPEC=enteropathogenic Escherichia coli; EAggEC=enteroagenteroaggregative E coli; STEC-Shiga toxin-producing E coli,ETEC=enterotoxigenic strainsof Ecoli
Pathogens for acute gastroenteritis in children Frequency of enteropathogens in E u r o p e an children (0–5 y) 9
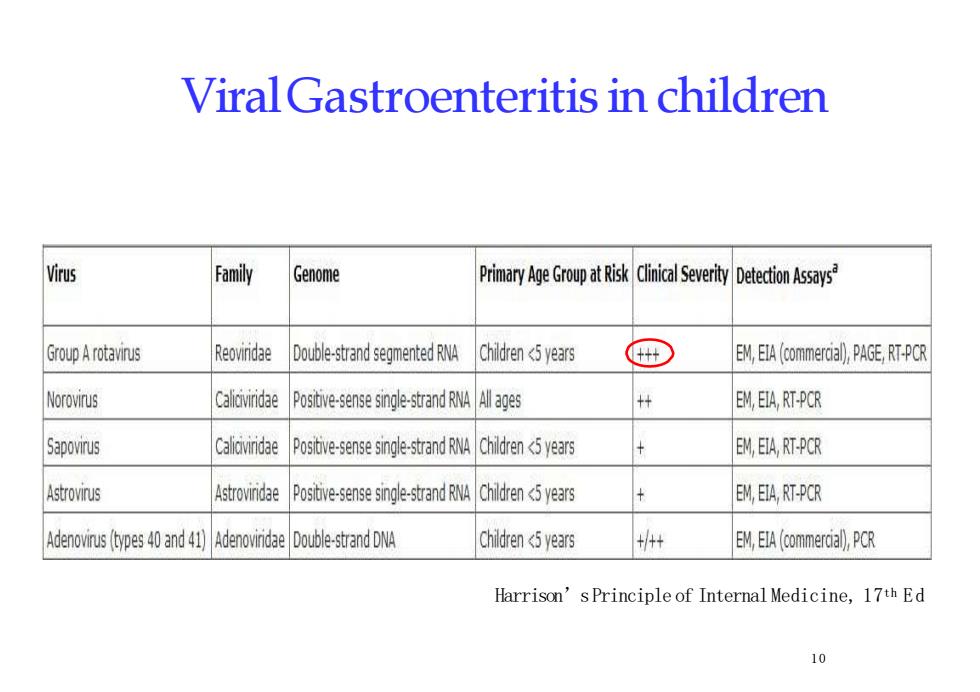
ViralGastroenteritis in childrenFamilyVirusPrimary Age Group at Risk Clnial Severty Detection AssaysGenomeReoviridaeDouble-strand segmented RNAChildren<5 years+EM,EIA(commercal),PAGERT-PCRGroup ArotavirusNorovrusCaliviridaeEM,EIA, RT-PCRPositive-sense single-strand RNA Allages++CaliviridaeEM,EIA,RT-PCRSapovirusPositive-sense single-strand RNA Children<5 yearsAstrovrusAstrovidaePositivesensesinglestrandRNhildrenyearsEM, EIA, RT-PCR+++chidren<5 earsAdenovirus (types 40 and 41)Adenovinidae Double-strand DNAEM, EIA (commercial,CRHarrison'sPrinciple of Internal Medicine,17th Ed10
Viral Gastroenteritis in children Harrison’sPrinciple of InternalMedicine, 17th E d 1 0