
Inhibitory pathways Results in a hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane.Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP)are 1.releases neurons releases neurotransmitter molecules, such as y-aminobutyric acid (GABA)or glycine.Increase in the permeability of specific ions,such as,potassium and chloride ions 2.the influx of chloride and efflux of potassium cause a weak hyperpolarization or IPSP that moves the postsynaptic potential away from its firing threshold
Inhibitory pathways • Results in a hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane. Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP) are 1. releases neurons releases neurotransmitter molecules, such as γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) or glycine. Increase in the permeability of specific ions, such as, potassium and chloride ions 2. the influx of chloride and efflux of potassium cause a weak hyperpolarization or IPSP that moves the postsynaptic potential away from its firing threshold

Overview of parkinson's disease Parkinson's disease(PD)is a progressive disorder of the nervous system.With an annual incidence of approximately 20 new cases per 100,000 people. PD is generally age-specific;it is estimated that approximately 1%of the population over age 60 has PD
Overview of parkinson’s disease • Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive disorder of the nervous system. With an annual incidence of approximately 20 new cases per 100,000 people. • PD is generally age-specific; it is estimated that approximately 1% of the population over age 60 has PD
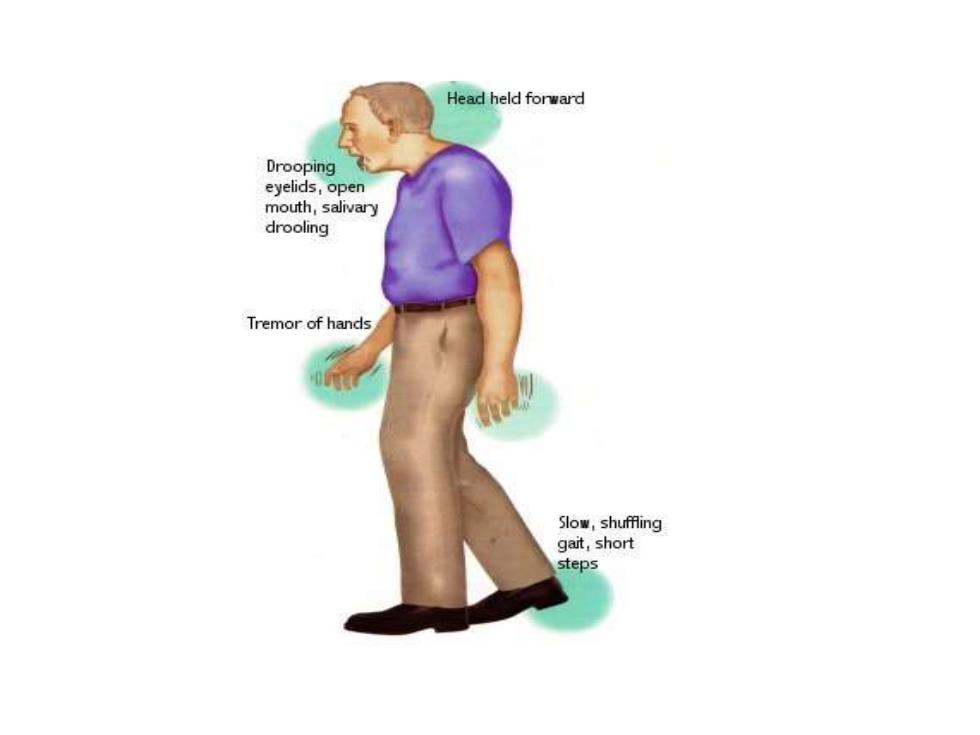
Head held forward Drooping eyelids,open mouth,salivary drooling Tremor of hands Slow,shuffing gait,short steps