
上游充通大兽 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Chapter 8: Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics 酶:基本概念及动力学 Berg·Tymoczko·Stryer Biochemistry Sixth Edition
Berg • Tymoczko • Stryer Biochemistry Sixth Edition Chapter 8: Enzymes: Basic Concepts and Kinetics 酶:基本概念及动力学
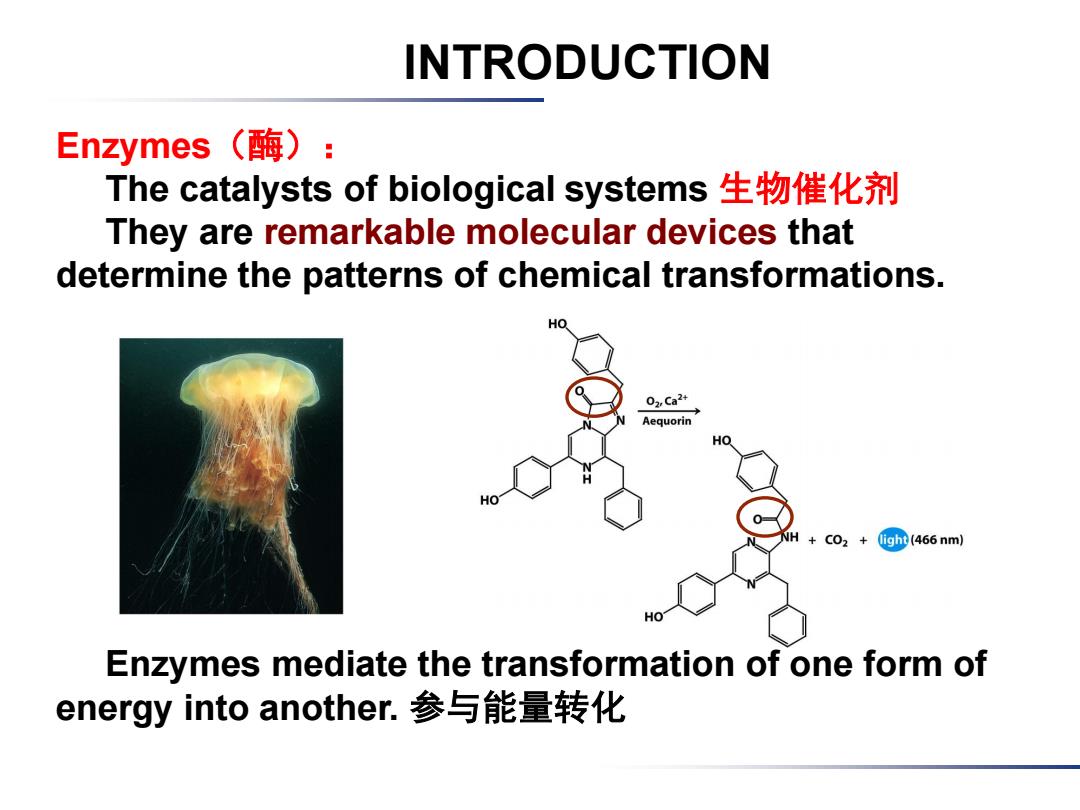
INTRODUCTION Enzymes(酶): The catalysts of biological systems生物催化剂 They are remarkable molecular devices that determine the patterns of chemical transformations. HO 02,Ca24 Aequorin HO NH + CO2 (ig (466 nm) Enzymes mediate the transformation of one form of energy into another.参与能量转化
Enzymes(酶): The catalysts of biological systems 生物催化剂 They are remarkable molecular devices that determine the patterns of chemical transformations. Enzymes mediate the transformation of one form of energy into another. 参与能量转化 INTRODUCTION
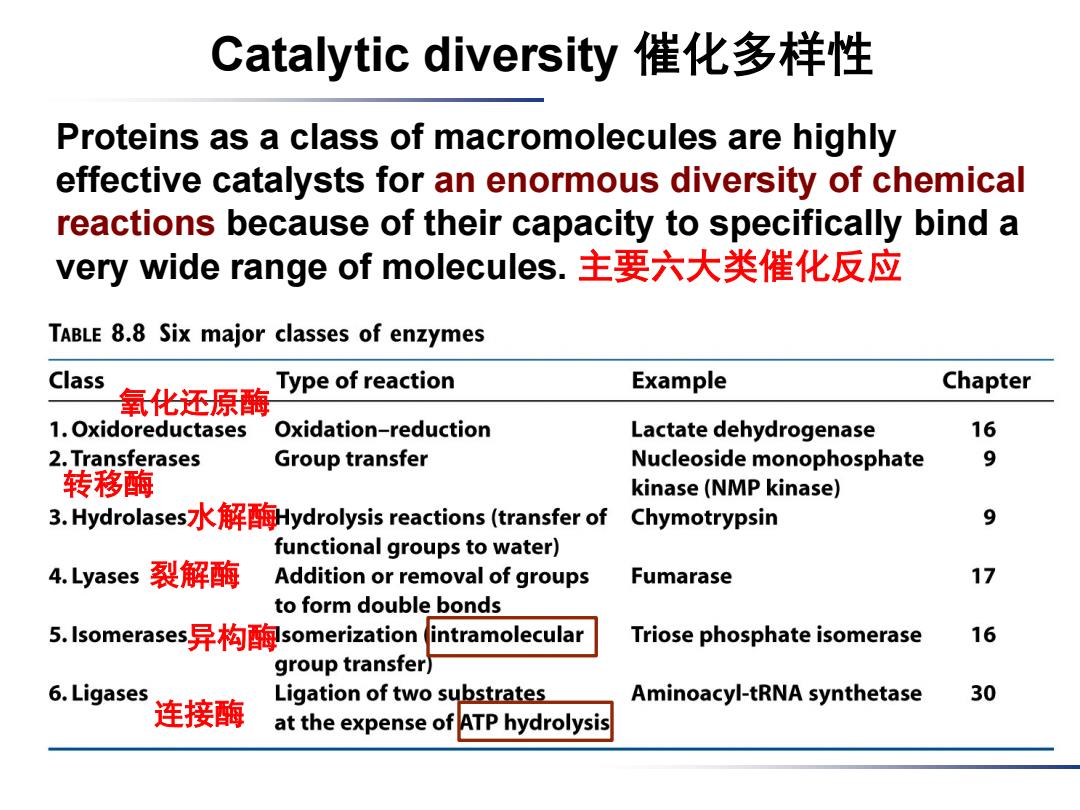
Catalytic diversity催化多样性 Proteins as a class of macromolecules are highly effective catalysts for an enormous diversity of chemical reactions because of their capacity to specifically bind a very wide range of molecules.主要六大类催化反应 TABLE 8.8 Six major classes of enzymes Class Example Chapter 氧化还原酶 Type of reaction 1.Oxidoreductases Oxidation-reduction Lactate dehydrogenase 16 2.Transferases Group transfer Nucleoside monophosphate 9 转移酶 kinase(NMP kinase) 3.Hydrolases:水解酶Hydrolysis reactions(transfer of Chymotrypsin 9 functional groups to water) 4.Lyases 裂解酶 Addition or removal of groups Fumarase 17 to form double bonds 5.Isomerases!异构酶somerization(intramolecular Triose phosphate isomerase 16 group transfer) 6.Ligases Ligation of two substrates Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase 30 连接酶 at the expense of ATP hydrolysis
Catalytic diversity 催化多样性 Proteins as a class of macromolecules are highly effective catalysts for an enormous diversity of chemical reactions because of their capacity to specifically bind a very wide range of molecules. 主要六大类催化反应 氧化还原酶 转移酶 水解酶 裂解酶 异构酶 连接酶
Enzymes Are Classified on the Basis of the Types of Reactions That They Catalyze Nomenclature命名: 1.Common names:with little information about the reactions. trypsin:a proteolytic enzyme secreted by the pancreas. 2.Most enzymes are named for their substrates and for the reactions that they catalyze,with the suffix "ase"added. ATPase:an enzyme that breaks down ATP, ATP synthase:an enzyme that synthesizes ATP. Nomenclature for enzymes:in 1964,Enzyme Commission of the International Union of Biochemistry(国际生化联盟) .Reactions were divided into six major groups.These groups were subdivided and further subdivided,so that a four-digit number preceded by the letters EC for Enzyme Commission could precisely identify all enzymes
Enzymes Are Classified on the Basis of the Types of Reactions That They Catalyze Nomenclature命名: 1. Common names: with little information about the reactions. - trypsin: a proteolytic enzyme secreted by the pancreas. 2. Most enzymes are named for their substrates and for the reactions that they catalyze, with the suffix "ase" added. - ATPase: an enzyme that breaks down ATP, - ATP synthase: an enzyme that synthesizes ATP. Nomenclature for enzymes:in 1964,Enzyme Commission of the International Union of Biochemistry(国际生化联盟) •Reactions were divided into six major groups. These groups were subdivided and further subdivided, so that a four-digit number preceded by the letters EC for Enzyme Commission could precisely identify all enzymes
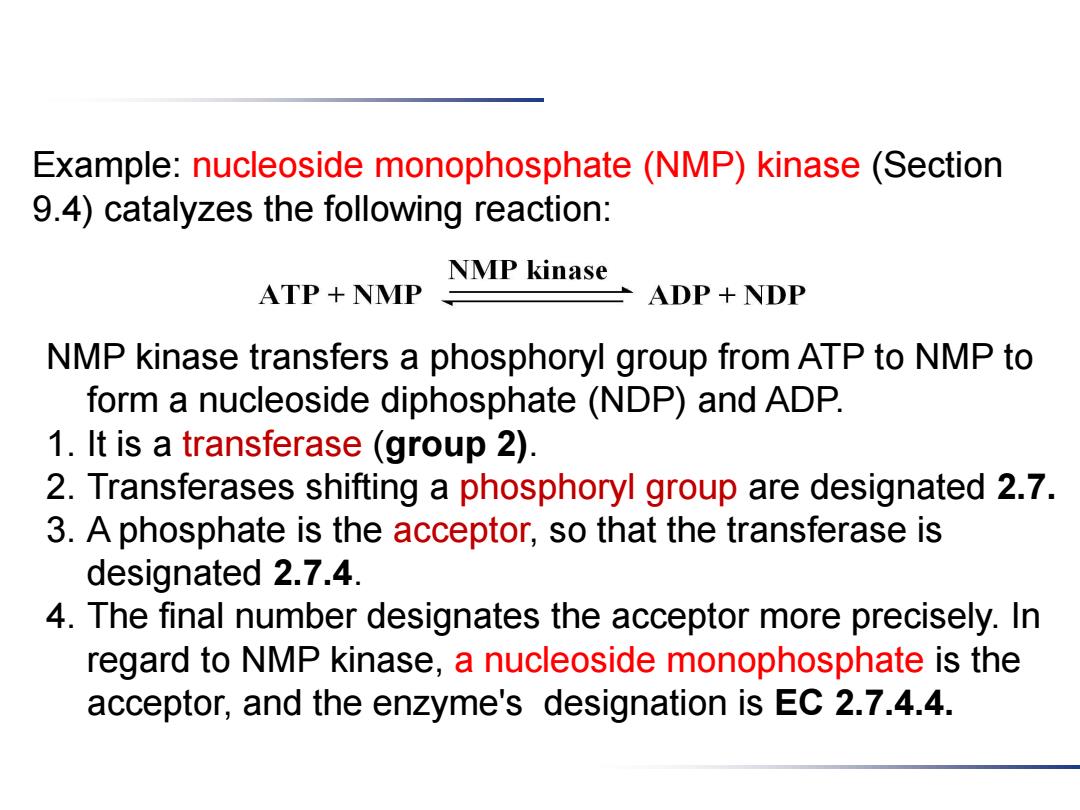
Example:nucleoside monophosphate (NMP)kinase(Section 9.4)catalyzes the following reaction: NMP kinase ATP NMP ADP+NDP NMP kinase transfers a phosphoryl group from ATP to NMP to form a nucleoside diphosphate(NDP)and ADP. 1.It is a transferase (group 2). 2.Transferases shifting a phosphoryl group are designated 2.7. 3.A phosphate is the acceptor,so that the transferase is designated 2.7.4. 4.The final number designates the acceptor more precisely.In regard to NMP kinase,a nucleoside monophosphate is the acceptor,and the enzyme's designation is EC 2.7.4.4
Example: nucleoside monophosphate (NMP) kinase (Section 9.4) catalyzes the following reaction: NMP kinase transfers a phosphoryl group from ATP to NMP to form a nucleoside diphosphate (NDP) and ADP. 1. It is a transferase (group 2). 2. Transferases shifting a phosphoryl group are designated 2.7. 3. A phosphate is the acceptor, so that the transferase is designated 2.7.4. 4. The final number designates the acceptor more precisely. In regard to NMP kinase, a nucleoside monophosphate is the acceptor, and the enzyme's designation is EC 2.7.4.4