
The most striking characteristics:特点 一 Catalytic power(催化高效性) Specificity(选择性) Chemical nature: 一Proteins蛋白质(Nearly all known enzymes are proteins,but proteins are not an absolute monopoly on catalysis); Catalytically active RNA molecules a biocatalyst early in evolution (Section 2.2.2)
The most striking characteristics:特点 - Catalytic power (催化高效性) - Specificity (选择性) Chemical nature: - Proteins 蛋白质 (Nearly all known enzymes are proteins, but proteins are not an absolute monopoly on catalysis); - Catalytically active RNA molecules : a biocatalyst early in evolution (Section 2.2.2)
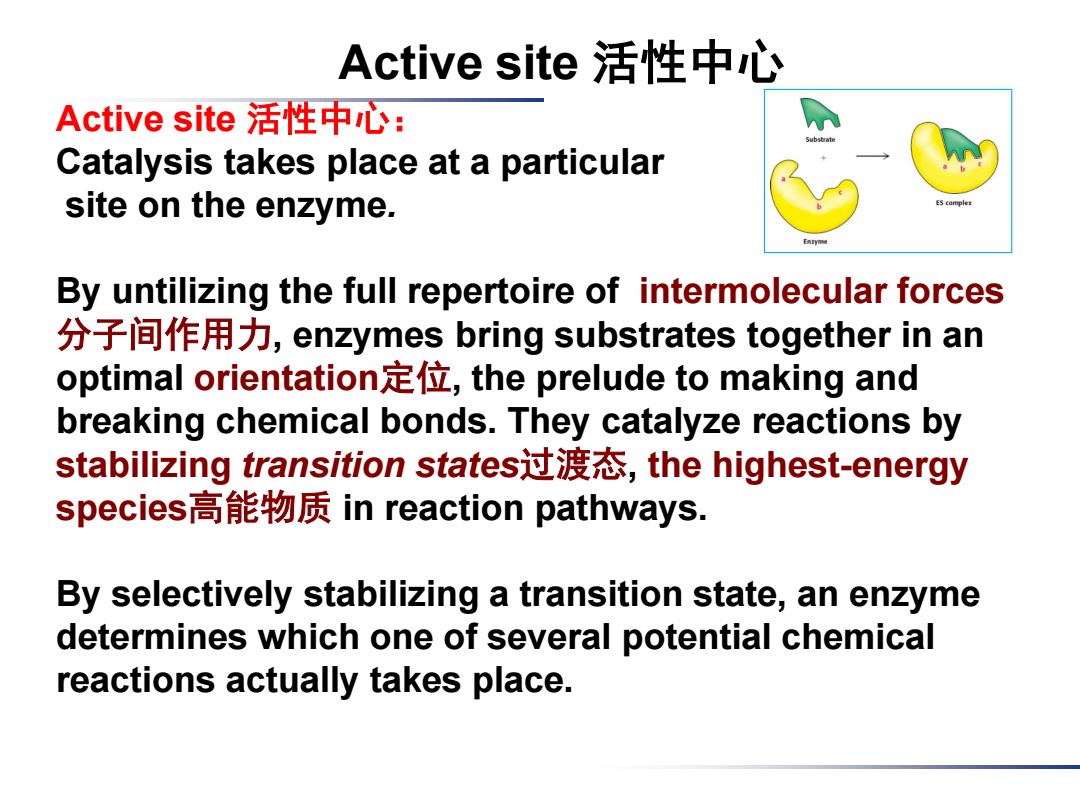
Active site活性中心 Active site活性中心: Catalysis takes place at a particular site on the enzyme. By untilizing the full repertoire of intermolecular forces 分子间作用力,enzymes bring substrates together in an optimal orientation定位,the prelude to making and breaking chemical bonds.They catalyze reactions by stabilizing transition states过渡态,the highest-.energy species高能物质in reaction pathways. By selectively stabilizing a transition state,an enzyme determines which one of several potential chemical reactions actually takes place
Active site 活性中心: Catalysis takes place at a particular site on the enzyme. By untilizing the full repertoire of intermolecular forces 分子间作用力, enzymes bring substrates together in an optimal orientation定位, the prelude to making and breaking chemical bonds. They catalyze reactions by stabilizing transition states过渡态, the highest-energy species高能物质 in reaction pathways. By selectively stabilizing a transition state, an enzyme determines which one of several potential chemical reactions actually takes place. Active site 活性中心

OUTLINES 1.Enzymes Are Powerful and Highly Specific Catalysts一概论 2.Free Energy Is a Useful Thermodynamic Function for Understanding Enzymes一热力学 3.Enzymes Accelerate Reactions by Facilitating the Formation of the Transition State一化学 4. The Michaelis-Menten Model Accounts for the Kinetic Properties of Many Enzymes一动力学 5.Enzymes Can Be Inhibited by Specific Molecules一抑制作用
1. Enzymes Are Powerful and Highly Specific Catalysts - 概论 2. Free Energy Is a Useful Thermodynamic Function for Understanding Enzymes -热力学 3. Enzymes Accelerate Reactions by Facilitating the Formation of the Transition State -化学 4. The Michaelis-Menten Model Accounts for the Kinetic Properties of Many Enzymes -动力学 5. Enzymes Can Be Inhibited by Specific Molecules -抑制作用 OUTLINES

OUTLINES 1.Enzymes Are Powerful and Highly Specific Catalysts 2.Free Energy Is a Useful Thermodynamic Function for Understanding Enzymes一热力学 3. Enzymes Accelerate Reactions by Facilitating the Formation of the Transition State一化学 4.The Michaelis-Menten Model Accounts for the Kinetic Properties of Many Enzymes一动力学 5.Enzymes Can Be Inhibited by Specific Molecules一抑制作用
1. Enzymes Are Powerful and Highly Specific Catalysts 2. Free Energy Is a Useful Thermodynamic Function for Understanding Enzymes -热力学 3. Enzymes Accelerate Reactions by Facilitating the Formation of the Transition State -化学 4. The Michaelis-Menten Model Accounts for the Kinetic Properties of Many Enzymes -动力学 5. Enzymes Can Be Inhibited by Specific Molecules -抑制作用 OUTLINES
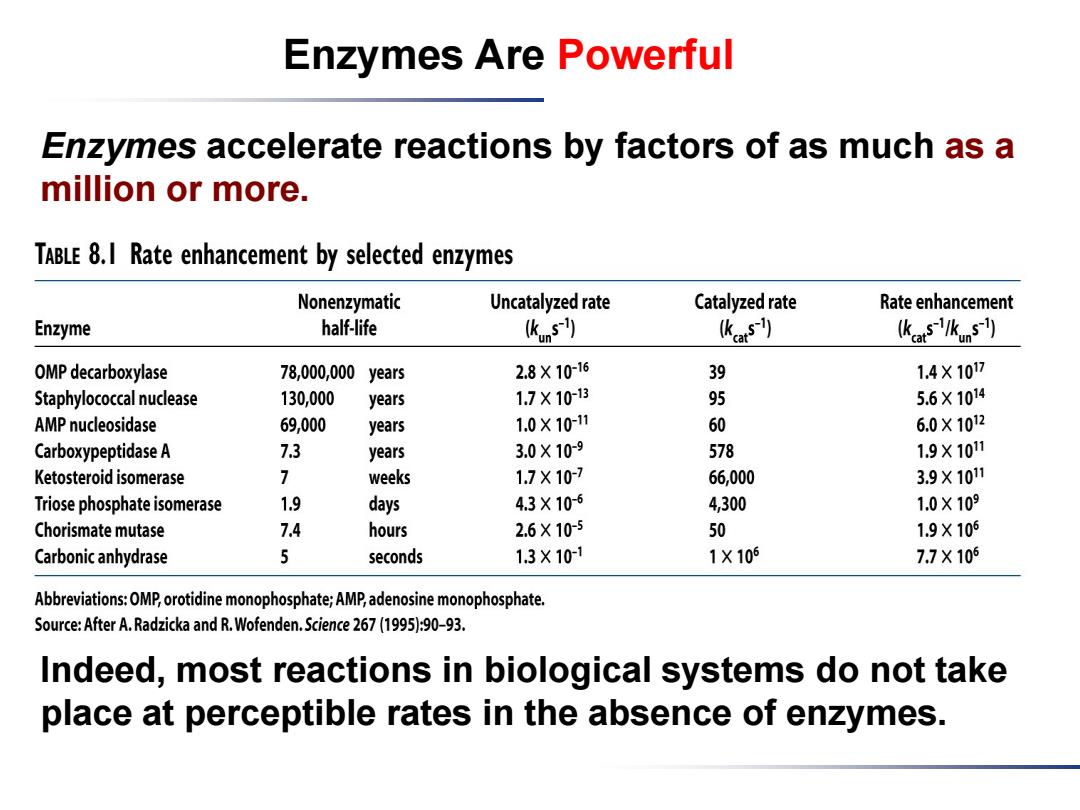
Enzymes Are Powerful Enzymes accelerate reactions by factors of as much as a million or more. TABLE 8.I Rate enhancement by selected enzymes Nonenzymatic Uncatalyzed rate Catalyzed rate Rate enhancement Enzyme half-life (kun-) (kat) (kcatS-/kunS-l) OMP decarboxylase 78,000,000 years 2.8X10-16 39 1.4×107 Staphylococcal nuclease 130,000 years 1.7X10-13 95 5.6X1014 AMP nucleosidase 69,000 years 1.0×10-11 60 6.0×1012 Carboxypeptidase A 7.3 years 3.0X109 578 1.9X1011 Ketosteroid isomerase 1 weeks 1.7×10-7 66,000 3.9X101 Triose phosphate isomerase 1.9 days 4.3X106 4,300 1.0X109 Chorismate mutase 7.4 hours 2.6X10-5 50 1.9X105 Carbonic anhydrase 5 seconds 1.3×101 1×105 7.7X105 Abbreviations:OMP,orotidine monophosphate;AMP,adenosine monophosphate. Source:After A.Radzicka and R.Wofenden.Science 267(1995):90-93. Indeed,most reactions in biological systems do not take place at perceptible rates in the absence of enzymes
Enzymes Are Powerful Enzymes accelerate reactions by factors of as much as a million or more. Indeed, most reactions in biological systems do not take place at perceptible rates in the absence of enzymes