
Chapter 28: Antidiabetic drugs Prof.R.D.Ye 2012-11-21
Chapter 28: Antidiabetic Drugs Prof. R.D. Ye 2012-11-21
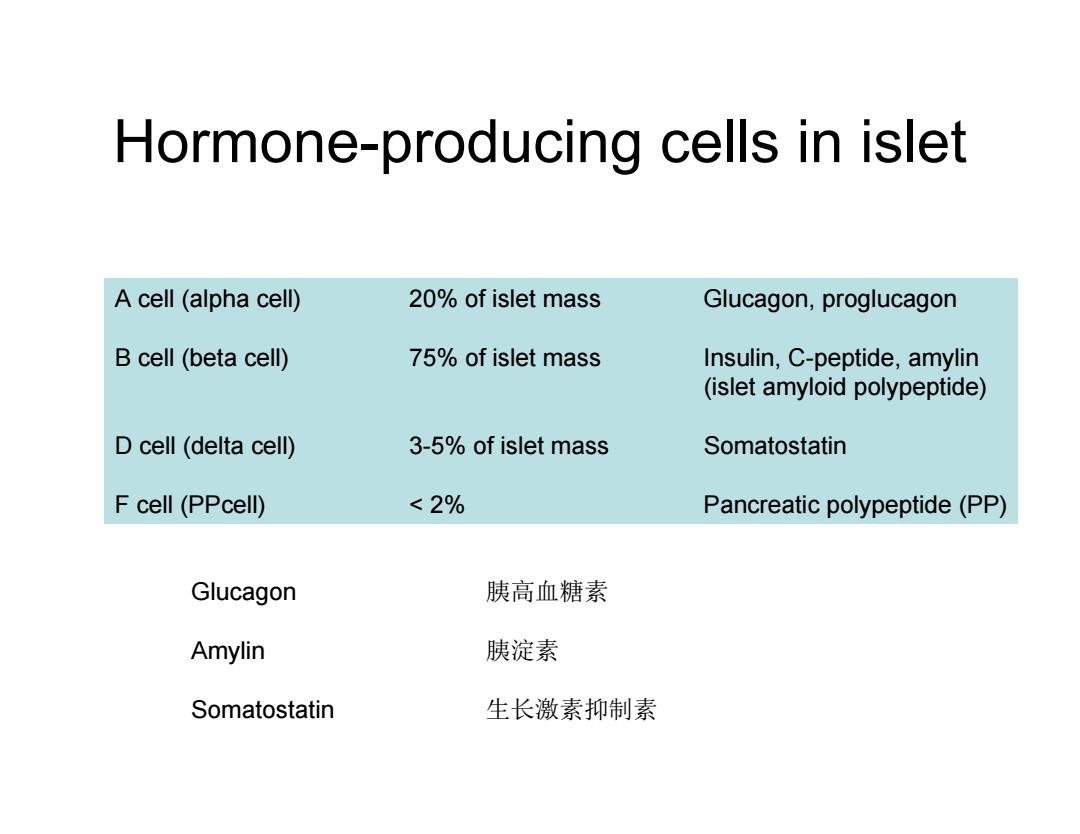
Hormone-producing cells in islet A cell (alpha cell) 20%of islet mass Glucagon,proglucagon B cell (beta cell) 75%of islet mass Insulin,C-peptide,amylin (islet amyloid polypeptide) D cell(delta cell) 3-5%of islet mass Somatostatin F cell (PPcell) <2% Pancreatic polypeptide(PP) Glucagon 胰高血糖素 Amylin 胰淀素 Somatostatin 生长激素抑制素
Hormone-producing cells in islet A cell (alpha cell) 20% of islet mass Glucagon, proglucagon B cell (beta cell) 75% of islet mass Insulin, C-peptide, amylin (islet amyloid polypeptide) D cell (delta cell) 3-5% of islet mass Somatostatin F cell (PPcell) < 2% Pancreatic polypeptide (PP) Glucagon 胰高血糖素 Amylin 胰淀素 Somatostatin 生长激素抑制素

Human insulin: 51 amino acids consisting of A chain(21 a.a.)and B chain(30 a.a.) Molecular weight 5808 Preproinsulin:A 30-a.a.C-chain connects A and B chains through dipeptide linkage A-chain and B-chain are connected through 2 disulfide bridges B30 828 A1 Gly Ha 81@@@s@
Human insulin: • 51 amino acids consisting of A chain (21 a.a.) and B chain (30 a.a.) • Molecular weight :5808 • Preproinsulin: A 30-a.a. C-chain connects A and B chains through dipeptide linkage • A-chain and B-chain are connected through 2 disulfide bridges
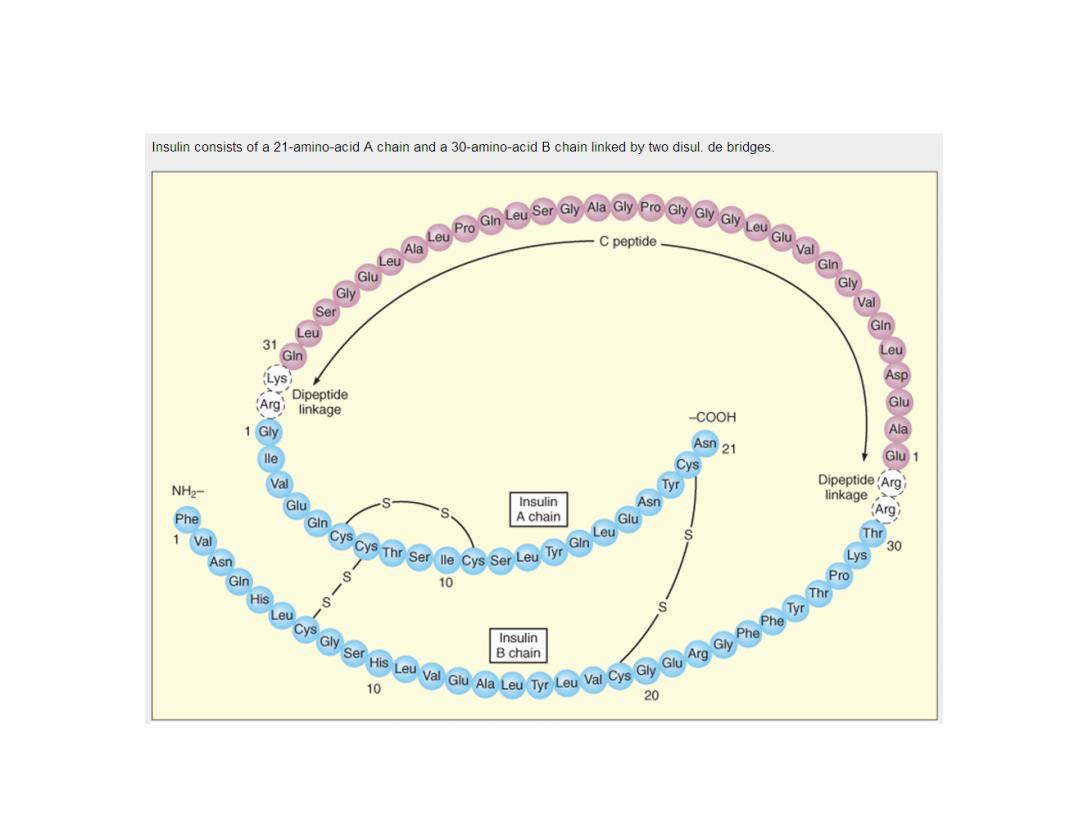
Insulin consists of a 21-amino-acid A chain and a 30-amino-acid B chain linked by two disul.de bridges. ooo0aaocodddaddde C peptide 31 GIn Arg Dipeptide linkage -COOH 1 Gly Asn 21 lle Cys NH2- Val Tyr Dipeptide(Arg lu Insulin linkage Phe A chain Glu g中e@8@w 00008e@0@80列0g66国ss586② GIn Thr s 30 10 Insulin Bchain 10 20

Insulin secretion and functions Secreted from beta-cells in pancreatic islet High glucose level increases intracellular ATP level, which closes ATP-dependent potassium channel, causing depolarization Depolarization of beta-cell opens voltage-gated calcium channel.Ca2+influx increases intracellular Ca2+level. leading to secretion of insulin Insulin promotes synthesis and storage of glycogen, triglycerides and proteins Major target organs are liver,fat tissue and muscle
Insulin secretion and functions • Secreted from beta-cells in pancreatic islet • High glucose level increases intracellular ATP level, which closes ATP-dependent potassium channel, causing depolarization • Depolarization of beta-cell opens voltage-gated calcium channel. Ca2+ influx increases intracellular Ca2+ level, leading to secretion of insulin • Insulin promotes synthesis and storage of glycogen, triglycerides and proteins • Major target organs are liver, fat tissue and muscle