图 上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Capillary Diuretics Filtraion Reabsorption Lymph Flow Lymphatic Excretion of Water and Electrolytes G AI JIAO TONG UNIVE
Diuretics Excretion of Water and Electrolytes

上浒充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction 漏 。Diuretics agents that increase the renal excretion of sodium and water classification based on site of action knowledge of the normal renal physiology is important
• Diuretics – agents that increase the renal excretion of sodium and water – classification based on site of action – knowledge of the normal renal physiology is important Introduction
上浒充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Background Primary effect of diuretics is to increase solute excretion,mainly as NaCl Certain disease states may cause blood volume to increase outside of narrowly defined limits Hypertension Congestive heart failure Liver cirrhosis Nephrotic syndrome Renal failure AO TONG Dietary Na restriction often not enough to prevent edema diuretics needed
Background Primary effect of diuretics is to increase solute excretion, mainly as NaCl Certain disease states may cause blood volume to increase outside of narrowly defined limits Hypertension Congestive heart failure Liver cirrhosis Nephrotic syndrome Renal failure Dietary Na restriction often not enough to prevent edema diuretics needed
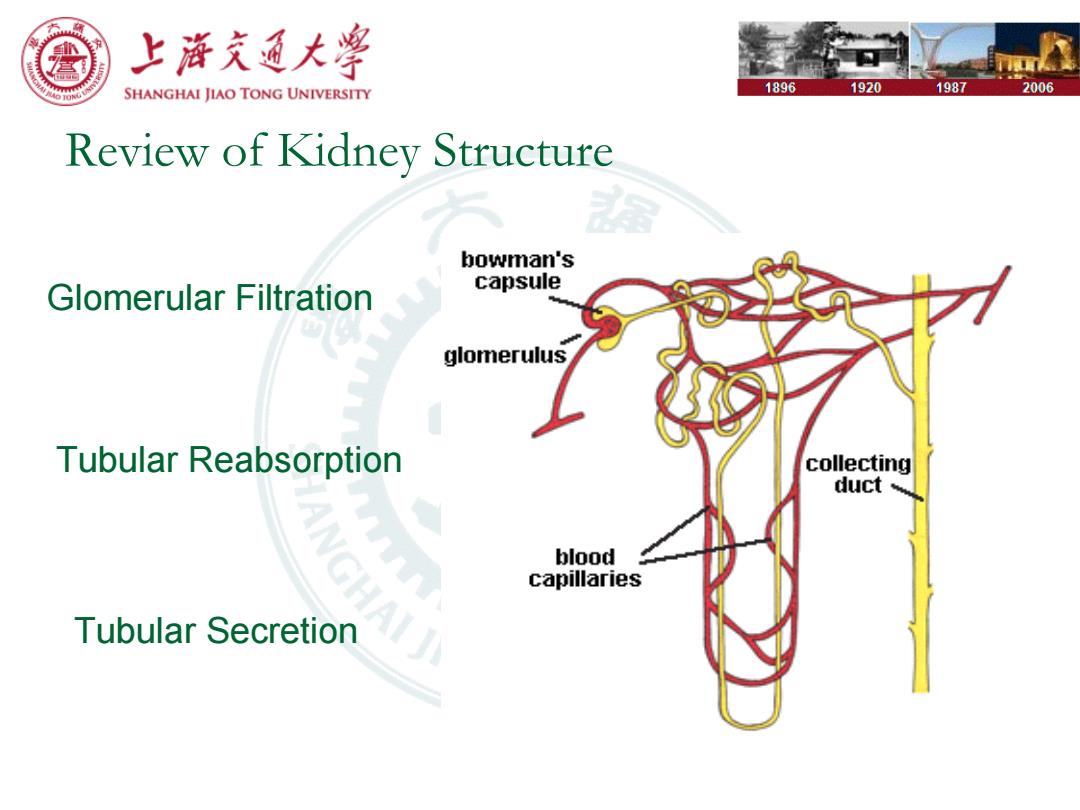
上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Review of Kidney Structure bowman's Glomerular Filtration capsule glomerulus Tubular Reabsorption collecting duct blood capillaries Tubular Secretion
Review of Kidney Structure Glomerular Filtration Tubular Reabsorption Tubular Secretion
上游充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Background to Mechanisms of Action of Diuretics Movement from tubular fluid through renal epithelial cells and into peritubular capillaries accomplished by three transport mechanisms after cell interior is polarized by Na+/K+pump 1. Channels formed by membrane proteins Allows only sodium to pass through 2. Cotransport Carrier mediated Simultaneously transports both Na+and other solute(Cl-,glucose,etc) from tubular lumen into renal epithelial cell 3. Countertransport Carrier mediated Transports Na in,another solute(H+)out of renal epithelial cell Water moves transcellularly in permeable segments or via tight junctions between renal epithelial cells
Background to Mechanisms of Action of Diuretics Movement from tubular fluid through renal epithelial cells and into peritubular capillaries accomplished by three transport mechanisms after cell interior is polarized by Na+/K+ pump 1. Channels formed by membrane proteins Allows only sodium to pass through 2. Cotransport Carrier mediated Simultaneously transports both Na+ and other solute (Cl-, glucose, etc) from tubular lumen into renal epithelial cell 3. Countertransport Carrier mediated Transports Na in, another solute (H+) out of renal epithelial cell Water moves transcellularly in permeable segments or via tight junctions between renal epithelial cells