
Types of Diabetes Diabetes is a chronic disease,which occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin,or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. This leads to an increased concentration of glucose in the blood (hyperglycaemia) Type 1 diabetes(previously known as insulin-dependent or childhood-onset diabetes,IDDM)is characterized by a lack of insulin production. Type 2 diabetes(formerly called non-insulin-dependent or adult-onset diabetes, NIDDM)is caused by the body's ineffective use of insulin.It often results from excess body weight and physical inactivity. Gestational diabetes is hyperglycaemia that is first recognized during pregnancy
Diabetes is a chronic disease, which occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. This leads to an increased concentration of glucose in the blood (hyperglycaemia). Type 1 diabetes (previously known as insulin-dependent or childhood-onset diabetes, IDDM) is characterized by a lack of insulin production. Type 2 diabetes (formerly called non-insulin-dependent or adult-onset diabetes, NIDDM) is caused by the body’s ineffective use of insulin. It often results from excess body weight and physical inactivity. Gestational diabetes is hyperglycaemia that is first recognized during pregnancy. Types of Diabetes

Insulin for treatment of diabetes Used for treatment of all types of diabetes.For Type 1 diabetes,insulin provides the best therapy. Also used for treatment of hyperkalemia. Usually given by subcutaneous injection;new methods(inhaled,patch,etc.) are being developed. Promotes uptake of glucose by skeletal muscle and adipose tissue by activating a glucose transporter(GLUT 4);facilitates the metabolism of glucose to provide energy for skeletal muscle contraction;stimulates glycogen synthesis; increase the conversion of glucose to fatty acids for storage as triglyceride; inhibits lipolysis;inhibits protein catabolism. Acts through insulin receptors in primarily cells of the liver,skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Adverse effects:Hypoglycemia;insulin resistance;insulin allergies
Insulin for treatment of diabetes • Used for treatment of all types of diabetes. For Type 1 diabetes, insulin provides the best therapy. • Also used for treatment of hyperkalemia. • Usually given by subcutaneous injection; new methods (inhaled, patch, etc.) are being developed. • Promotes uptake of glucose by skeletal muscle and adipose tissue by activating a glucose transporter (GLUT 4); facilitates the metabolism of glucose to provide energy for skeletal muscle contraction; stimulates glycogen synthesis; increase the conversion of glucose to fatty acids for storage as triglyceride; inhibits lipolysis; inhibits protein catabolism. • Acts through insulin receptors in primarily cells of the liver, skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. • Adverse effects: Hypoglycemia; insulin resistance; insulin allergies
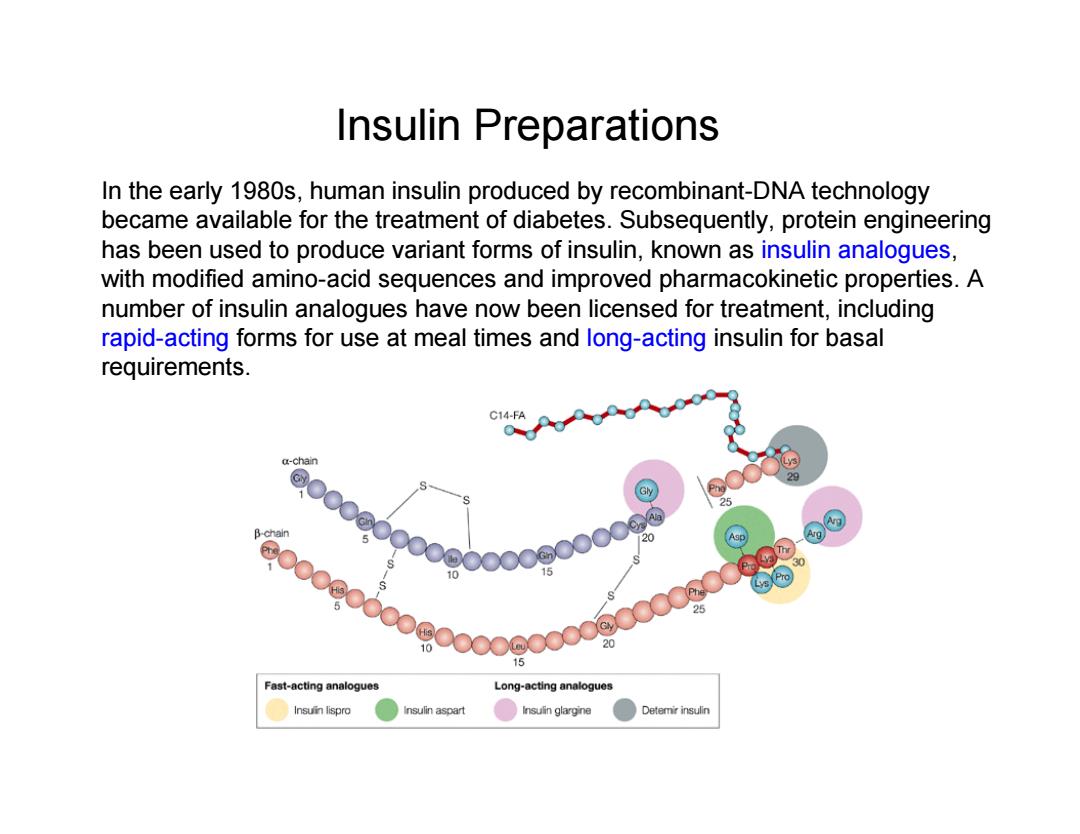
Insulin Preparations In the early 1980s,human insulin produced by recombinant-DNA technology became available for the treatment of diabetes.Subsequently,protein engineering has been used to produce variant forms of insulin,known as insulin analogues, with modified amino-acid sequences and improved pharmacokinetic properties.A number of insulin analogues have now been licensed for treatment,including rapid-acting forms for use at meal times and long-acting insulin for basal requirements. C14-FA a-chain 29 d00oooooooo00oooooo9 oooeobooeoooopoooopoooos β-chan 20 10 ©西 15 Fast-acting analogues Long-acting analogues Insuin lispro Insulin aspart Insuin glargine Detemirinsulin
In the early 1980s, human insulin produced by recombinant-DNA technology became available for the treatment of diabetes. Subsequently, protein engineering has been used to produce variant forms of insulin, known as insulin analogues, with modified amino-acid sequences and improved pharmacokinetic properties. A number of insulin analogues have now been licensed for treatment, including rapid-acting forms for use at meal times and long-acting insulin for basal requirements. Insulin Preparations
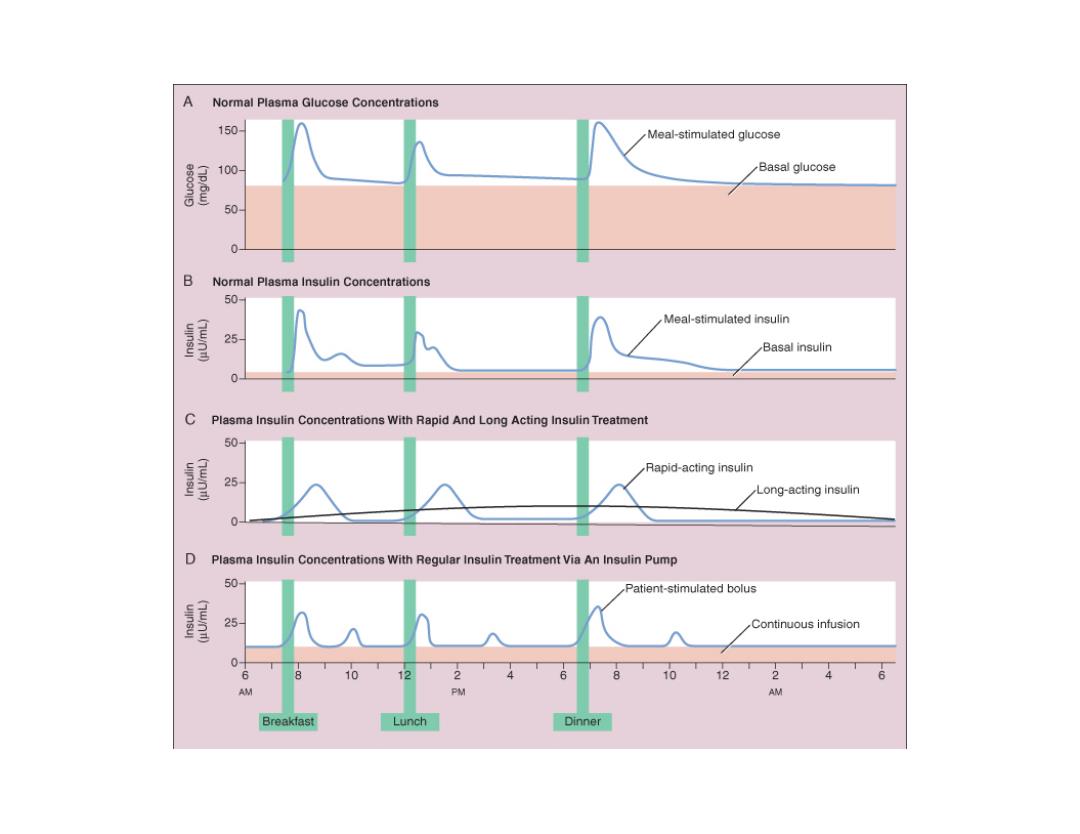
A Normal Plasma Glucose Concentrations 150 Meal-stimulated glucose 100 Basal glucose 50 0- B Normal Plasma Insulin Concentrations 50 Meal-stimulated insulin uinsu (wn) 25 Basal insulin C Plasma Insulin Concentrations With Rapid And Long Acting Insulin Treatment 50- Rapid-acting insulin Long-acting insulin 0 0 Plasma Insulin Concentrations With Regular Insulin Treatment Via An Insulin Pump 50- Patient-stimulated bolus 25 Continuous infusion 0 6 8 10 2 0 12 AM PM 多 Breakfast Lunch Dinner