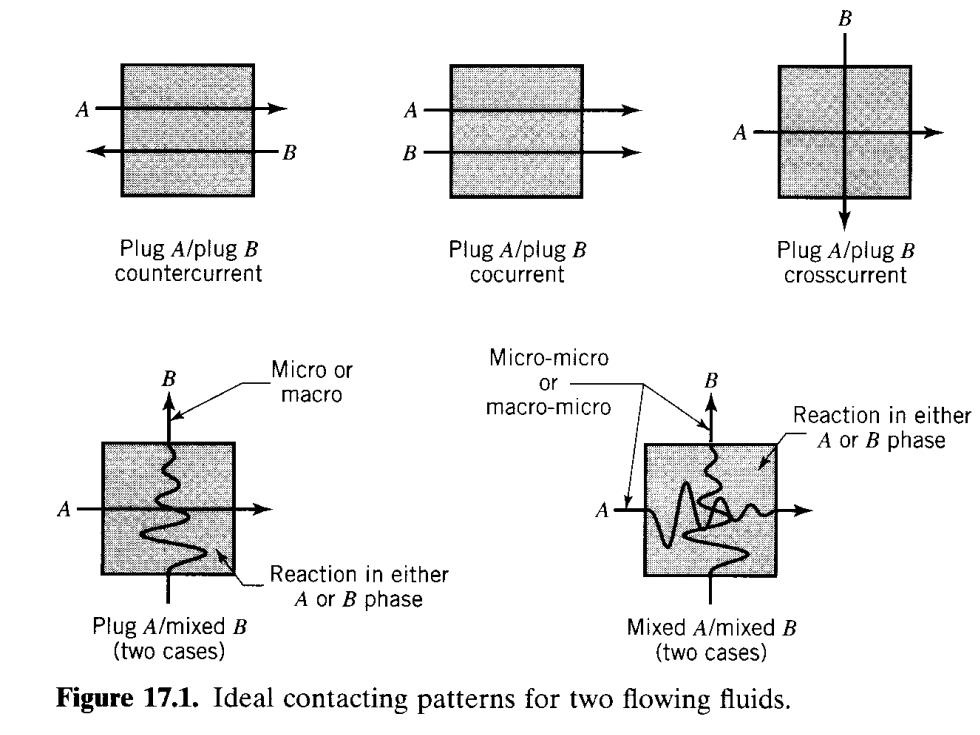
B Plug A/plug B Plug A/plug B Plug A/plug B countercurrent cocurrent crosscurrent Micro-micro B Micro or or B macro macro-micro Reaction in either A or B phase Reaction in either A or B phase Plug A/mixed B Mixed A/mixed B (two cases) (two cases) Figure 17.1.Ideal contacting patterns for two flowing fluids
11

Final Thoughts of Flow Modeling In reactor design and scale-up,it is essential to select a flow model which reasonably represents our setup.Too often we put too little thought here, carelessly picking a nonrepresentative model and then doing computer calculations to the nth degree of accuracy.And then we are surprised when design and scale-up do not agree with our predictions.A simple reasonable model is much better than a precise and detailed model which does not represent the contacting 12
12 • Final Thoughts of Flow Modeling • In reactor design and scale-up, it is essential to select a flow model which reasonably represents our setup. Too often we put too little thought here, carelessly picking a nonrepresentative model and then doing computer calculations to the nth degree of accuracy. And then we are surprised when design and scale-up do not agree with our predictions. A simple reasonable model is much better than a precise and detailed model which does not represent the contacting

Chapter 18 Solid Catalyzed Reactions .With many reactions,the rates are affected by materials which are neither reactants nor products.Such materials called catalysts can speed a reaction by a factor of a million or much more,or they may slow a reaction(negative catalysts) 13
13 Chapter 18 Solid Catalyzed Reactions •With many reactions, the rates are affected by materials which are neither reactants nor products. Such materials called catalysts can speed a reaction by a factor of a million or much more, or they may slow a reaction(negative catalysts)

General observations The selection of a catalyst to promote a reaction is not well understood. Duplication of the chemical constitution of a good catalyst is no guarantee that the solid produced will have any catalytic activity. To explain the action of catalysts,it is thought that reactant molecules are somehow changed,energized,or affected to form intermediates in the regions close to the catalyst surface
14 • General observations • The selection of a catalyst to promote a reaction is not well understood. • Duplication of the chemical constitution of a good catalyst is no guarantee that the solid produced will have any catalytic activity. • To explain the action of catalysts, it is thought that reactant molecules are somehow changed, energized, or affected to form intermediates in the regions close to the catalyst surface

In terms of the transition-state theory,the catalyst reduces the potential energy barrier over which the reactants must pass to form products. Though a catalyst may speed up a reaction, it never determines the equilibrium or endpoint of a reaction. Since the solid surface is responsible for catalytic activity,a large readily accessible surface in easily handled materials is desirable. 15
15 • In terms of the transition-state theory, the catalyst reduces the potential energy barrier over which the reactants must pass to form products. • Though a catalyst may speed up a reaction, it never determines the equilibrium or endpoint of a reaction. • Since the solid surface is responsible for catalytic activity, a large readily accessible surface in easily handled materials is desirable