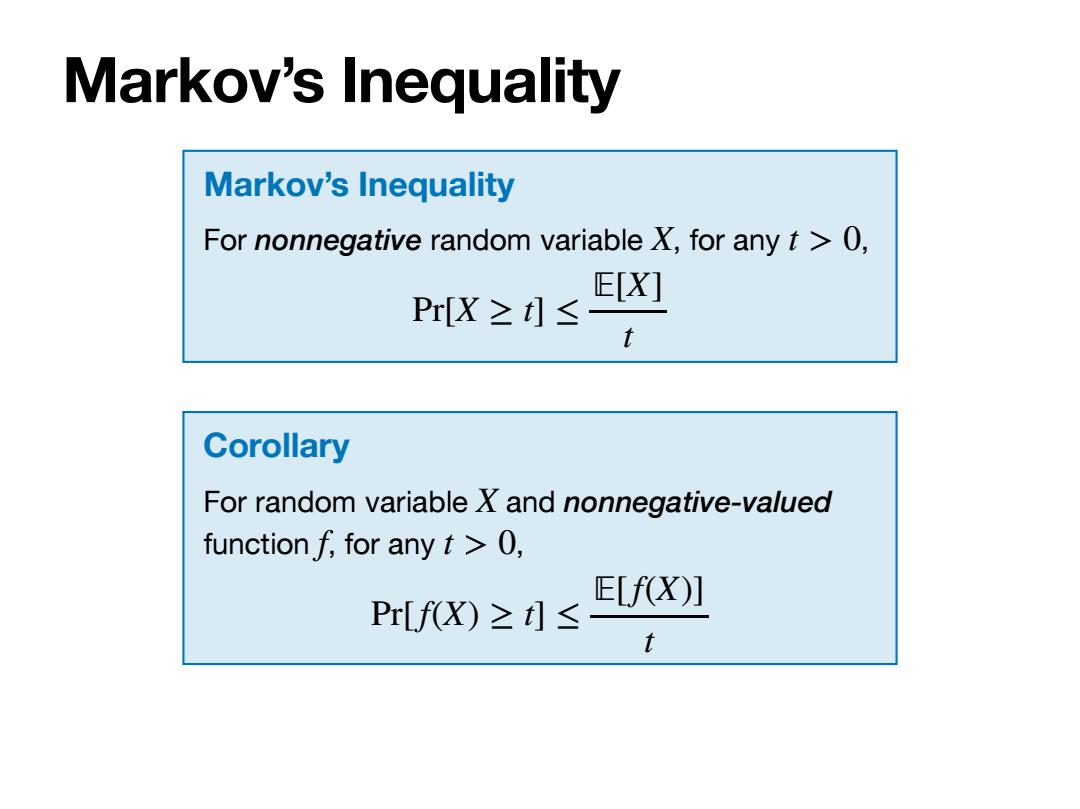
Markov's Inequality Markov's Inequality For nonnegative random variable X,for any t >0, E[X] Pr[X≥t]≤ t Corollary For random variable X and nonnegative-valued function f,for any t >0, E[f(X)] Pr[fX)≥t]≤ t
Markov’s Inequality Markov’s Inequality For nonnegative random variable , for any , X t > 0 Pr[X ≥ t] ≤ 𝔼[X] t Corollary For random variable and nonnegative-valued function , for any , X f t > 0 Pr[f(X) ≥ t] ≤ 𝔼[f(X)] t
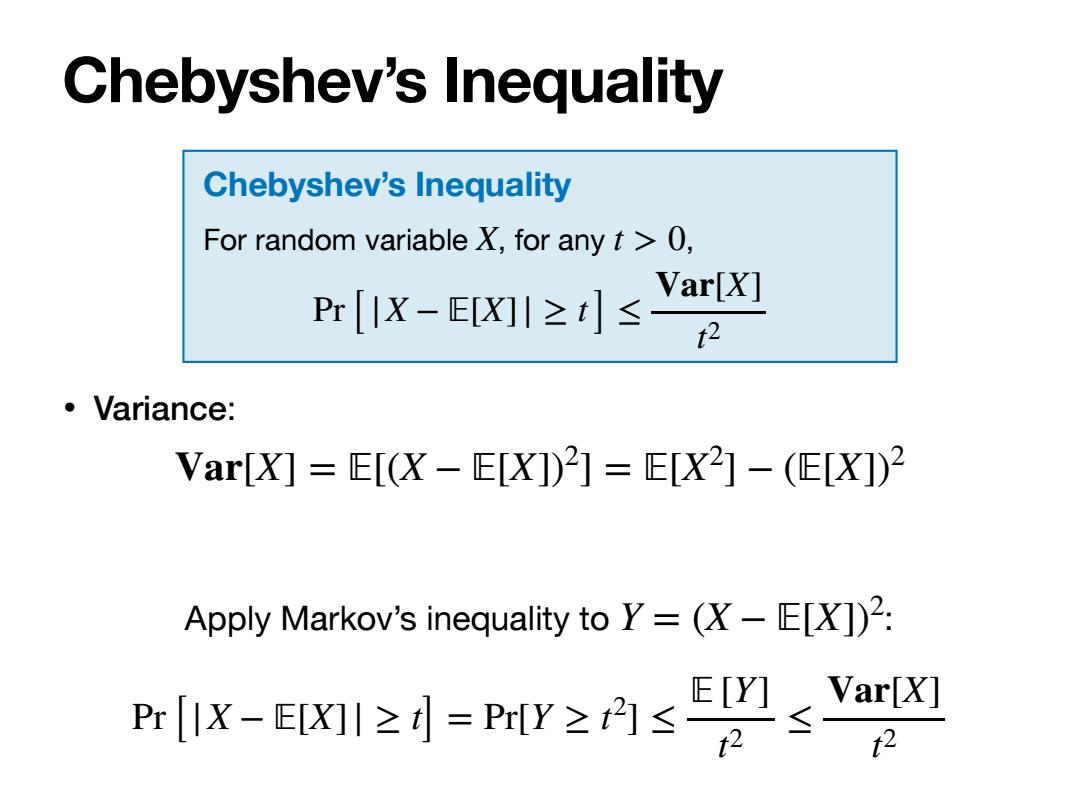
Chebyshev's Inequality Chebyshev's Inequality For random variable X,for any t >0, Var[X] Pr[IX-EX川≥t]≤ 2 ·Variance: Var[X]=E[(X-E[X])2]=EX2]-(E[X])2 Apply Markov's inequality to Y=(X-E[X])2: Pr[IX-EWI≥=PY≥内Er Yarlx] 12 2
Chebyshev’s Inequality Chebyshev’s Inequality For random variable , for any , X t > 0 Pr[|X − 𝔼[X]| ≥ t] ≤ Var[X] t2 • Variance: Var[X] = 𝔼[(X − 𝔼[X]) 2 ] = 𝔼[X2 ] − (𝔼[X]) 2 Apply Markov’s inequality to Y = (X − 𝔼[X]) : 2 Pr[|X − 𝔼[X]| ≥ t] = Pr[Y ≥ t 2 ] ≤ 𝔼 [Y] t2 ≤ Var[X] t2
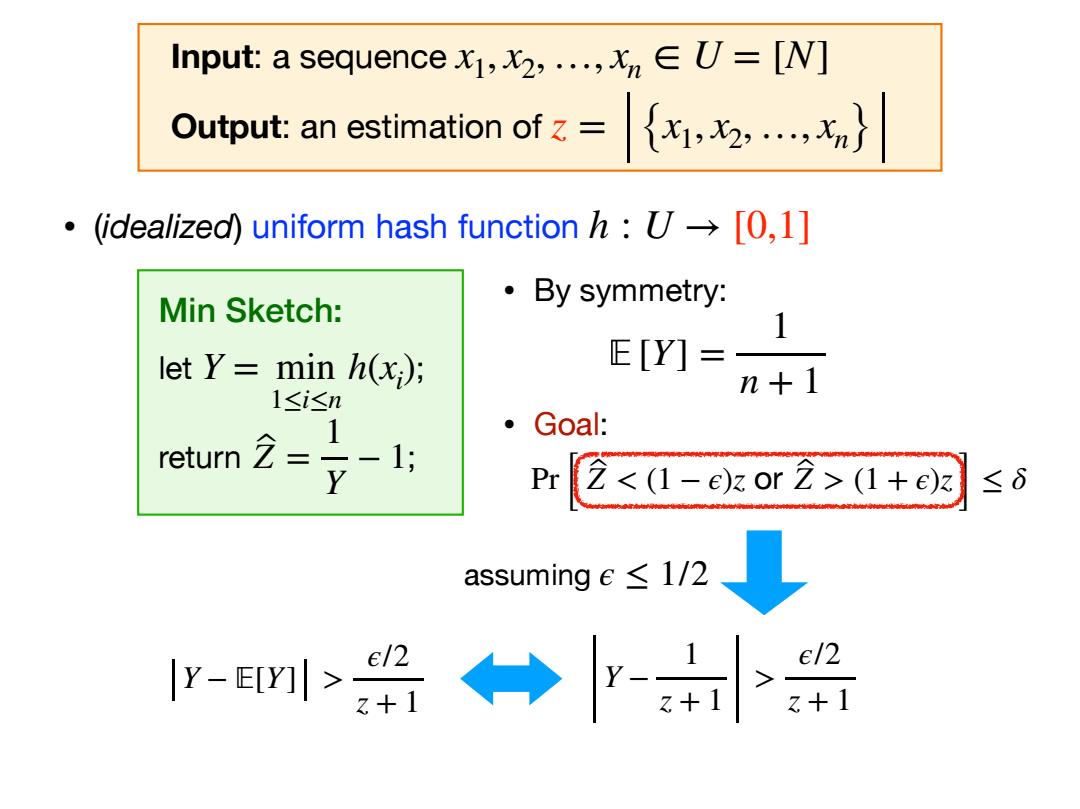
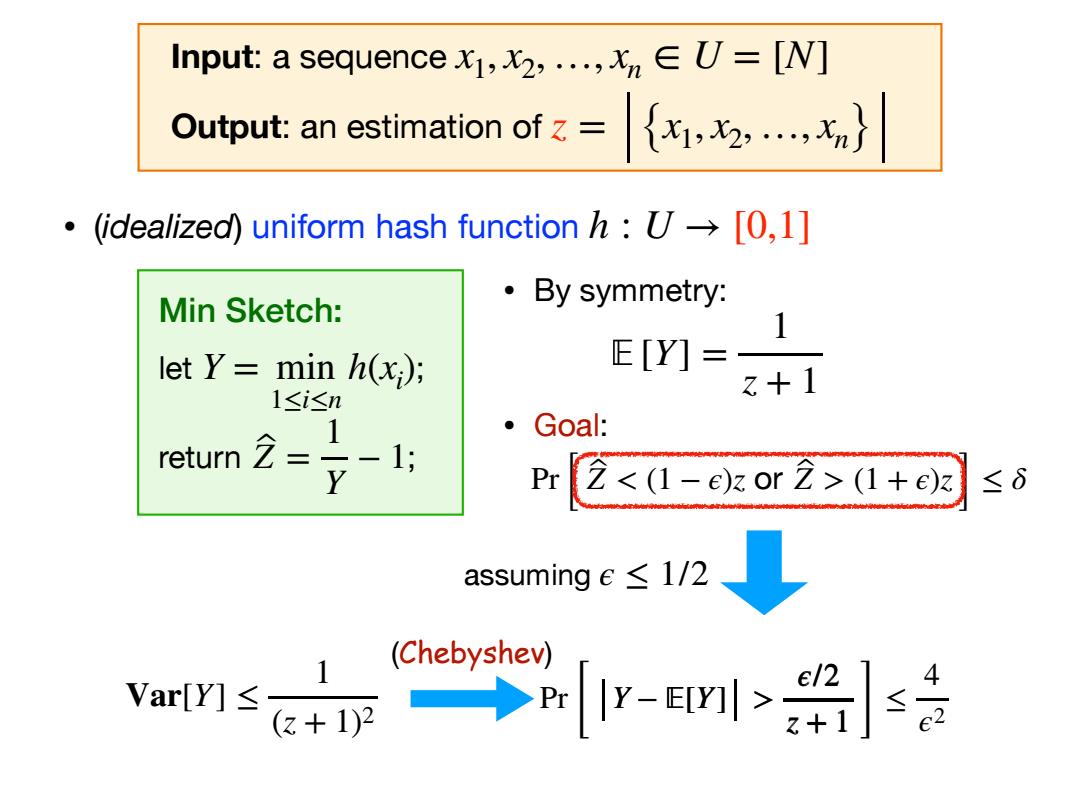
Input:a sequencex,..,U=[N] Output:an estimation of= ={x,2,,} ·(idealized)uniform hash function h:U→[0,l] Min Sketch: ·By symmetry: 1 let Y=1 min h(); E[Y]= n+1 1≤i≤n 1 Goal: return 2= -1; Pr②<1-ezor2>(1+e02 ≤6 assuming e≤1/2 ↓ y->¥ →本器
Pr [ Z ̂ < (1 − ϵ)z or Z ̂ > (1 + ϵ)z ] ≤ δ • (idealized) uniform hash function h : U → [0,1] Min Sketch: let ; return ; Y = min 1≤i≤n h(xi ) Z ̂ = 1 Y − 1 • By symmetry: • Goal: 𝔼 [Y] = 1 n + 1 Y − 1 z + 1 > ϵ/2 z + 1 assuming ϵ ≤ 1/2 Y − 𝔼[Y] > ϵ/2 z + 1 Input: a sequence Output: an estimation of x1, x2,…, xn ∈ U = [N] z = {x1, x2, …, xn}
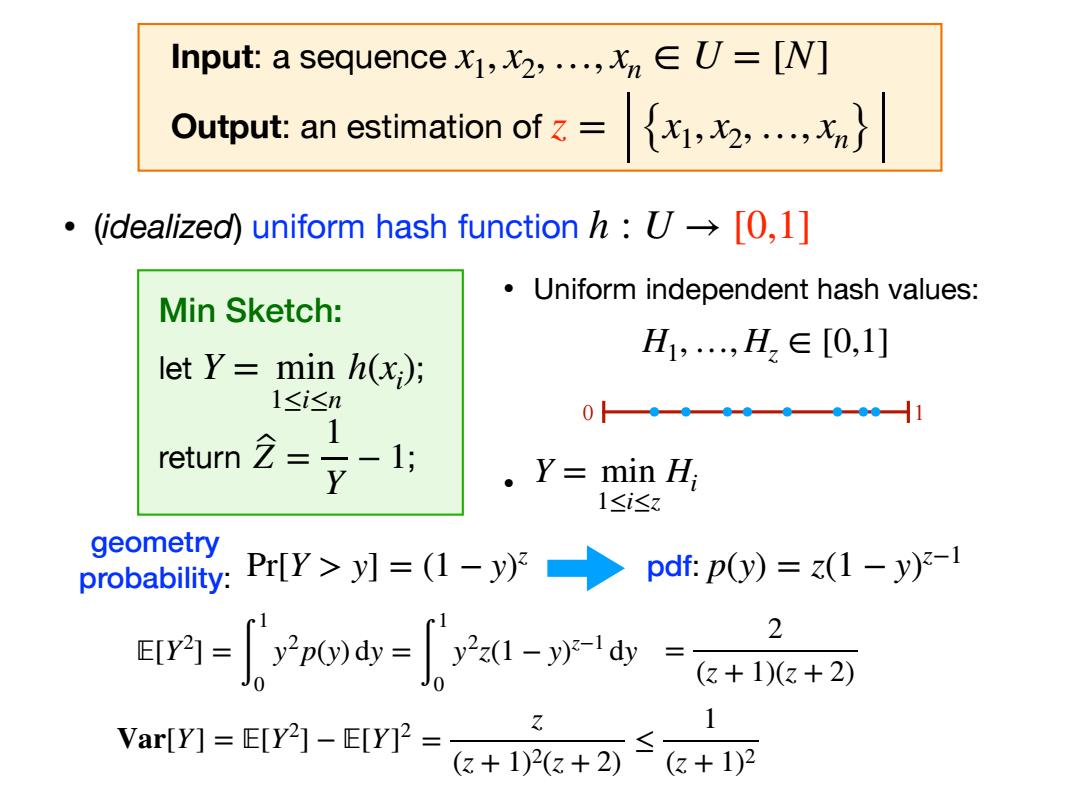
Input:a sequence,...,=[N] Output:an estimation of= ={x,2,,} ·(idealized)uniform hash function h:U→[0,l] Uniform independent hash values: Min Sketch: let Y=1 min h(); H1,,H2∈[0,1] 1≤i≤n 0— -01 1 return 2= 。Y=minH; 1≤i≤z geometry probability:Pr[Y>]=(1-y) pdf:p(y)=(1-y)2-1 =n0=2z1-yd= 2 (z+1)(z+2) Var[Y]=E[Y]-EYP=+1+2) 1 (3+1)2
• Uniform independent hash values: • H1, …, Hz ∈ [0,1] Y = min 1≤i≤z Hi 0 1 geometry probability: pdf: p(y) = z(1 − y) z−1 𝔼[Y2 ] = ∫ 1 0 y2p(y) dy = ∫ 1 0 y2z(1 − y) z−1 dy Pr[Y > y] = (1 − y) z = 2 (z + 1)(z + 2) Var[Y] = 𝔼[Y2 ] − 𝔼[Y] 2 = z (z + 1)2(z + 2) ≤ 1 (z + 1)2 • (idealized) uniform hash function h : U → [0,1] Min Sketch: let ; return ; Y = min 1≤i≤n h(xi ) Z ̂ = 1 Y − 1 Input: a sequence Output: an estimation of x1, x2,…, xn ∈ U = [N] z = {x1, x2, …, xn}
Input:a sequencex,...,U=[N] Output:an estimation of z= ·(idealized)uniform hash function h:U→[0,l] Min Sketch: ·By symmetry: 1 let Y=1 min h(); E[Y]= 1≤i≤n +1 1 Goal: return -1; Pr⑦<(1-e)zor2>(1+e3 ≤6 assuminge≤1/2 1 (Chebyshev) 4 Var[Y]≤ +p→n[-E>s
Y − 𝔼[Y] > ϵ/2 z + 1 Pr [ Y − 𝔼[Y] > ϵ/2 z + 1 ] ≤ 4 ϵ2 Pr [ Z ̂ < (1 − ϵ)z or Z ̂ > (1 + ϵ)z ] ≤ δ assuming ϵ ≤ 1/2 Var[Y] ≤ 1 (z + 1)2 (Chebyshev) • (idealized) uniform hash function h : U → [0,1] • By symmetry: • Goal: 𝔼 [Y] = 1 z + 1 Input: a sequence Output: an estimation of x1, x2,…, xn ∈ U = [N] z = {x1, x2, …, xn} Min Sketch: let ; return ; Y = min 1≤i≤n h(xi ) Z ̂ = 1 Y − 1