
Advanced Algorithms Dimension Reduction 尹一通Nanjing University,2022Fall
尹⼀通 Nanjing University, 2022 Fall Advanced Algorithms Dimension Reduction
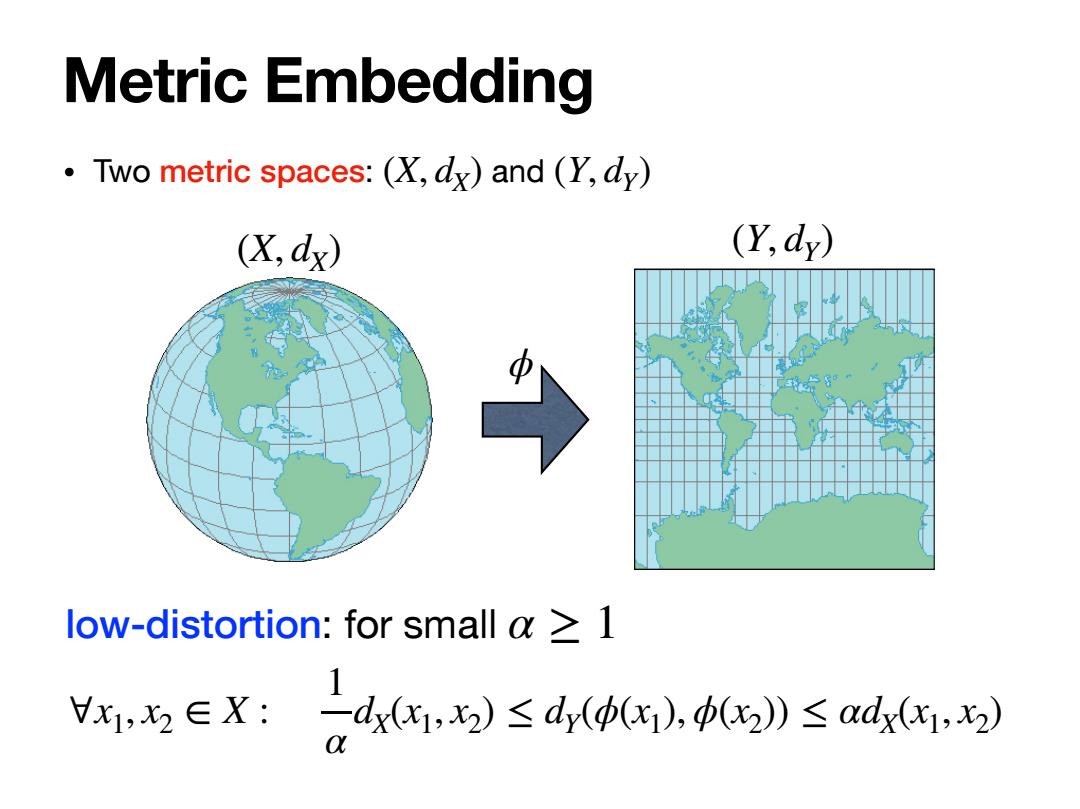
Metric Embedding Two metric spaces:(X,dx)and (Y,dy) (X,dx) (Y,d) low-distortion:for small a 1 x1,2∈X:-dxx1,x2)≤dy((x1),(x2》≤adxx1,x2)
Metric Embedding low-distortion: for small α ≥ 1 ∀x1, x2 ∈ X : 1 α dX(x1, x2) ≤ dY(ϕ(x1), ϕ(x2)) ≤ αdX(x1, x2) ϕ (X, dX) (Y, dY) • Two metric spaces: (X, d and X) (Y, dY)
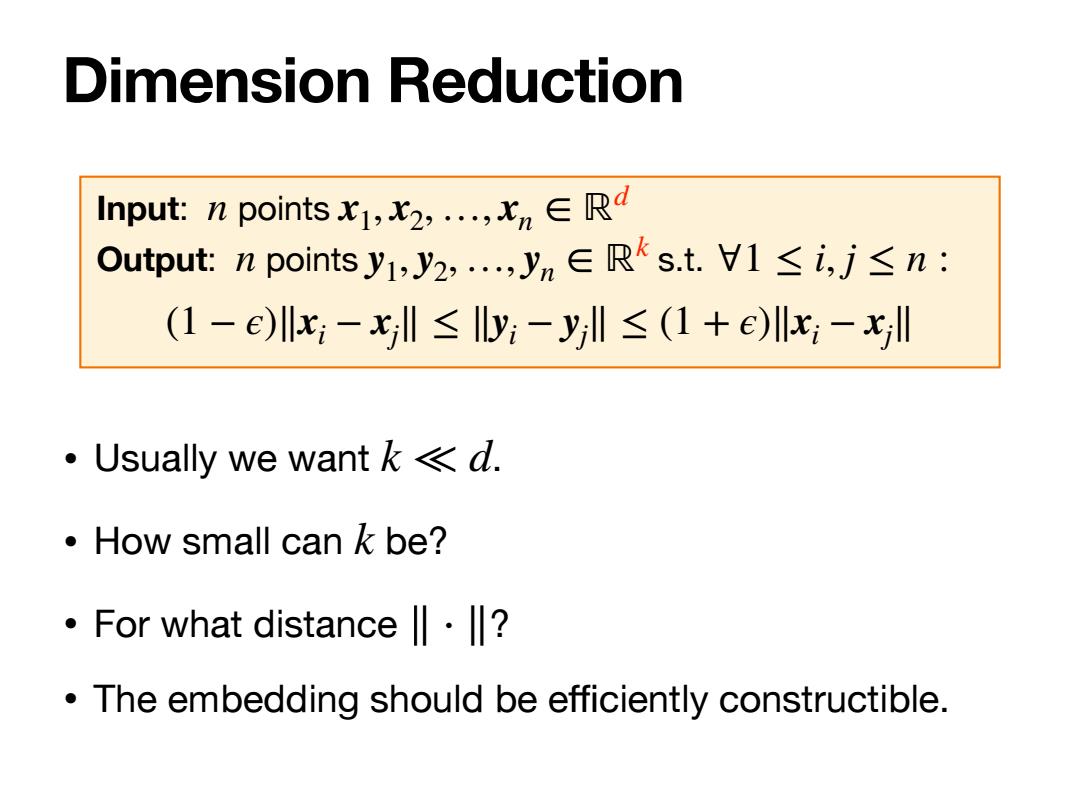
Dimension Reduction Input:n points,...,R Output::n pointsy1,y2,,yn∈Rkst.1≤i,j≤n: (1-e)x;-xl≤Ily:-yl≤(1+e)l:-xl ·Usually we want k<d. ·How small can k be? ·For what distance‖l·l? The embedding should be efficiently constructible
• Usually we want . • How small can be? • For what distance ? • The embedding should be efficiently constructible. k ≪ d k ∥ ⋅ ∥ Dimension Reduction Input: points Output: points s.t. n x1, x2, …, xn ∈ ℝd n y1, y2, …, yn ∈ ℝk ∀1 ≤ i, j ≤ n : (1 − ϵ)∥xi − xj ∥ ≤ ∥yi − yj ∥ ≤ (1 + ϵ)∥xi − xj ∥

Johonson-Linenstrauss Theorem/Transformation (JLT)
Johonson-Linenstrauss Theorem/Transformation (JLT)
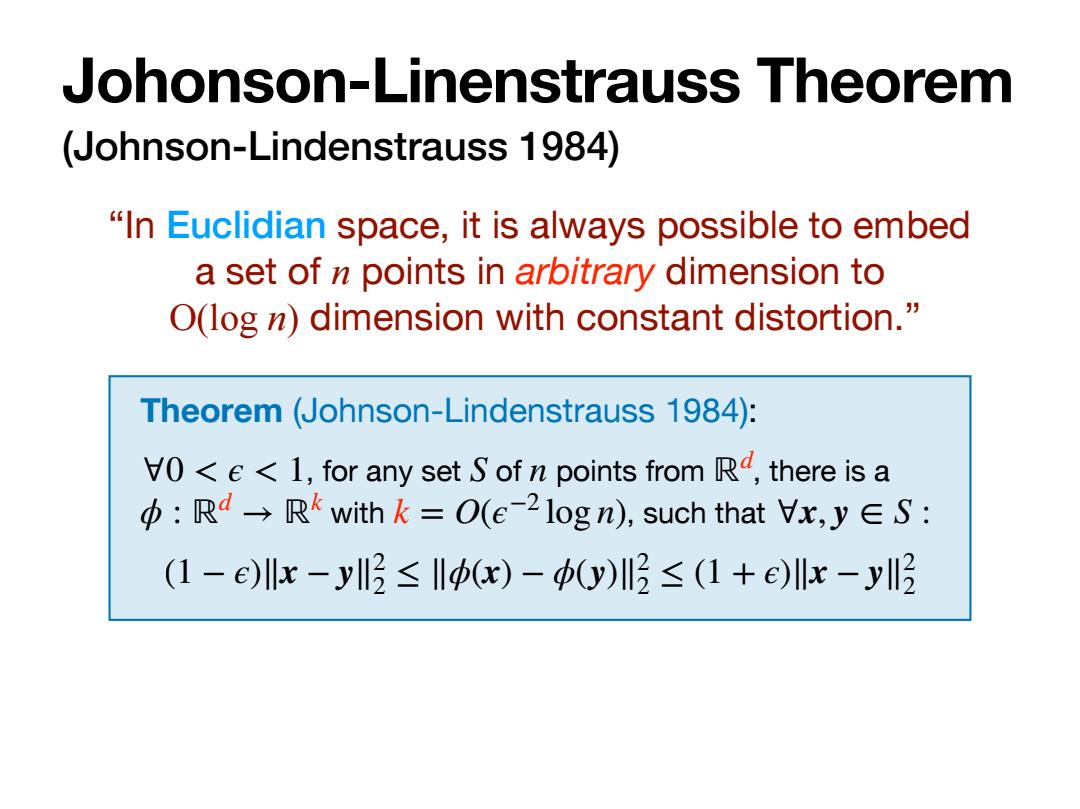
Johonson-Linenstrauss Theorem (Johnson-Lindenstrauss 1984) "In Euclidian space,it is always possible to embed a set of n points in arbitrary dimension to O(log n)dimension with constant distortion. Theorem (Johnson-Lindenstrauss 1984): VO<e<1,for any set S of n points from R,there is a 中:Rd→R with k=O(e-2logn),such that Vx,y∈S: (1-e)x-yl2≤lφ(x)-(y)川l2≤(1+e)lx-y2
(Johnson-Lindenstrauss 1984) Johonson-Linenstrauss Theorem Theorem (Johnson-Lindenstrauss 1984): , for any set of points from , there is a with , such that ∀0 < ϵ < 1 S n ℝd ϕ : ℝd → ℝk k = O(ϵ−2 log n) ∀x, y ∈ S : (1 − ϵ)∥x − y∥2 2 ≤ ∥ϕ(x) − ϕ(y)∥2 2 ≤ (1 + ϵ)∥x − y∥2 2 “In Euclidian space, it is always possible to embed a set of n points in arbitrary dimension to O(log n) dimension with constant distortion