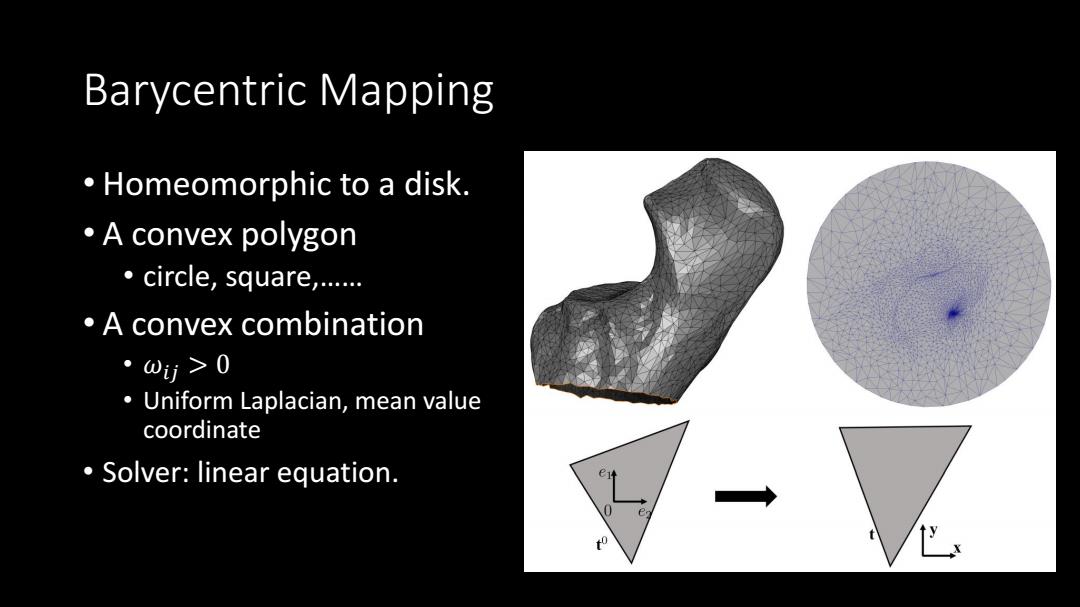
Barycentric Mapping Homeomorphic to a disk. ·A convex polygon 。circle,square,… A convex combination ·ω>0 Uniform Laplacian,mean value coordinate Solver:linear equation. ty
Barycentric Mapping • Homeomorphic to a disk. • A convex polygon • circle, square,…… • A convex combination • 𝜔𝑖𝑗 > 0 • Uniform Laplacian, mean value coordinate • Solver: linear equation
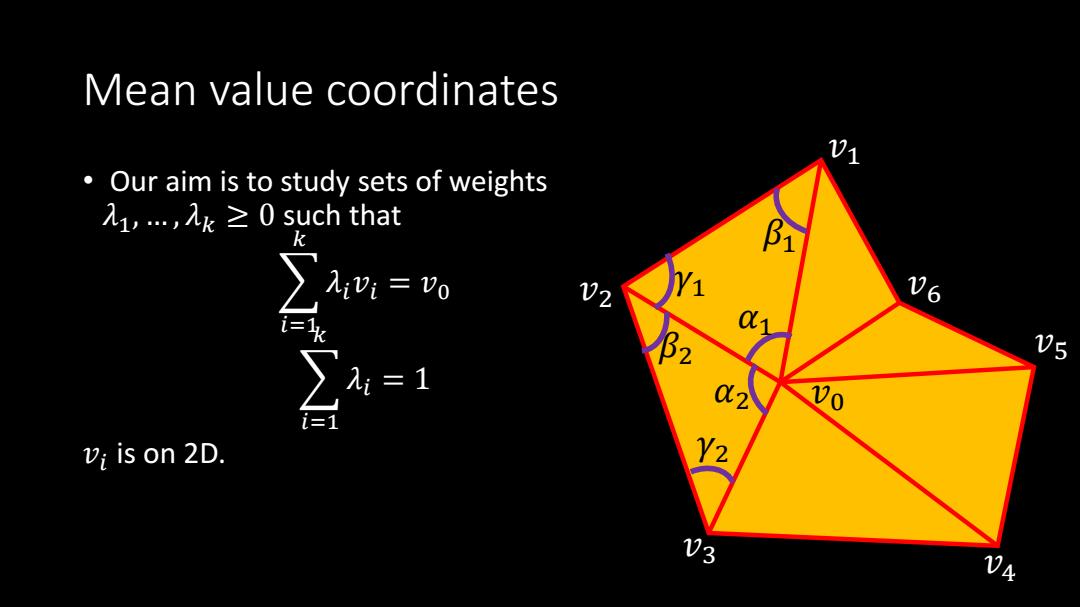
Mean value coordinates 0 Our aim is to study sets of weights 1,…,k≥0 such that 入:vi=v0 02 06 i=k 05 λ=1 02 i=1 vi is on 2D. Y2 03 04
Mean value coordinates • Our aim is to study sets of weights 𝜆1, … , 𝜆𝑘 ≥ 0 such that 𝑖=1 𝑘 𝜆𝑖𝑣𝑖 = 𝑣0 𝑖=1 𝑘 𝜆𝑖 = 1 𝑣𝑖 is on 2D. 𝑣0 𝑣3 𝑣2 𝑣1 𝑣4 𝑣5 𝑣6 𝛼1 𝛽1 𝛾1 𝛽2 𝛾2 𝛼2
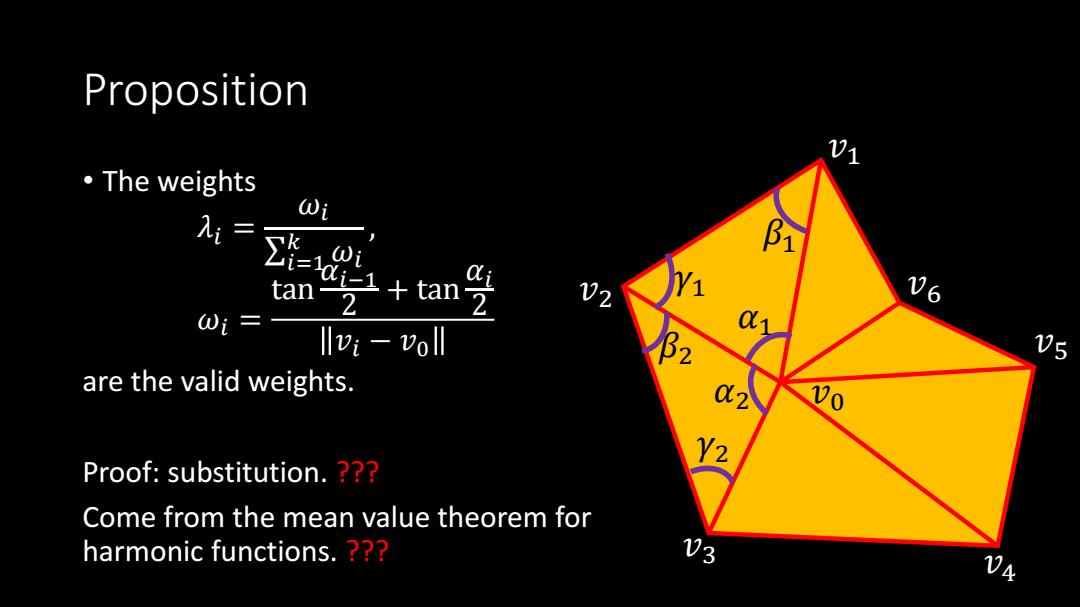
Proposition ·The weights i +ta tan2 ai 02 06 0i= llvi -voll are the valid weights. 02 00 Proof:substitution.?? Come from the mean value theorem for harmonic functions.?? 03
Proposition • The weights 𝜆𝑖 = 𝜔𝑖 𝑖=1 𝑘 𝜔𝑖 , 𝜔𝑖 = tan 𝛼𝑖−1 2 + tan 𝛼𝑖 2 𝑣𝑖 − 𝑣0 are the valid weights. Proof: substitution. ??? Come from the mean value theorem for harmonic functions. ??? 𝑣0 𝑣3 𝑣2 𝑣1 𝑣4 𝑣5 𝑣6 𝛼1 𝛽1 𝛾1 𝛽2 𝛾2 𝛼2
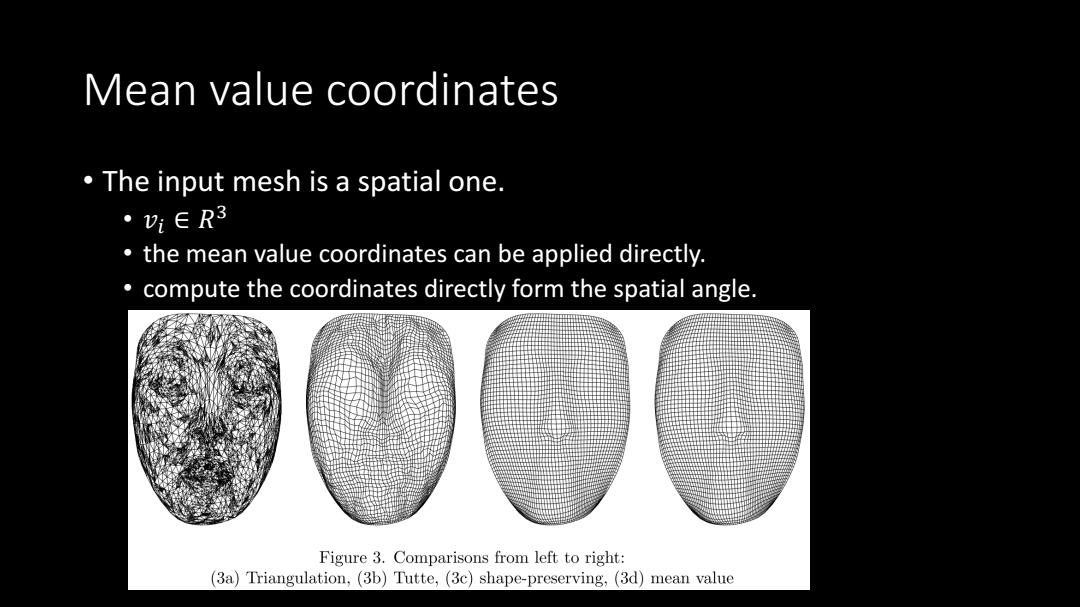
Mean value coordinates The input mesh is a spatial one. ·Vi∈R3 the mean value coordinates can be applied directly. compute the coordinates directly form the spatial angle Figure 3.Comparisons from left to right: (3a)Triangulation,(3b)Tutte,(3c)shape-preserving,(3d)mean value
Mean value coordinates • The input mesh is a spatial one. • 𝑣𝑖 ∈ 𝑅 3 • the mean value coordinates can be applied directly. • compute the coordinates directly form the spatial angle

Outline ·Definition Tutte's barycentric mapping Least squares conformal maps(LSCM,ASAP) Angle-Based Flattening (ABF) ·ABF++,LABF As-rigid-as-possible (ARAP) ·Simplex Assembly
Outline • Definition • Tutte’s barycentric mapping • Least squares conformal maps(LSCM, ASAP) • Angle-Based Flattening (ABF) • ABF++, LABF • As-rigid-as-possible (ARAP) • Simplex Assembly