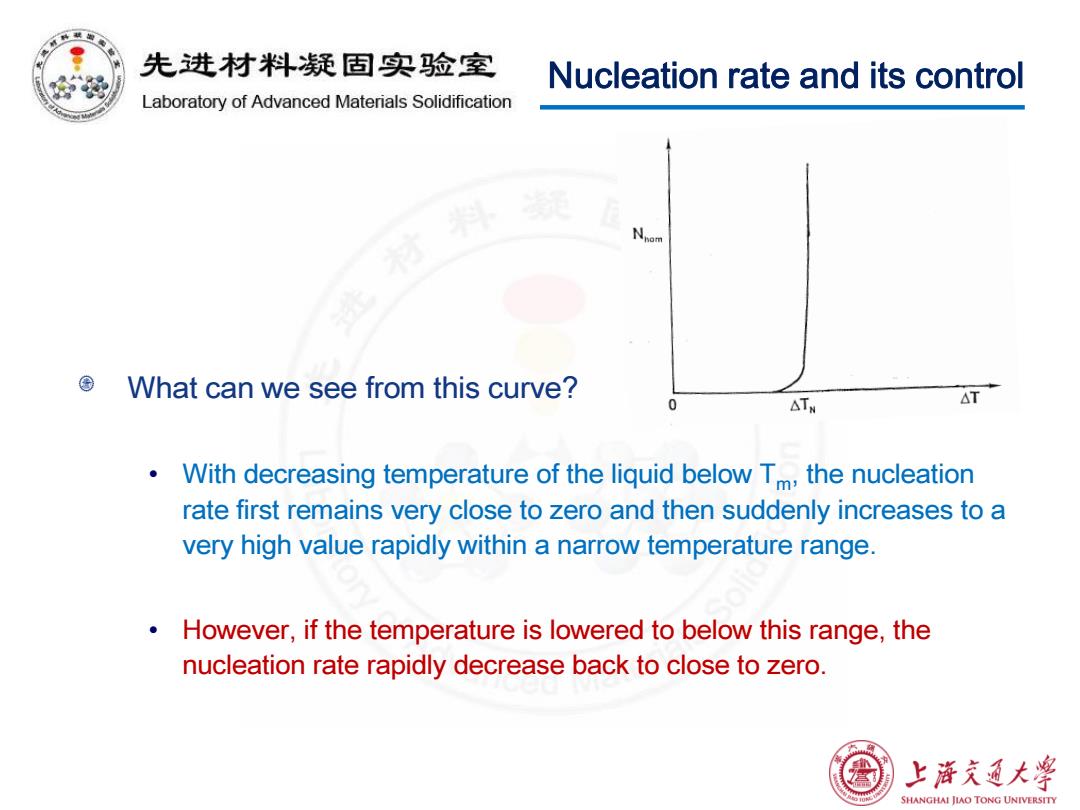
先进材料疑固实验室 Nucleation rate and its control Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification What can we see from this curve? △TW △T o With decreasing temperature of the liquid below Tm,the nucleation rate first remains very close to zero and then suddenly increases to a very high value rapidly within a narrow temperature range. However,if the temperature is lowered to below this range,the nucleation rate rapidly decrease back to close to zero. 上游文通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
What can we see from this curve? • With decreasing temperature of the liquid below Tm, the nucleation rate first remains very close to zero and then suddenly increases to a very high value rapidly within a narrow temperature range. • However, if the temperature is lowered to below this range, the nucleation rate rapidly decrease back to close to zero. Nucleation rate and its control
先进材料疑固实验室 Nucleation rate and its control Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification The reasons for this phenomenon: With decreasing temperature of the liquid,the magnitude of the nucleation barrier decreases>a higher nucleation rate,but atom diffusivity also decreases >a lower nucleation rate. These two opposite effects of decreasing temperature lead to a temperature at which the nucleation rate reaches its maximum. vanced Materd 上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Nucleation rate and its control The reasons for this phenomenon: • With decreasing temperature of the liquid, the magnitude of the nucleation barrier decreases a higher nucleation rate, but atom diffusivity also decreases a lower nucleation rate. • These two opposite effects of decreasing temperature lead to a temperature at which the nucleation rate reaches its maximum

先进材料疑固实验室 Nucleation rate and its control Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification When the cooling rate is very high,the nucleation of solid crystal may be avoided in the process of rapid cooling of the liquid metal or alloy until the liquid turns into a solid through glass transition.This solid is called metallic glass. vanced Materials S 上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Nucleation rate and its control • When the cooling rate is very high, the nucleation of solid crystal may be avoided in the process of rapid cooling of the liquid metal or alloy until the liquid turns into a solid through glass transition. This solid is called metallic glass
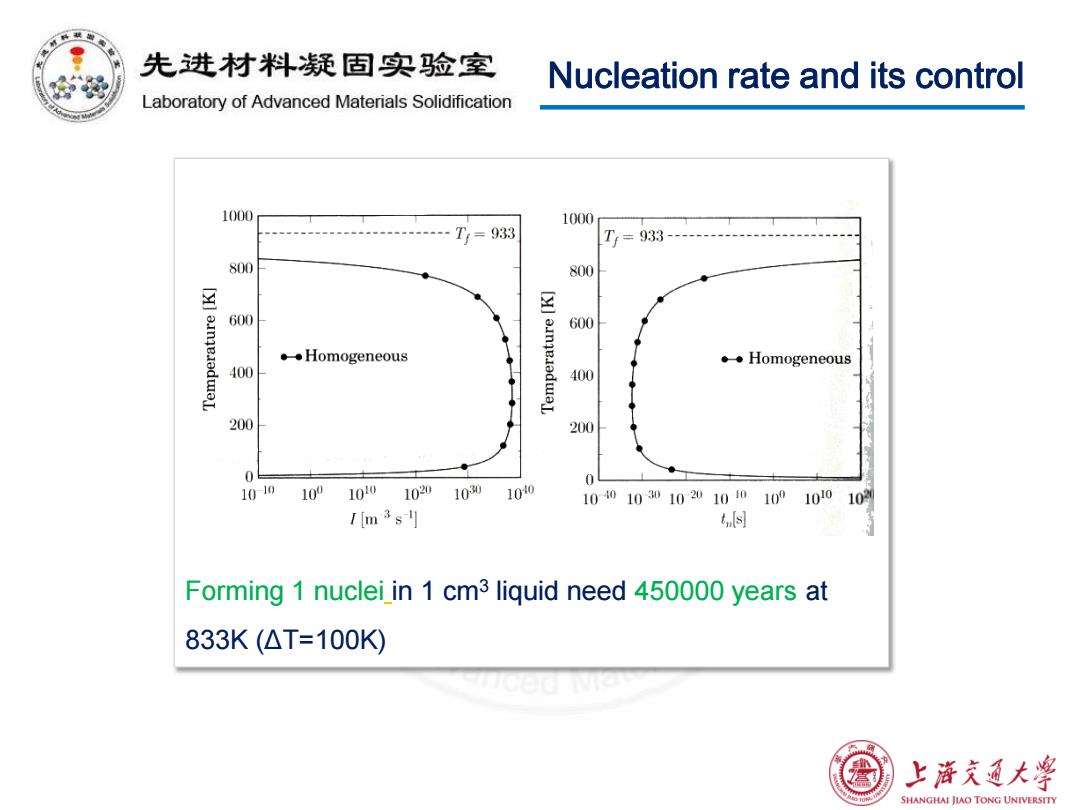
先进材料疑固实验室 Nucleation rate and its control Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification 1(000 1000 T=933 Tr=933 800 800 600 [y]ainqeiadwaL 600 ◆◆Homogeneous 。◆Homogeneous 400 400 200 200 0 1010 109 100 1020 1030 100 10401030102010101001010 102 1m3s1 n母 Forming 1 nuclei in 1 cm3 liquid need 450000 years at 833K(△T=100K 上游文通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Nucleation rate and its control Forming 1 nuclei in 1 cm3 liquid need 450000 years at 833K (ΔT=100K)
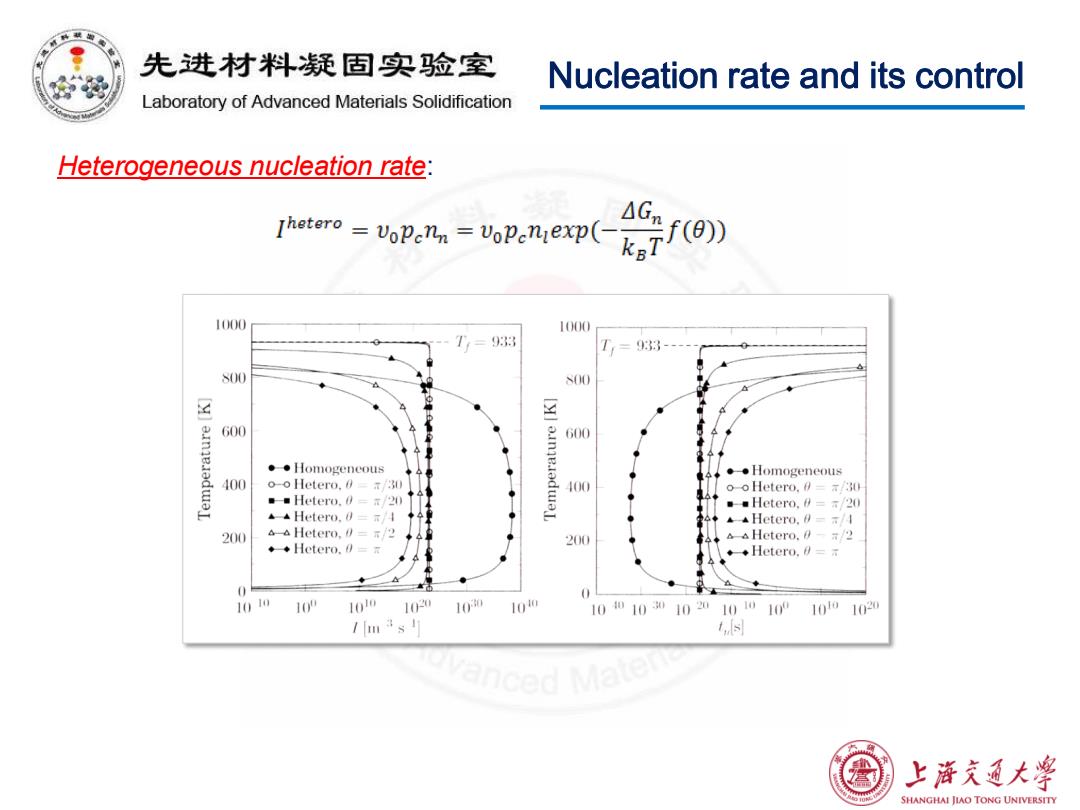
先进材料疑固实验室 Nucleation rate and its control Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Heterogeneous nucleation rate: Thotero vopenn=VoPeniexp( 1000 1000 T,=933 T= 33- S00 S00 三 600 00 。◆Homogeneous ◆◆Homogeneous 400 o-o Hetero.030 o-o Hetero.30 。■Hetero.0=r/20) 。Hetero.∥=T/20 Hetero,0=π/A ▲Hetero.∥=a/I 200 Hetero,∥=r/2 Hetero.0/2 ◆◆Hetero.0=r 200 ◆Hetero,a=r 直 1010 1 10o 10 10 10 10010010201010100 1010 102 /3s Ls ced 上游文通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Nucleation rate and its control Heterogeneous nucleation rate: