
先进材料疑固实验室 Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification 1896 1920 1987 2006 道清什--土 Transport phenomena in solidification(2) Dr.Mingxu Xia 上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSTTY
1896 19 02 1987 2006 Transport phenomena in solidification (2) Dr. Mingxu Xia

先进材料疑固实验室 Outline Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Brief introduction Momentum transport ⑧Heat transfer Mass transfer Commonalities among phenomena 上谱克通大睾 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSTTY
Outline Brief introduction Momentum transport Heat transfer Mass transfer Commonalities among phenomena
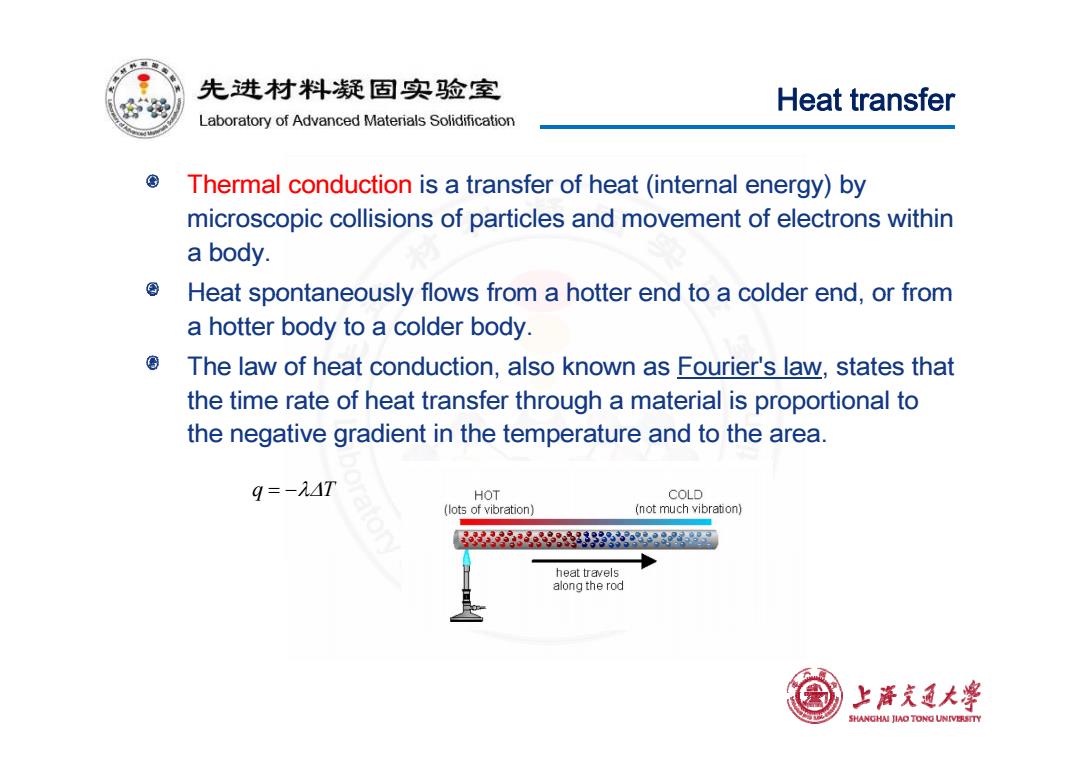
先进材料疑固实验室 Heat transfer Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Thermal conduction is a transfer of heat (internal energy)by microscopic collisions of particles and movement of electrons within a body. Heat spontaneously flows from a hotter end to a colder end,or from a hotter body to a colder body. The law of heat conduction,also known as Fourier's law,states that the time rate of heat transfer through a material is proportional to the negative gradient in the temperature and to the area. q=-MAT HOT COLD (lots of vibration) (not much vibration) 号88892828 heat travels along the rod 上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSTTY
Heat transfer Thermal conduction is a transfer of heat (internal energy) by microscopic collisions of particles and movement of electrons within a body. Heat spontaneously flows from a hotter end to a colder end or from Heat spontaneously flows from a hotter end to a colder end, or from a hotter body to a colder body. The law of heat conduction, also known as Fourier's law, states that the time rate of heat transfer through a material is proportional to the negative gradient in the temperature and to the area. q T

先进材料疑固实验室 Heat transfer Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Convective heat transfer,referred to simply as convection,is the transfer of heat from HO T weter rises one place to another by the movement of to the surface fluids.Convection is usually the dominant COLD water form of heat transfer in liquids and gases. circulates to the bottomto be reheated Convection can be "forced"by movement of heating element a fluid by means other than buoyancy forces (for example,a water pump in an automobile engine).Thermal expansion of fluids may also force convection. HGEMatsnle 上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSTTY
Heat transfer Convective heat transfer, referred to simply as convection, is the transfer of heat from one place to another by the movement of fluids. Convection nvection is usually the dominant form of heat transfer in liquids and gases. Convection can be "forced" by movement of a fluid by means other than buoyancy forces (for example a water pump in an automobile (for example, a water pump in an automobile engine). Thermal expansion of fluids may also force convection

先进材料疑固实验室 Heat transfer Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification In side a substance: e=mc,(T-T2) Between the substance(Newton's law of cooling): Q=h(T;-T:)4=h4TA O-heat transferred; M---the mass of the substance; vanced Materials Solid cp---heat capacity of the substance; h-heat exchange rate. 上降文通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSTTY
Heat transfer In side a substance: ( f) Q mcp T1 T2 Between the substance (Newton’s law of cooling): Q hT1 T2 A hTA Q—heat transferred; M--- the mass of the substance; cP---heat capacity of the substance; h—ht h t eat exchange rate