
先进材料疑固实验室 Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification 1896 1920 1987 2006 Crystal growth of single element solids(1) Dr.Mingxu Xia anced Mat 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
1896 1920 1987 2006 Crystal growth of single element solids (1) Dr. Mingxu Xia

先进材料疑固实验室 OUTLINE Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Liquid/solid interface Crystal growth of single element solids Crystal growth methods A00 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
OUTLINE Liquid/solid interface Crystal growth of single element solids Crystal growth methods

先进材料疑固实验室 Liquid/Solid interface Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Crystal growth from liquid is an essential Solid Liquid step in the process of solidification. Crystal growth is virtually a process of transferring atoms from liquid to solid. Similar to nucleation,this step can determine how fast the solidification is and the microstructure of the solid resulting from the solidification. nced Matere 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Liquid/Solid interface Crystal growth from liquid is an essential step in the process of solidification. Crystal growth is virtually a process of transferring atoms from liquid to solid. Similar to nucleation, this step can determine how fast the solidification is and the microstructure of the solid resulting from the solidification
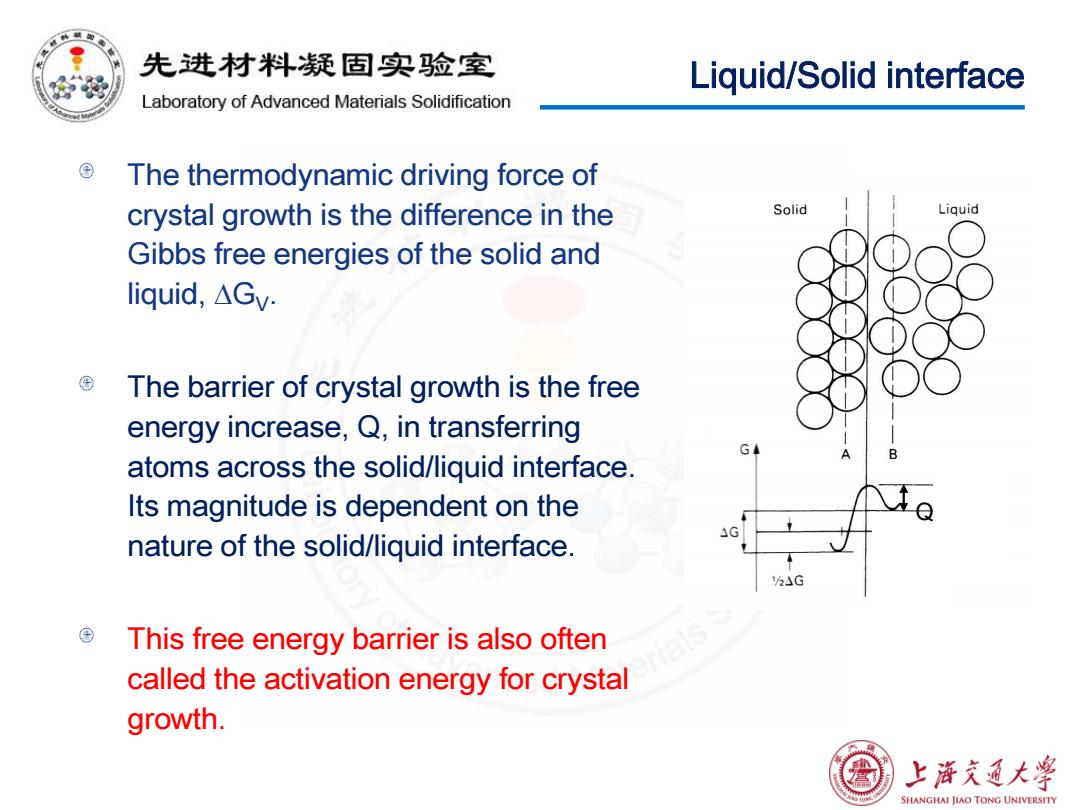
先进材料疑固实验室 Liquid/Solid interface Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification The thermodynamic driving force of crystal growth is the difference in the Solid Liquid Gibbs free energies of the solid and liquid,△Gv. The barrier of crystal growth is the free energy increase,Q,in transferring G atoms across the solid/liquid interface. Its magnitude is dependent on the nature of the solid/liquid interface. This free energy barrier is also often called the activation energy for crystal growth. 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Liquid/Solid interface The thermodynamic driving force of crystal growth is the difference in the Gibbs free energies of the solid and liquid, ∆GV. The barrier of crystal growth is the free energy increase, Q, in transferring atoms across the solid/liquid interface. Its magnitude is dependent on the nature of the solid/liquid interface. This free energy barrier is also often called the activation energy for crystal growth. Q

先进材料疑固实验室 Liguid/Solid interface Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification The rate of atom movement from solid to liquid: )s-.-NsfAmbsexp(-) The rate of atom movement from liquid to solid: ()L-=Ni.fi.Arbiexp() Ns and N are the numbers of atoms in the solid side and the liquid side of the S/L interface per unit area of the interface,respectively.For a flat S/L interface, Ns=NL=N. fs and fL are the probability of atoms in the solid and liquid,respectively,that can jump to the other side of the interface(normally,fs=f=1/6). 上海充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Liquid/Solid interface The rate of atom movement from solid to liquid: The rate of atom movement from liquid to solid: NS and NL are the numbers of atoms in the solid side and the liquid side of the S/L interface per unit area of the interface, respectively. For a flat S/L interface, NS=NL=N. fS and fL are the probability of atoms in the solid and liquid, respectively, that can jump to the other side of the interface (normally, fS=fL=1/6)