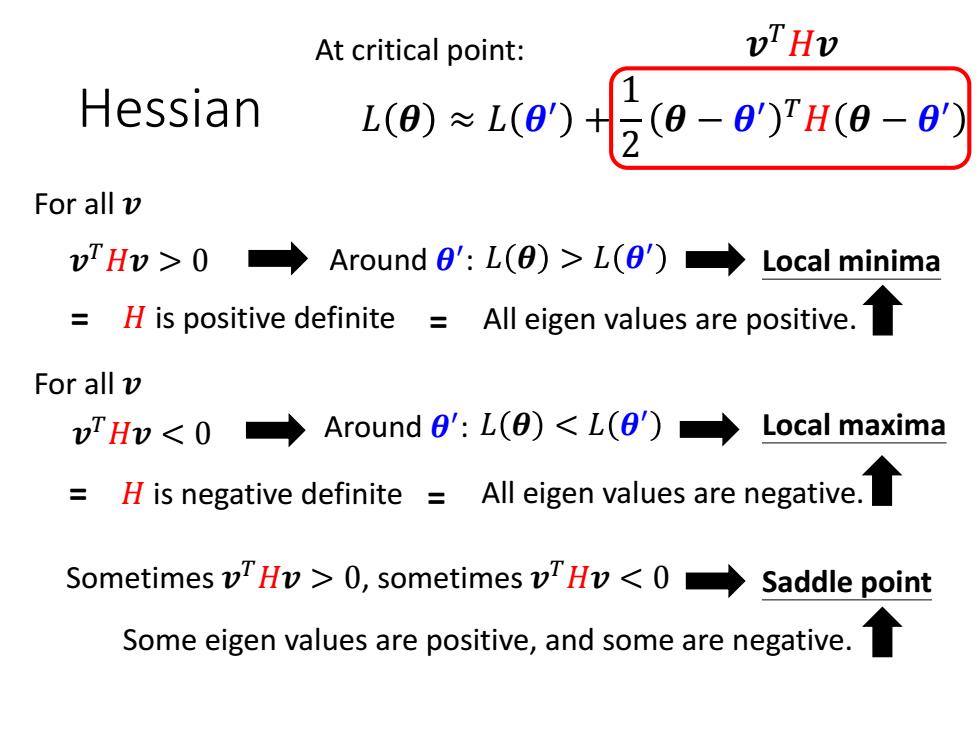
At critical point: vTHv Hessian 1 L(8)≈L(8)t(8-8)H(8-8) For all v vTHv>0→ Around 0':L(O)>L(θ')→Local minima H is positive definite All eigen values are positive. For all v vTHv<0 Around0':L(8)<L(0)◆ Local maxima H is negative definite =All eigen values are negative. Sometimes vTHv>0,sometimes vHv<0 Saddle point Some eigen values are positive,and some are negative
Hessian At critical point: 𝐻 is positive definite 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 > 0 Around 𝜽 Local minima ′ : 𝐿 𝜽 > 𝐿 𝜽 ′ All eigen values are positive. 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 < 0 Local maxima Sometimes 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 > 0, sometimes 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 < 0 Saddle point 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 𝐿 𝜽 ≈ 𝐿 𝜽 ′ + 1 2 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ 𝑇𝐻 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ Around 𝜽 ′ : 𝐿 𝜽 < 𝐿 𝜽 ′ = = = 𝐻 is negative definite = All eigen values are negative. Some eigen values are positive, and some are negative. For all 𝒗 For all 𝒗
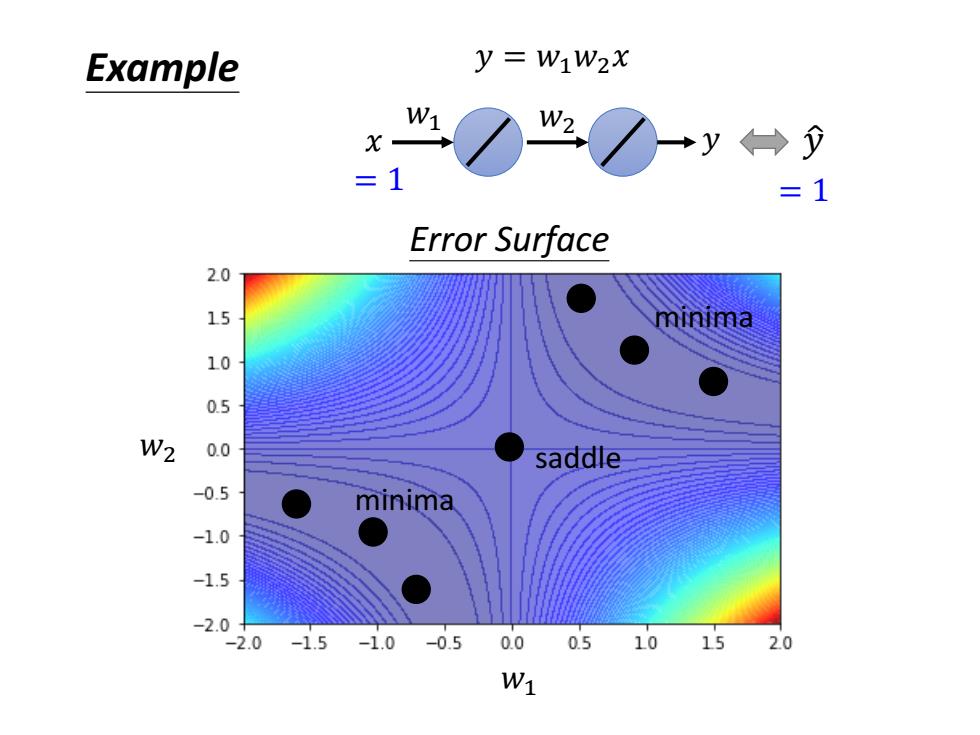
Example y=W1W2X W1 W2 →y←→ =1 =1 Error Surface 2.0 15 minima 10 W2 0.0 saddle -0.5 minima -1.0 -1.5 -2.0 2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 10 15 20 W1
𝑤1 𝑤2 𝑥 𝑦 𝑦 ො = 1 = 1 𝑦 = 𝑤1𝑤2𝑥 Example 𝑤1 𝑤2 Error Surface saddle minima minima

20 15 W1 W2 y →夕 106 =1 0.5 o L=(⊙-w1w2x)2=(1-w1w2)2 15 2.0 .0 -15 -10 -0.5 0.0 05 10 15 0W1 2(1-w1w2)(-w2) Critical point: W1=0,W2=0 =0 aL H=[9201a=22=-2 0W2 2(1-w1w2)(-w1) Saddle point =0 021 2(-w2)(-w2) 02L 0w1 -2+4W1W2 H =0 0w1∂w, =-2 02L -2+4W1W2 0w20W1 2(-w1)(-w1) =-2 =0
𝐿 = 𝑦 ො − 𝑤1𝑤2𝑥 2 𝜕𝐿 𝜕𝑤1 = 2 1 − 𝑤1𝑤2 −𝑤2 𝜕𝐿 𝜕𝑤2 = 2 1 − 𝑤1𝑤2 −𝑤1 𝜕 2𝐿 𝜕𝑤1 2 = 2 −𝑤2 −𝑤2 𝜕 2𝐿 𝜕𝑤2 2 = 2 −𝑤1 −𝑤1 𝜕 2𝐿 𝜕𝑤1𝜕𝑤2 = −2 + 4𝑤1𝑤2 𝜕 2𝐿 𝜕𝑤2𝜕𝑤1 = −2 + 4𝑤1𝑤2 𝑤1 𝑤2 𝑥 𝑦 𝑦 ො = 1 = 1 = 1 − 𝑤1𝑤2 2 Critical point: 𝑤1 = 0, 𝑤2 = 0 𝐻 = 0 −2 −2 0 𝜆1 = 2, 𝜆2 = −2 Saddle point = 0 = 0 = 0 = −2 = 0 = −2 𝒈 𝐻
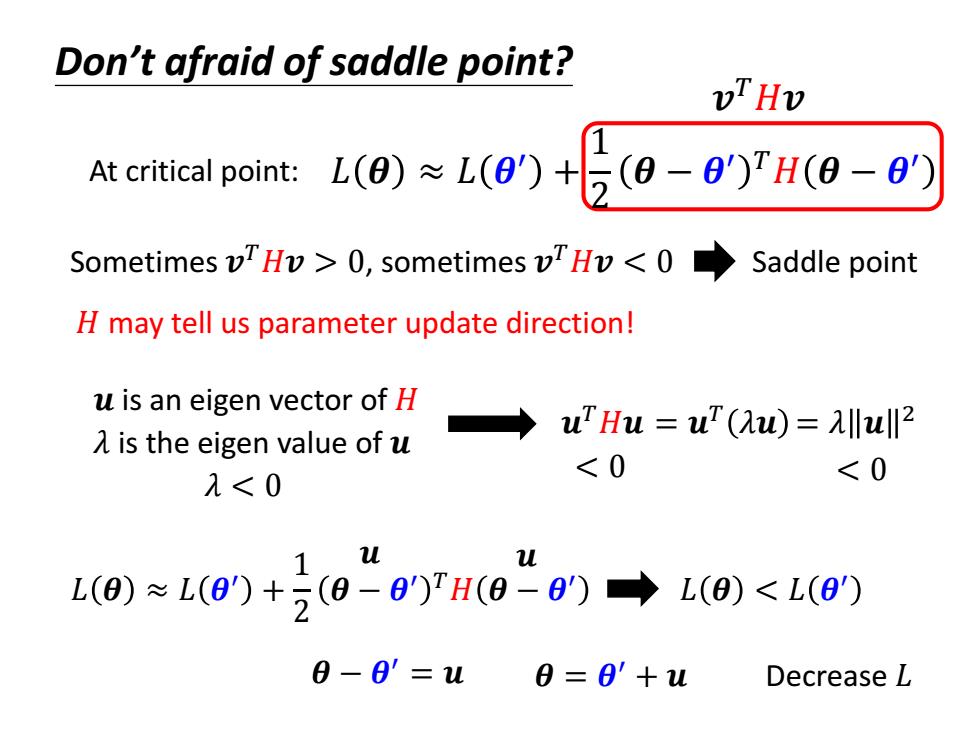
Don't afraid of saddle point? vTHv At critical point:L()L(+-)TH(-0' Sometimes vTHv>0,sometimes vTHv<0 Saddle point H may tell us parameter update direction! u is an eigen vector of H →uTHu=u(2u)=lul2 λis the eigen value of u λ<0 <0 <0 1 u L(0)≈L(0)+2(0-8)TH(0-6)→L(0)<L(8) 0-0'=2u 0=0'+u Decrease L
𝐿 𝜽 ≈ 𝐿 𝜽 ′ + 1 2 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ 𝑇𝐻 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ Sometimes 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 > 0, sometimes 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 < 0 Saddle point 𝒖 is an eigen vector of 𝐻 𝒖 𝑇𝐻𝒖 = 𝒖 𝑇 𝜆𝒖 = 𝜆 𝒖 2 𝜆 is the eigen value of 𝒖 𝐻 may tell us parameter update direction! 𝜆 < 0 < 0 < 0 At critical point: 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 Don’t afraid of saddle point? 𝒖 𝒖 𝐿 𝜽 < 𝐿 𝜽 ′ 𝜽 = 𝜽 ′ + 𝒖 Decrease 𝐿 𝐿 𝜽 ≈ 𝐿 𝜽 ′ + 1 2 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ 𝑇𝐻 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ = 𝒖
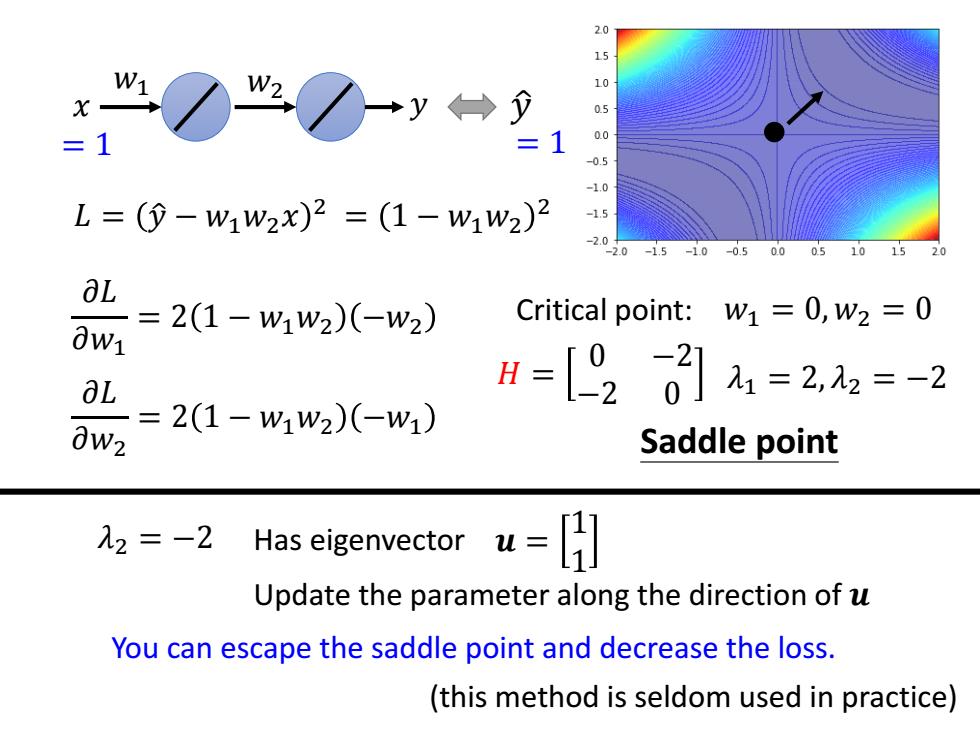
20 15 W2 +y←→ 09 1.0 L=(⊙-w1w2x)2=(1-w1w2)2 -15 2.0 2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 05 =21-w1w2)-w) Critical point: W1=0,W2=0 0W1 0L=2(1-ww2)(-w1) H=[920]=2,=-2 0W2 Saddle point =-2 Has sigenvector Update the parameter along the direction of u You can escape the saddle point and decrease the loss. (this method is seldom used in practice)
𝐿 = 𝑦 ො − 𝑤1𝑤2𝑥 2 𝜕𝐿 𝜕𝑤1 = 2 1 − 𝑤1𝑤2 −𝑤2 𝜕𝐿 𝜕𝑤2 = 2 1 − 𝑤1𝑤2 −𝑤1 𝑤1 𝑤2 𝑥 𝑦 𝑦 ො = 1 = 1 = 1 − 𝑤1𝑤2 2 Critical point: 𝑤1 = 0, 𝑤2 = 0 𝐻 = 0 −2 −2 0 𝜆1 = 2, 𝜆2 = −2 Saddle point Has eigenvector 𝒖 = 1 1 𝜆2 = −2 You can escape the saddle point and decrease the loss. Update the parameter along the direction of 𝒖 (this method is seldom used in practice)