
Chapter 10 Manipulating(处理),Computing,and Compensation(补偿)Devices by Yixin Ma 22/05/2013 Contents 2/26 1.Bridge Circuits 2.Amplifiers 3.Filters 4.Mathematic Operations: Integration and Differentiation Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division 5.Function Generation and Linearization 6.Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation 7.Voltage-to-frequency and Frequency-to-Voltage Converters 8.ADC and DAC;SHA
Chapter 10 Manipulating(处理), Computing, and Compensation(补偿) Devices by Yixin Ma 22/05/2013 Contents 1. Bridge Circuits 2. Amplifiers 3. Filters 4. Mathematic Operations: z Integration and Differentiation z Addition and Subtraction z Multiplication and Division 5. Function Generation and Linearization 6. Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation 7. Voltage-to-frequency and Frequency-to-Voltage Converters 8. ADC and DAC; SHA 2/26
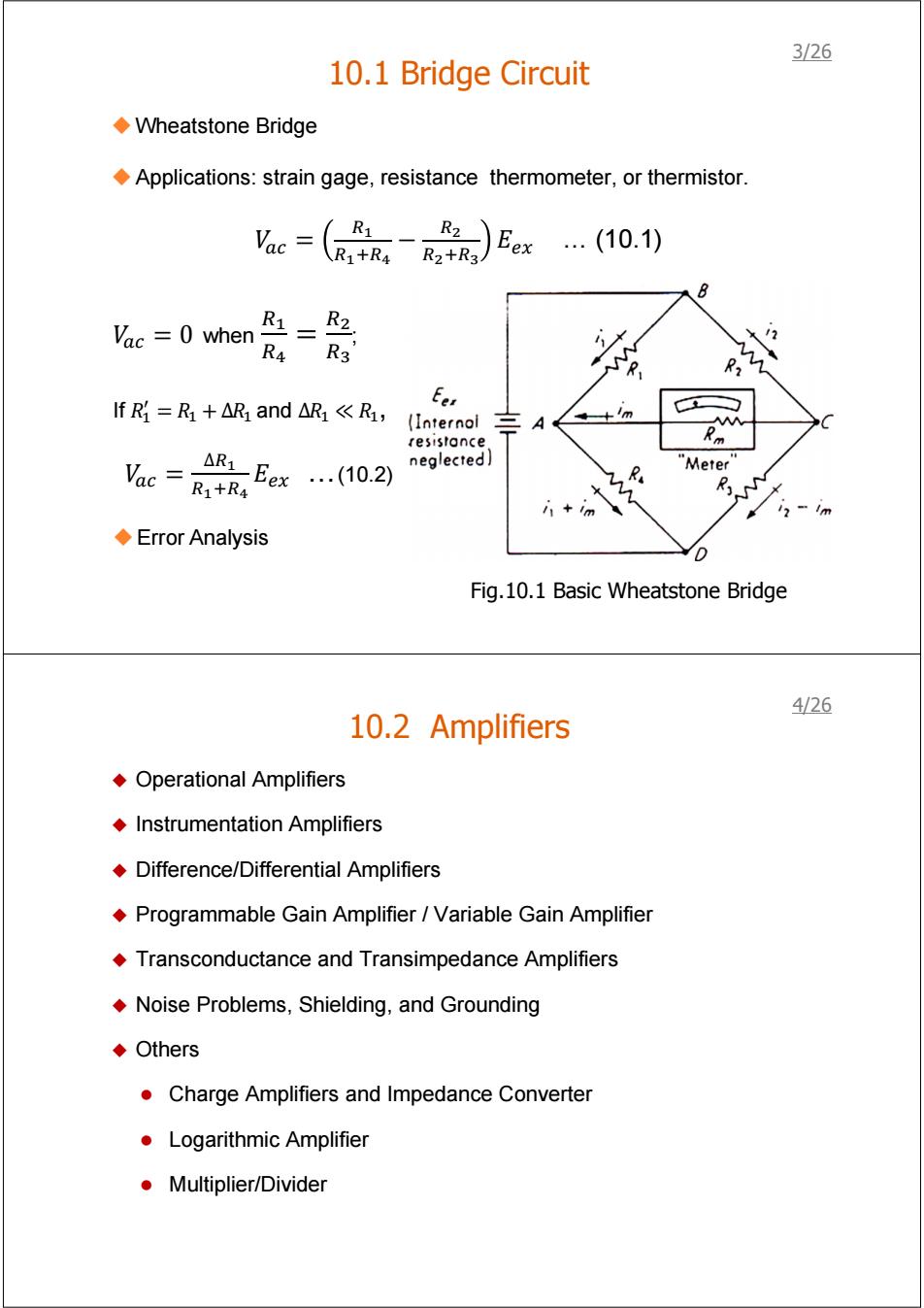
3/26 10.1 Bridge Circuit ◆Wheatstone Bridge Applications:strain gage,resistance thermometer,or thermistor. Vac= R1 )Eex(10.1) R1+R4R2+R3 Vac =0 when =2 R4 R3' Eer fR=R+AR and△R《R,(Interol m A AA resistance △R2Eex(10.2) Vac=R+R neglected R "Meter i+im 12-Im ◆Error Analysis D Fig.10.1 Basic Wheatstone Bridge 426 10.2 Amplifiers Operational Amplifiers Instrumentation Amplifiers Difference/Differential Amplifiers Programmable Gain Amplifier /Variable Gain Amplifier Transconductance and Transimpedance Amplifiers Noise Problems,Shielding,and Grounding ◆Others Charge Amplifiers and Impedance Converter Logarithmic Amplifier ●Multiplier/Divider
10.1 Bridge Circuit Fig.10.1 Basic Wheatstone Bridge Wheatstone Bridge Applications: strain gage, resistance thermometer, or thermistor. ܸ = ோభ ோభାோర − ோమ ோమାோయ ܧ௫ … (10.1) ܸ = 0 when ோభ ோర ோమ ோయ ; If ܴଵ ᇱ = ܴଵ + ∆ܴଵ and ∆ܴଵ ≪ ܴଵ, ܸ = ∆ோభ ோభାோర ܧ௫ …(10.2) Error Analysis 3/26 10.2 Amplifiers Operational Amplifiers Instrumentation Amplifiers Difference/Differential Amplifiers Programmable Gain Amplifier / Variable Gain Amplifier Transconductance and Transimpedance Amplifiers Noise Problems, Shielding, and Grounding Others z Charge Amplifiers and Impedance Converter z Logarithmic Amplifier z Multiplier/Divider 4/26
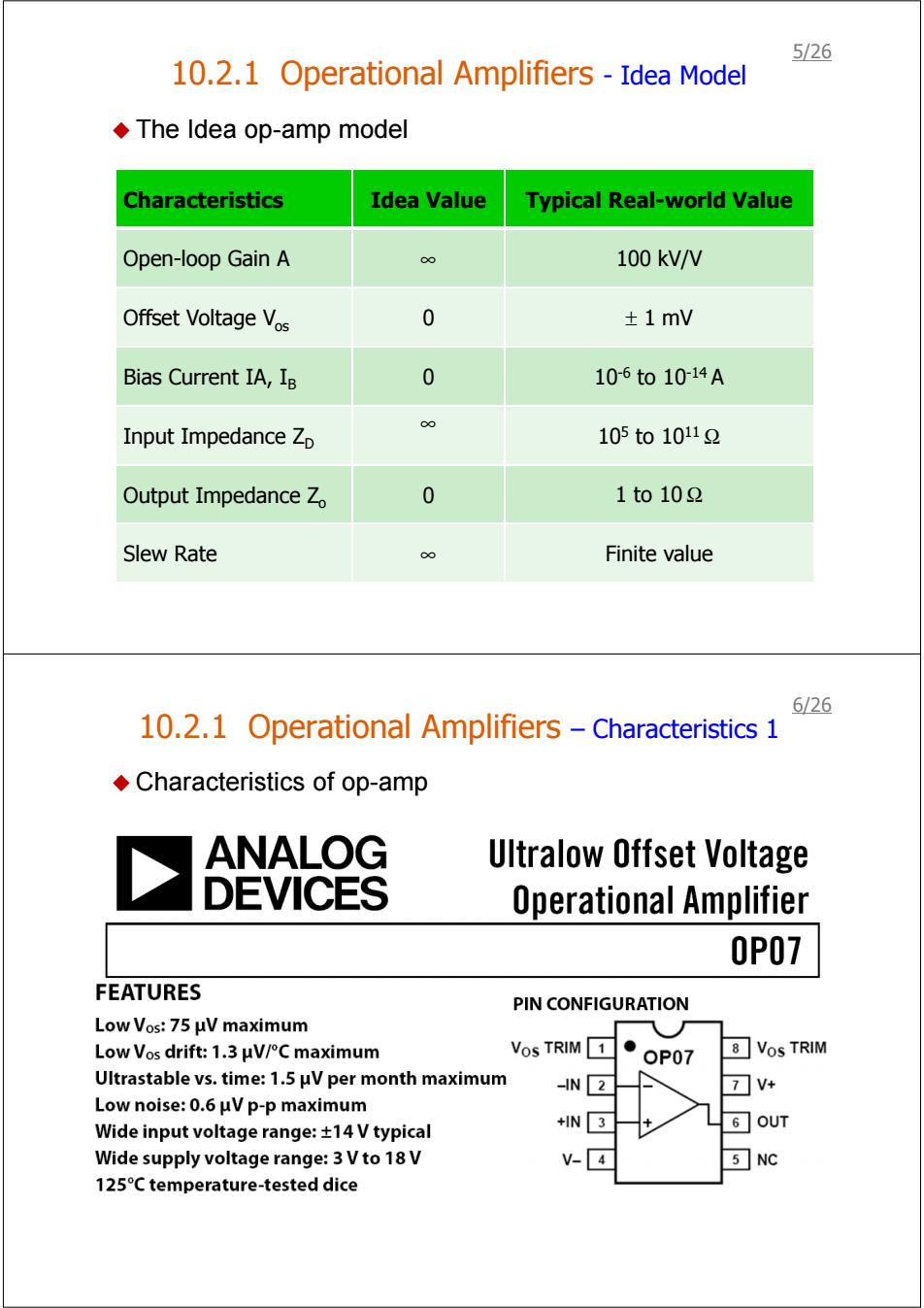
5/26 10.2.1 Operational Amplifiers-Idea Model ◆The Idea op-amp model Characteristics Idea Value Typical Real-world Value Open-loop Gain A 100 kV/V Offset Voltage Vos 0 ±1mv Bias Current IA,IB 0 106to10-14A Input Impedance Zp 105to10112 Output Impedance Zo 0 1to102 Slew Rate Finite value 6126 10.2.1 Operational Amplifiers-Characteristics 1 Characteristics of op-amp ANALOG Ultralow Offset Voltage DEVICES Operational Amplifier 0P07 FEATURES PIN CONFIGURATION Low Vos::75μVmaximum Low Vos drift:1.3μV/°C maximum Vos TRIM1 ● OP07 8☐Vos TRIM Ultrastable vs.time:1.5 uV per month maximum -N2 7☑V+ Low noise:0.6 uV p-p maximum Wide input voltage range:+14 V typical 6OUT Wide supply voltage range:3 Vto 18V v-4 5 NC 125C temperature-tested dice
10.2.1 Operational Amplifiers - Idea Model The Idea op-amp model Characteristics Idea Value Typical Real-world Value Open-loop Gain A ∞ 100 kV/V Offset Voltage Vos 0 ± 1 mV Bias Current IA, IB 0 10-6 to 10-14 A Input Impedance ZD ∞ 105 to 1011 Ω Output Impedance Zo 0 1 to 10 Ω Slew Rate ∞ Finite value 5/26 10.2.1 Operational Amplifiers – Characteristics 1 Characteristics of op-amp 6/26
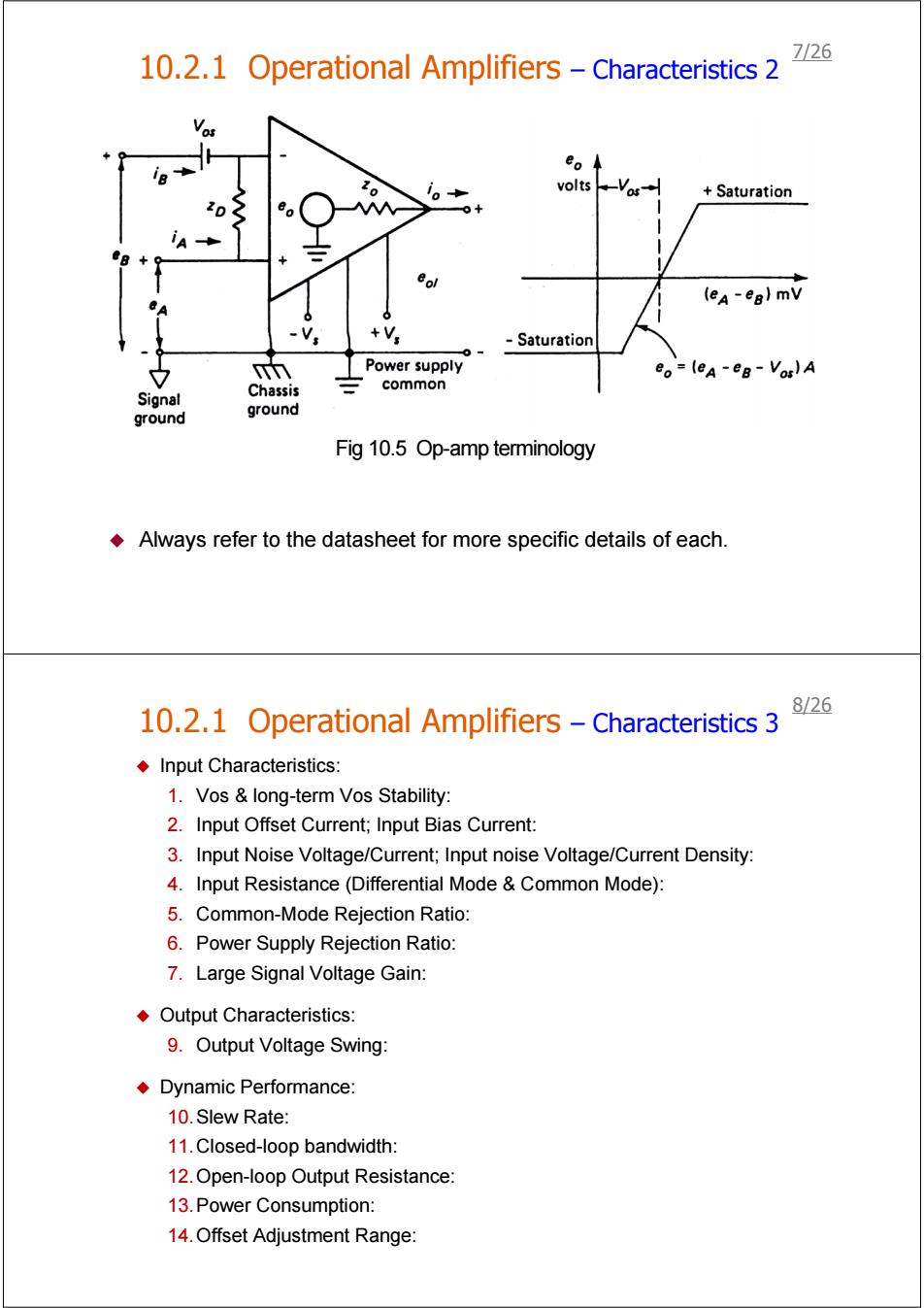
10.2.1 Operational Amplifiers-Characteristics 2 7/26 e。 voltsVas Saturation eol (ea-eg)mV -Saturation 中 Power supply eo=(eA-eB-Vos)A common Signal Chassis ground ground Fig 10.5 Op-amp terminology Always refer to the datasheet for more specific details of each. 8/26 10.2.1 Operational Amplifiers-Characteristics 3 Input Characteristics: 1.Vos long-term Vos Stability: 2.Input Offset Current;Input Bias Current: 3.Input Noise Voltage/Current;Input noise Voltage/Current Density: 4.Input Resistance(Differential Mode Common Mode): 5.Common-Mode Rejection Ratio: 6.Power Supply Rejection Ratio: 7.Large Signal Voltage Gain: Output Characteristics: 9.Output Voltage Swing: Dynamic Performance: 10.Slew Rate: 11.Closed-loop bandwidth: 12.Open-loop Output Resistance: 13.Power Consumption: 14.Offset Adjustment Range:
Always refer to the datasheet for more specific details of each. 10.2.1 Operational Amplifiers – Characteristics 2 Fig 10.5 Op-amp terminology 7/26 10.2.1 Operational Amplifiers – Characteristics 3 Input Characteristics: 1. Vos & long-term Vos Stability: 2. Input Offset Current; Input Bias Current: 3. Input Noise Voltage/Current; Input noise Voltage/Current Density: 4. Input Resistance (Differential Mode & Common Mode): 5. Common-Mode Rejection Ratio: 6. Power Supply Rejection Ratio: 7. Large Signal Voltage Gain: Output Characteristics: 9. Output Voltage Swing: Dynamic Performance: 10.Slew Rate: 11.Closed-loop bandwidth: 12.Open-loop Output Resistance: 13.Power Consumption: 14.Offset Adjustment Range: 8/26
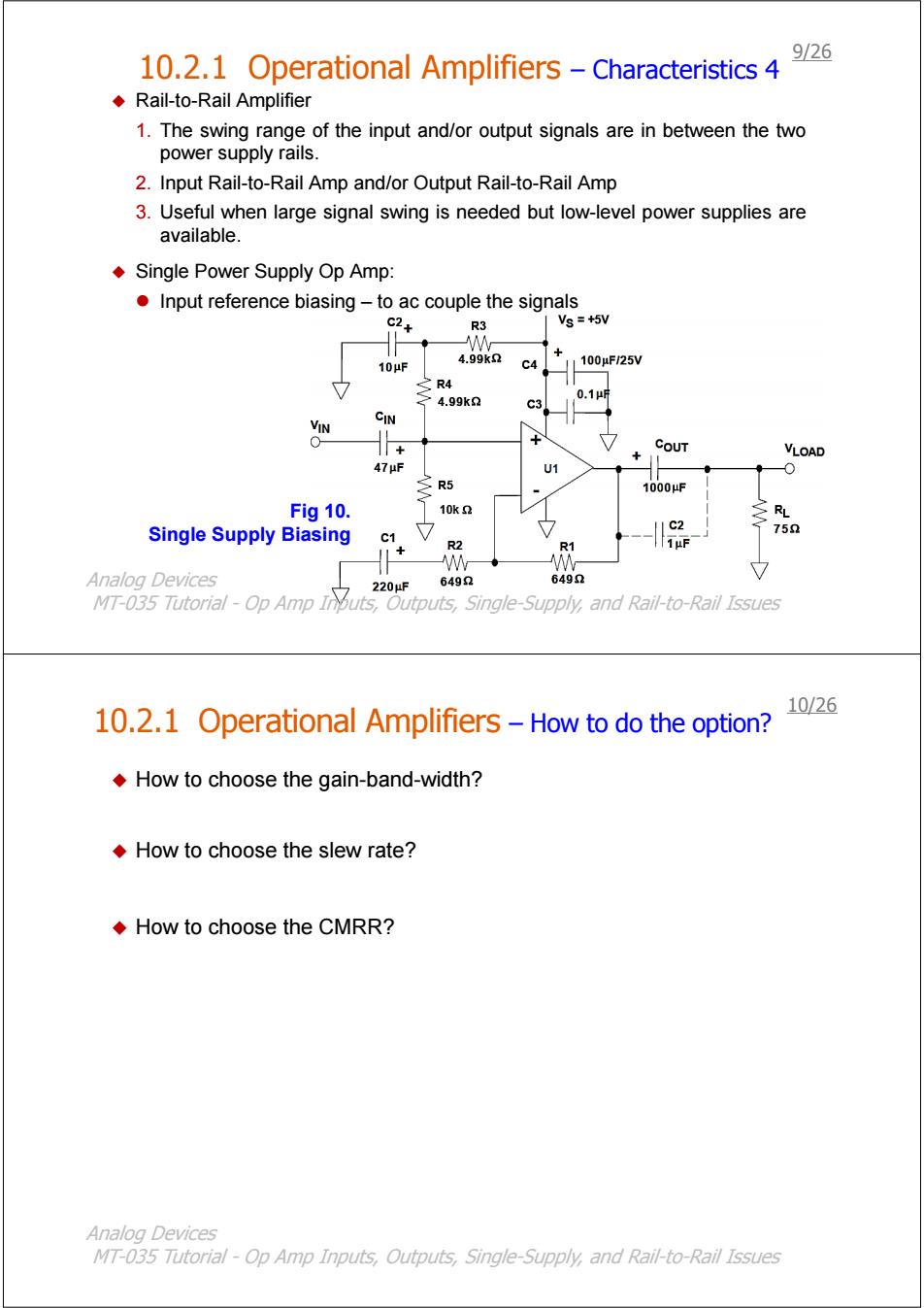
9/26 10.2.1 Operational Amplifiers -Characteristics 4 Rail-to-Rail Amplifier 1.The swing range of the input and/or output signals are in between the two power supply rails. 2.Input Rail-to-Rail Amp and/or Output Rail-to-Rail Amp 3.Useful when large signal swing is needed but low-level power supplies are available. Single Power Supply Op Amp: Input reference biasing-to ac couple the signals R3 Vs =+5V 10μF 4.99kn C4 1100μF/25V 之R4 4.99k2 0.1μ c3 CIN COUT VLOAD 47μF U1 0 三R5 1000μF Fig 10. 10k2 RL Single Supply Biasing C2 75Ω C1 R2 R1 1μF Analog Devices 6492 6492 220μF MT-035 Tutorial-Op Amp Inouts,Outputs,Single-Supply,and Rail-to-Rail Issues 10/26 10.2.1 Operational Amplifiers-How to do the option? How to choose the gain-band-width? How to choose the slew rate? How to choose the CMRR? Analog Devices MT-035 Tutorial-Op Amp Inputs,Outputs,Single-Supply,and Rail-to-Rail Issues
10.2.1 Operational Amplifiers – Characteristics 4 Rail-to-Rail Amplifier 1. The swing range of the input and/or output signals are in between the two power supply rails. 2. Input Rail-to-Rail Amp and/or Output Rail-to-Rail Amp 3. Useful when large signal swing is needed but low-level power supplies are available. Single Power Supply Op Amp: z Input reference biasing – to ac couple the signals Fig 10. Single Supply Biasing Analog Devices MT-035 Tutorial - Op Amp Inputs, Outputs, Single-Supply, and Rail-to-Rail Issues 9/26 10.2.1 Operational Amplifiers – How to do the option? How to choose the gain-band-width? How to choose the slew rate? How to choose the CMRR? Analog Devices MT-035 Tutorial - Op Amp Inputs, Outputs, Single-Supply, and Rail-to-Rail Issues 10/26