
上游克通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Measurement Systems: Application and Design Lectured by Yixin Ma 27/02/2013 上游充通大¥ Chapter 1 applications of SHANGHAI JAO TONG UNIVERSITY Measurement Instrumentation Contents 1.1 Why Study Measurement System? 1.2 Types of Measurement Applications 1.3 Computer-Aided Machines and Process 1.4 Conclusion the purpose of this course 1.5 Contents of this course 1.6 Related Issues
Measurement Systems: Application and Design Lectured by Yixin Ma 27/02/2013 Chapter 1 Applications of Measurement Instrumentation Contents 1.1 Why Study Measurement System? 1.2 Types of Measurement Applications 1.3 Computer - Aided Machines and Process 1.4 Conclusion - the purpose of this course 1.5 Contents of this course 1.6 Related Issues
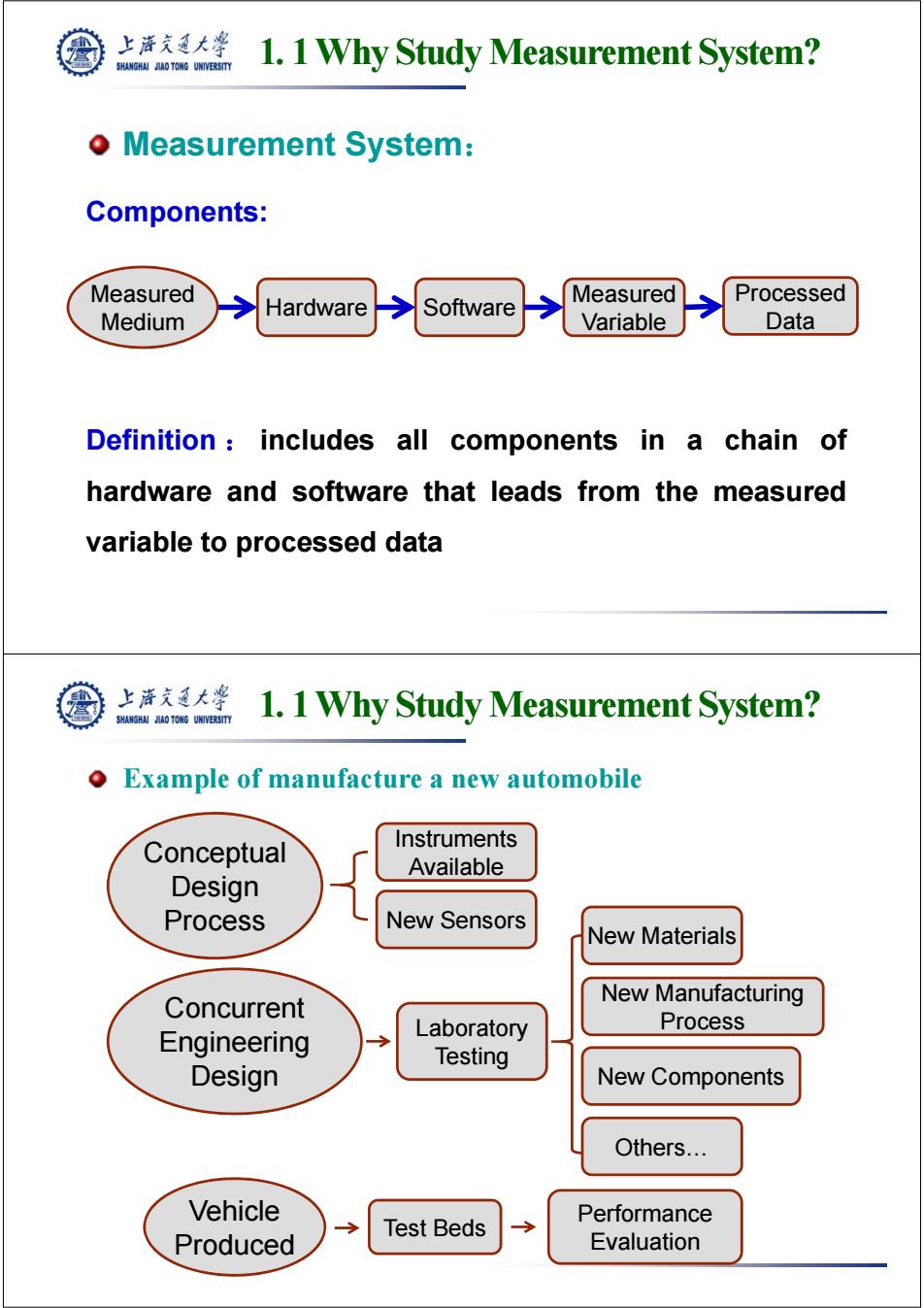
上海充通大学 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1.1 Why Study Measurement System? o Measurement System: Components: Measured Measured Processed Medium Hardware Software Variable Data Definition includes all components in a chain of hardware and software that leads from the measured variable to processed data 上海充通大粤 SHANGHAI JAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1.1 Why Study Measurement System? Example of manufacture a new automobile Conceptual Instruments Available Design Process New Sensors New Materials Concurrent New Manufacturing Laboratory Process Engineering Testing Design New Components Others.… Vehicle Test Beds Performance Produced Evaluation
1. 1 Why Study Measurement System? Measurement System: Hardware Measured Medium Software Measured Variable Processed Data Components: Definition : includes all components in a chain of hardware and software that leads from the measured variable to processed data 1. 1 Why Study Measurement System? Example of manufacture a new automobile Conceptual Design Process Concurrent Engineering Design Instruments Available New Sensors Test Beds Laboratory Testing New Materials New Manufacturing Process New Components Others… Vehicle Produced Performance Evaluation

上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1.1 Why Study Measurement System? Example-Sensors used in Vehicle Speedometer -Tachometers:measures the working speed of an engine (esp.in a road vehicle),typically in revolutions per minute(RPM) -Fuel Gages 一Temperature Sensors Global Positioning System(GPS) -Acceleration Sensor(Accelerometer) 一Gyroscopic(陀螺)Instrument:Measures Angular Velocity Engine Operation Sensors Atmospheric Pressure ●Air Flow Rate ●Fuel/Air ratio ●Engine Temperature 上游文更大学 SHANGHAI JAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1.2 Types of Measurement Applications Monitoring of Processes and Operations Control of Processes and Operations Experimental Engineering Analysis
1. 1 Why Study Measurement System? Example --- Sensors used in Vehicle ▬ Speedometer ▬ Tachometers: measures the working speed of an engine (esp. in a road vehicle), typically in revolutions per minute (RPM) ▬ Fuel Gages ▬ Temperature Sensors ▬ Global Positioning System (GPS) ▬ Acceleration Sensor (Accelerometer) ▬ Gyroscopic(陀螺) Instrument: Measures Angular Velocity ▬ Engine Operation Sensors z Atmospheric Pressure z Air Flow Rate z Fuel/Air ratio z Engine Temperature 1.2 Types of Measurement Applications Monitoring of Processes and Operations Control of Processes and Operations Experimental Engineering Analysis
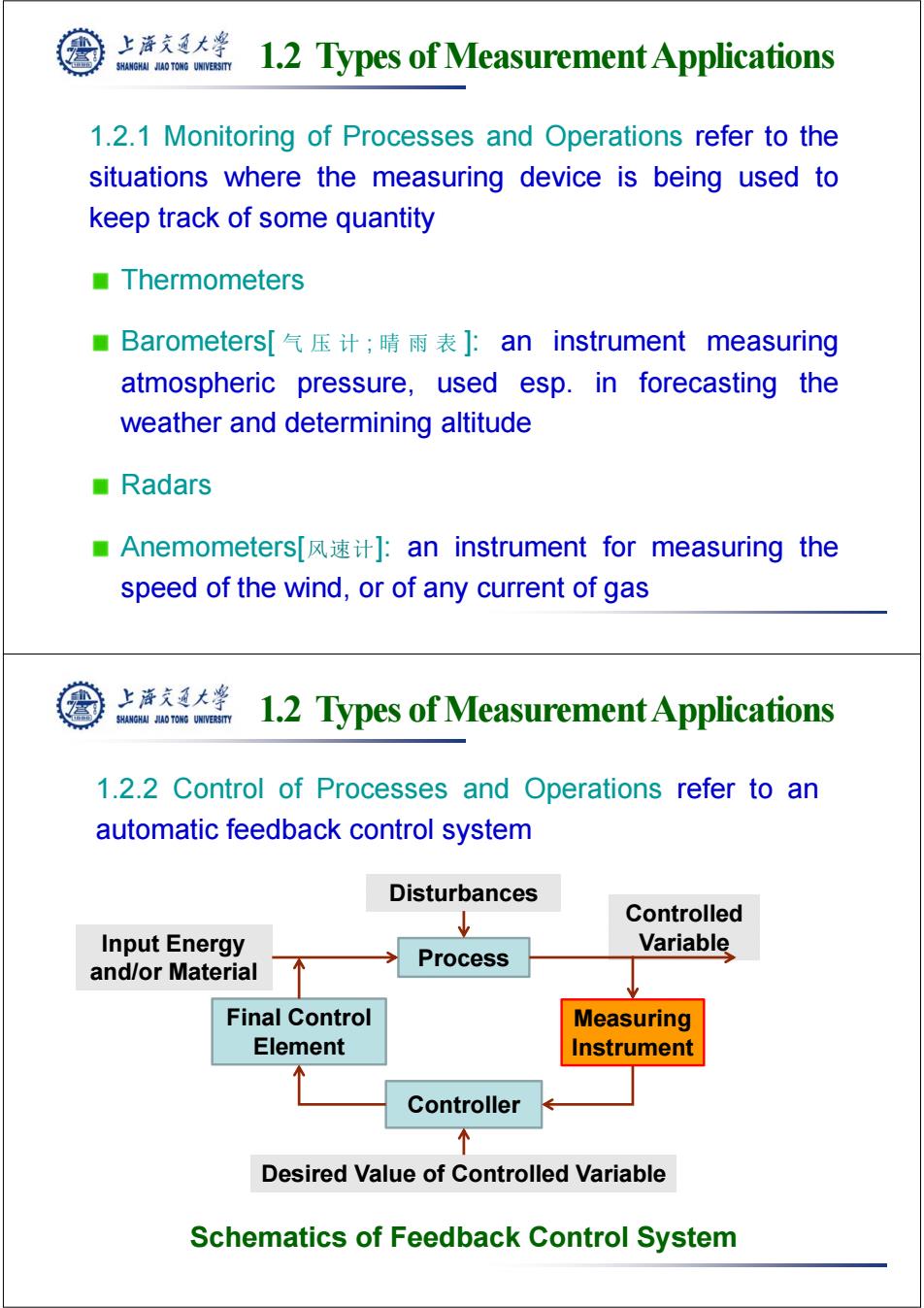
上游气通大¥ SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1.2 Types of Measurement Applications 1.2.1 Monitoring of Processes and Operations refer to the situations where the measuring device is being used to keep track of some quantity ■Thermometers ■Barometers[气压计;晴雨表:an instrument measuring atmospheric pressure,used esp.in forecasting the weather and determining altitude ■Radars ■Anemometers[风速计]:an instrument for measuring the speed of the wind,or of any current of gas 上海充通大学 SHANGHAI JAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1.2 Types of Measurement Applications 1.2.2 Control of Processes and Operations refer to an automatic feedback control system Disturbances Controlled Input Energy Process Variable and/or Material Final Control Measuring Element Instrument Controller 个 Desired Value of Controlled Variable Schematics of Feedback Control System
1.2 Types of Measurement Applications 1.2.1 Monitoring of Processes and Operations refer to the situations where the measuring device is being used to keep track of some quantity Thermometers Barometers[ 气压计 ; 晴雨表 ]: an instrument measuring atmospheric pressure, used esp. in forecasting the weather and determining altitude Radars Anemometers[风速计]: an instrument for measuring the speed of the wind, or of any current of gas 1.2 Types of Measurement Applications 1.2.2 Control of Processes and Operations refer to an automatic feedback control system Process Input Energy and/or Material Controller Measuring Instrument Disturbances Final Control Element Desired Value of Controlled Variable Controlled Variable Schematics of Feedback Control System
上誉克通大 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1.2 Types of Measurement Applications 1.2.2 Control of Processes and Operations refer to an automatic feedback control system Measurement Systems that used feedback principle: >Hotwire anemometer[热线风速仪] Feedback System that used Measurement Instruments. >Room temperature control >Antilock Braking System >Coolant Temperature Regulating System >Air-conditioning System >Engine Pollution Controls 上溶充通大粤 SHANGHAI JAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1.2 Types of Measurement Applications 1.2.3 Experimental Engineering Analysis is part of engineering design,development,and research that relies on laboratory testing of one kind or another to answer questions. Two ways to solve engineering problem: Theory Experiment
1.2 Types of Measurement Applications 1.2.2 Control of Processes and Operations refer to an automatic feedback control system Measurement Systems that used feedback principle; Hotwire anemometer [热线风速仪] Feedback System that used Measurement Instruments. Room temperature control Antilock Braking System Coolant Temperature Regulating System Air-conditioning System Engine Pollution Controls 1.2 Types of Measurement Applications 1.2.3 Experimental Engineering Analysis is part of engineering design, development, and research that relies on laboratory testing of one kind or another to answer questions. Two ways to solve engineering problem: Theory Experiment