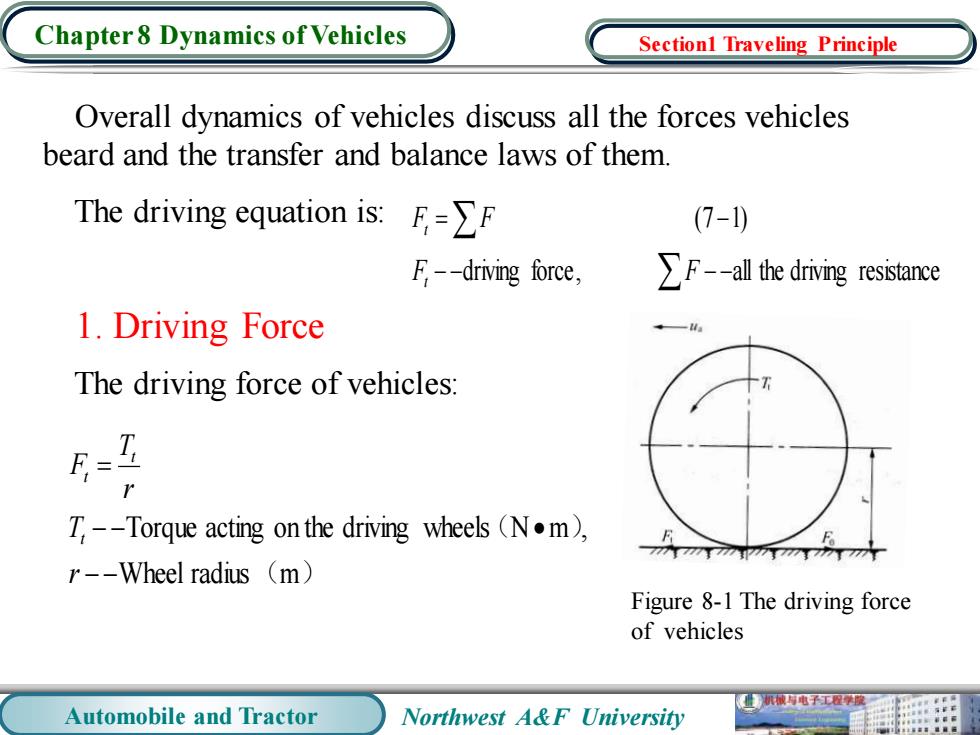
Chapter 8 Dynamics of Vehicles Sectionl Traveling Principle Overall dynamics of vehicles discuss all the forces vehicles beard and the transfer and balance laws of them. The driving equation is:FF (7-) F--driving force, Fall the driving resistance 1.Driving Force The driving force of vehicles: T--Torque acting on the driving wheels (N.m), r--Wheel radius (m) Figure 8-1 The driving force of vehicles 机械与电子工程学原 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 8 Dynamics of Vehicles Overall dynamics of vehicles discuss all the forces vehicles beard and the transfer and balance laws of them. The driving equation is: 1. Driving Force The driving force of vehicles: ( ) ( ) Wheel radius m Torque acting on the driving wheels N m , − − − − • = r T r T F t t t driving force, all the driving resistance (7 1) − − − − = − F F F F t t Section1 Traveling Principle Figure 8-1 The driving force of vehicles
Chapter 8 Dynamics of Vehicles Sectionl Traveling Principle Since the torque T:acting on the wheels is produced by the engine and transmitted to the wheels through the driven system,therefore: T:=Tigigion T--Engine torque ig--Transmissi on ratio; io--Final drive ratio; --Mechanical efficiency of transmiss ion. The above equation should be included corresponding gear ratio and mechanical efficiency for vehicles with devices such as transfer case,wheel reduction and dydraudynamic drive unit,thus the driving force is: Ta●ig●i●n 械电子工程学 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 8 Dynamics of Vehicles Since the torque Tt acting on the wheels is produced by the engine and transmitted to the wheels through the driven system, therefore: Final drive ratio Mechanical efficiency of transmiss ion . Engine torque Transmissi on ratio 0 0 − − − − − − − − = • • • T t q g t t q g T i T i T T i i ; ; ; The above equation should be included corresponding gear ratio and mechanical efficiency for vehicles with devices such as transfer case, wheel reduction and dydraudynamic drive unit, thus the driving force is: r T i i F t q g T t • • • = 0 Section1 Traveling Principle

Chapter 8 Dynamics of Vehicles Sectionl Traveling Principle Two requirements of generation driving force: (1)Engine torque is transmitted to the driving wheels as the driving moment after changing the magnitude and direction by the transmission,and then it provides the applied force along the tangential directions of the tires,which is the internal conditions of generating the driving force. (2)Depending on the interaction between the ground and driving wheels,the applied force that the driving wheels act on the ground is changed to the ground reacting force along the tangential directions of the tires,which is the external conditions of generating the driving force. 机被电子工程学聚 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 8 Dynamics of Vehicles Two requirements of generation driving force: (1) Engine torque is transmitted to the driving wheels as the driving moment after changing the magnitude and direction by the transmission, and then it provides the applied force along the tangential directions of the tires, which is the internal conditions of generating the driving force. (2) Depending on the interaction between the ground and driving wheels, the applied force that the driving wheels act on the ground is changed to the ground reacting force along the tangential directions of the tires, which is the external conditions of generating the driving force. Section1 Traveling Principle

Chapter 8 Dynamics of Vehicles Sectionl Traveling Principle 2.Driving Resistance The total driving resistance is ∑F=F+Fn+E+E, (7-5) F--Rolling resistance; F。--Air resistance; F--Slope resistance F--Accelerating resistance. By(7-1)and(7-5): F=F-E+E+) 械电子工程学度 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 8 Dynamics of Vehicles 2. Driving Resistance The total driving resistance is : 。 ; ; ; Accelerati ng resistance Slope resistance Air resistance Rolling resistance (7 5) − − − − − − − − = + + + − j i w f f w i j F F F F F F F F F By (7-1) and (7-5): ( ) Fj = Ft − Ff + Fw + Fi Section1 Traveling Principle

Chapter 8 Dynamics of Vehicles Sectionl Traveling Principle 3.The Driving and Adhesion Conditions of Vehicle Traveling 3.1 Driving Conditions The first condition of the vehicle traveling: ,≥Fr+Fw+F 3.2 Adhesion Conditions The second condition of the vehicle traveling E≤F。=Fop --Coefficien t of adhesion F--Weight beard by driving wheels; The driving and adhesion conditions of the vehicle traveling (necessary and sufficient conditions) F+Fn+F≤F≤Fo·p Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 8 Dynamics of Vehicles 3 . The Driving and Adhesion Conditions of Vehicle Traveling 3.1 Driving Conditions The first condition of the vehicle traveling: 3.2 Adhesion Conditions The second condition of the vehicle traveling: The driving and adhesion conditions of the vehicle traveling: (necessary and sufficient conditions) —— ; —— ; Weight beard by driving wheels Coefficien t of adhesion z t z F F F = F • Ft Ff + Fw + Fi Ff + Fw + Fi Ft Fz • Section1 Traveling Principle