
Chapter 12 Antibiotics
Chapter 12 Antibiotics

Some examples of classification of antibiotics Biochemical function: Inhibition of Example Nucleic acid synthesis Nalidixinic acid (DNA) Protein synthesis Streptomycin,Tetracycline,Chloramphenicol Cell wall synthesis Penicillin,Cephalosporin Membrane function Polymyxin Energy metabolism Gramicidin Structure: Class:Activity against Example B-lactams G+bacteria Penicillin,Cephalosporin Aminoglycosides G+&G-bacteria Streptomycin,Kanamycin Macrolides G+bacteria Erythromycin Polypeptides G+&G-bacteria Bacitracin,Polymyxin Kinons Broad-spectrum Tetracycline Polyenes Fungi Nystatin,Amphotericin Antimicrobial spectrum: Bactericide Kills bacteria Bacteristatic Inhibits bacteria Fungicide Kills fungi Fungistatic Inhibits fungi Antiviral Active against virus Broad-spectrum Active against many types of microorganisms
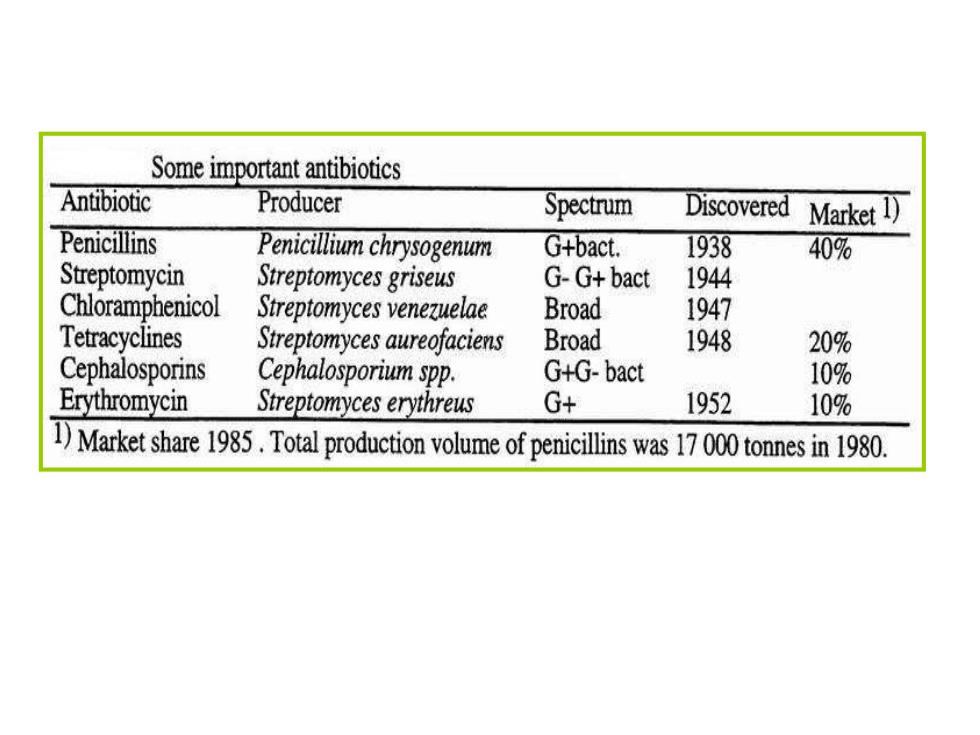
Some important antibiotics Antibiotic Producer Spectrum Discovered Market 1) Penicillins Penicillium chrysogenum G+bact. 1938 40% Streptomycin Streptomyces griseus G-G+bact 1944 Chloramphenicol Streptomyces venezuelae Broad 1947 Tetracyclines Streptomyces aureofaciens Broad 1948 20% Cephalosporins Cephalosporium spp. G+G-bact 10% Erythromycin Streptomyces erythreus G+ 1952 10% 1)Market share 195.Total production voume of penicillins was 17000tones in1980
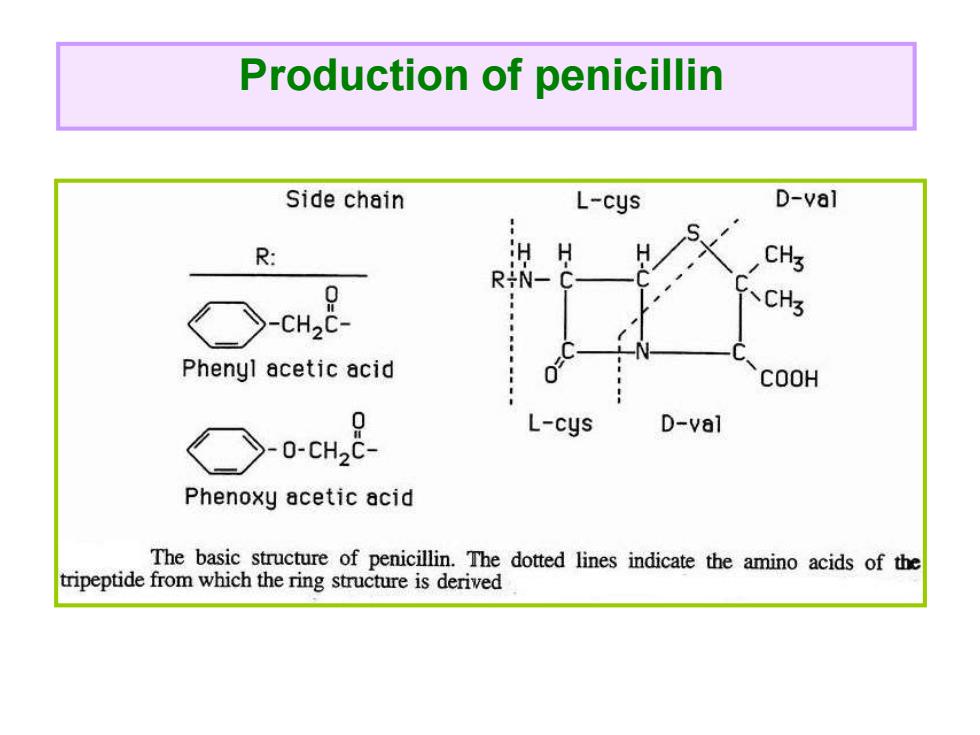
Production of penicillin Side chain L-cys D-val R: RiN- CHs -, 、CH Phenyl acetic acid COOH L-cys D-val Phenoxy acetic acid The basic structure of penicillin.The dotted lines indicate the amino acids of the tripeptide from which the ring structure is derived
Production of penicillin

Penicillin G:benzylpenicillin Penicillin V:phenoxymethypenicillin Strain: Penicillium notatum (1940s) Penicillium chrysogenum 6-APA
Penicillin G: benzylpenicillin Penicillin V: phenoxymethypenicillin Strain: Penicillium notatum (1940s) Penicillium chrysogenum 6-APA