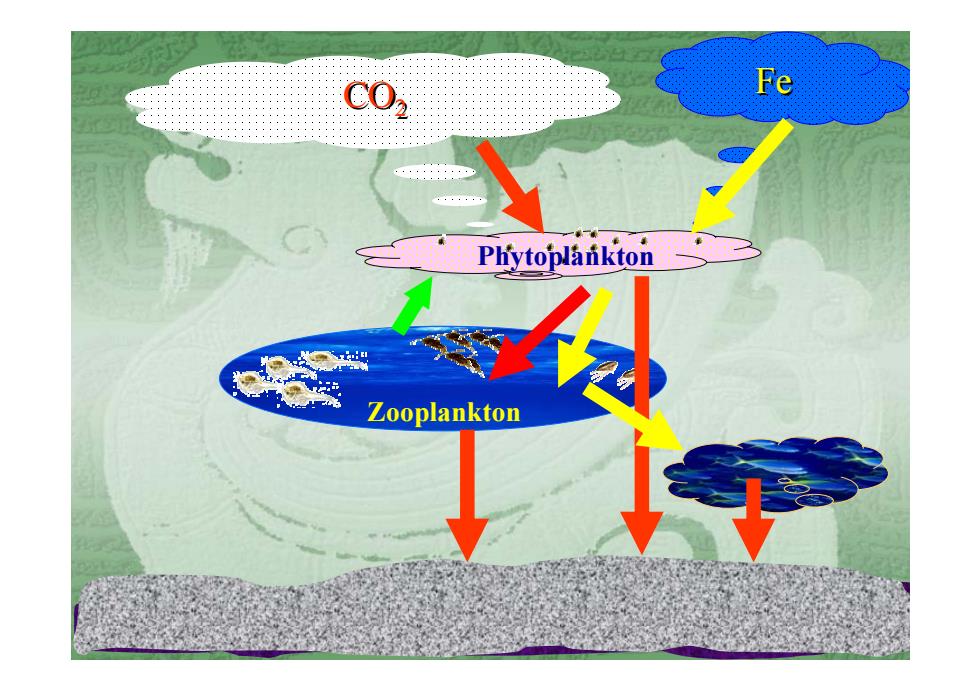
Phytoplankton Zooplankton 25 Fe CO 22
Phytoplankton Zooplankton 25 Fe CO 22

Introduction 1. Definition 2. The Relation Between Marine Planktology and Other Disciplines of Oceanography 3. Ecological Groups of Plankton 4. Economic Importance 5. Brief History and Prospects
Introduction 1. Definition 2. The Relation Between Marine Planktology and Other Disciplines of Oceanography 3. Ecological Groups of Plankton 4. Economic Importance 5. Brief History and Prospects

3 Ecological Groups 3.1 Type of Nutrition Phytoplankton: autotrophic bacteria and unicellular algae (Bacillariophyta, Pyrrophyta, Chlorophyta, Cyanophyta, Chrysophyta, Xanthophyta, Cryptophyta and Euglenophyta) Zooplankton: heterotrophic Protozoa, medusae, Rotifera, Crustacea, Chaetognatha, pelagic Mollusca, Tunicata, larvae of invertebrate and lower chordates
3 Ecological Groups 3.1 Type of Nutrition Phytoplankton: autotrophic bacteria and unicellular algae (Bacillariophyta, Pyrrophyta, Chlorophyta, Cyanophyta, Chrysophyta, Xanthophyta, Cryptophyta and Euglenophyta) Zooplankton: heterotrophic Protozoa, medusae, Rotifera, Crustacea, Chaetognatha, pelagic Mollusca, Tunicata, larvae of invertebrate and lower chordates

Phytoplankton 1: Diatom
Phytoplankton 1: Diatom