
C1B△1NT1 ATIVE FO0 OVIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISE.N Risk Factors Lung growth and development Exposure to particles Oxidative stress ·Tobacco smoke Gender Occupational dusts, Age organic and inorganic Genes Indoor air pollution from Respiratory infections heating and cooking with Socioeconomic status biomass in poorly ventilated dwellings Nutrition Outdoor air pollution Comorbidities Jobs HIV
Risk Factors Exposure to particles • Tobacco smoke • Occupational dusts, organic and inorganic • Indoor air pollution from heating and cooking with biomass in poorly ventilated dwellings • Outdoor air pollution Lung growth and development Oxidative stress Gender Age Genes Respiratory infections Socioeconomic status Nutrition Comorbidities Jobs HIV
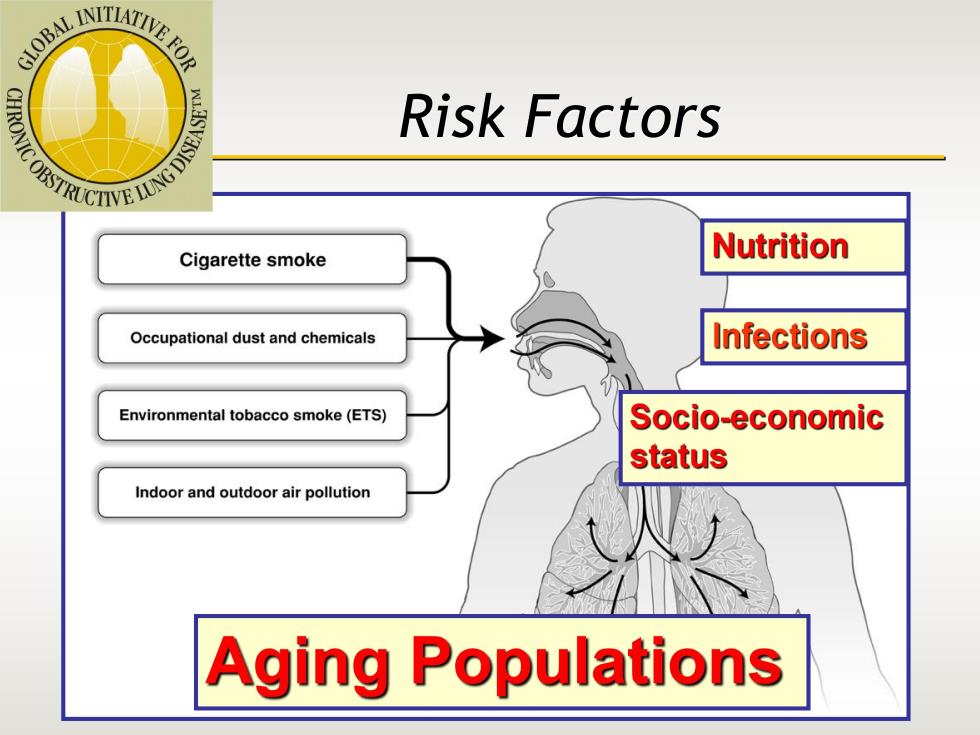
CLOBAINITIATIVE FOR VCOBSTRUCIIVE UNG DISENSE Risk Factors Cigarette smoke Nutrition Occupational dust and chemicals Infections Environmental tobacco smoke(ETS) Socio-economic status Indoor and outdoor air pollution Aging Populations
Risk Factors
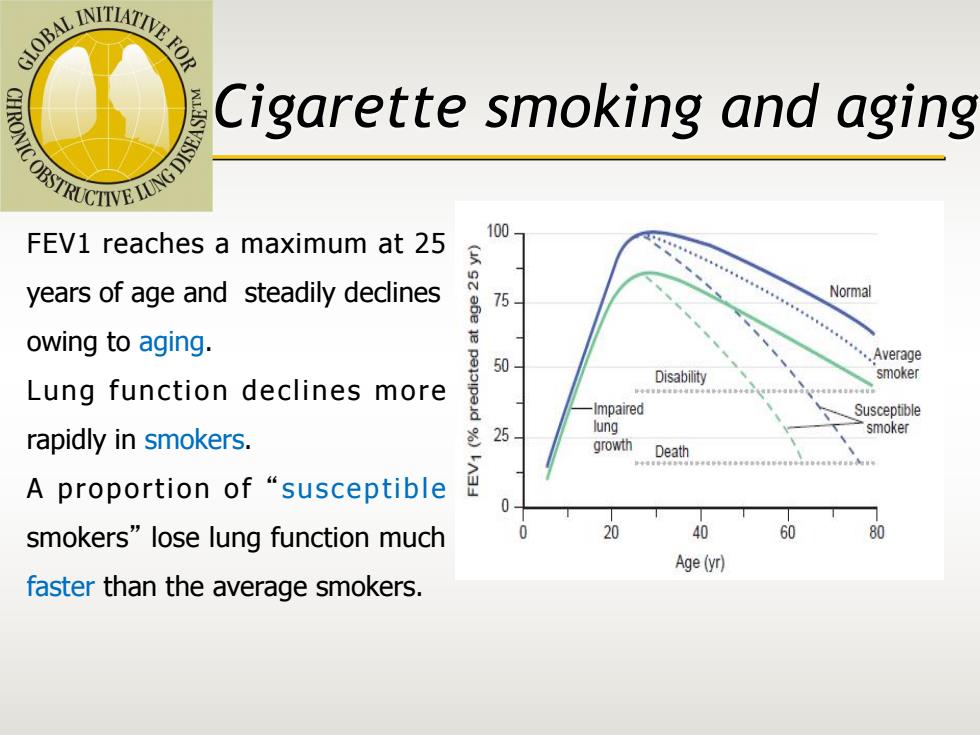
IOB△ITIATIVA】 OVIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISWN Cigarette smoking and aging FEV1 reaches a maximum at 25 100 years of age and steadily declines 75 Normal owing to aging. 50 ...Average Disability smoker Lung function declines more Impaired Susceptible lung rapidly in smokers. 25 smoker growth A proportion of "susceptible smokers"lose lung function much 20 40 60 0 Age(yr) faster than the average smokers
FEV1 reaches a maximum at 25 years of age and steadily declines owing to aging. Lung function declines more rapidly in smokers. A proportion of “susceptible smokers” lose lung function much faster than the average smokers. Cigarette smoking and aging

GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR DUCTTVE Pathology Pathological changes of COPD are found in: .proximal airways .peripheral airways .lung parenchyma .pulmonary vasculature. These changes include chronic inflammation and structural changes resulting from repeated injury and repair
Pathology Pathological changes of COPD are found in: •proximal airways •peripheral airways •lung parenchyma •pulmonary vasculature. These changes include chronic inflammation and structural changes resulting from repeated injury and repair

1ODB△s11TAT1VEFD UPONIC ORSTRUCIIVE LUNG DISEN Pathology Inhaled cigarette smoke and other noxious particles cause lung inflammation,a normal response which appears to be amplified in patients who develop COPD
Pathology • Inhaled cigarette smoke and other noxious particles cause lung inflammation, a normal response which appears to be amplified in patients who develop COPD