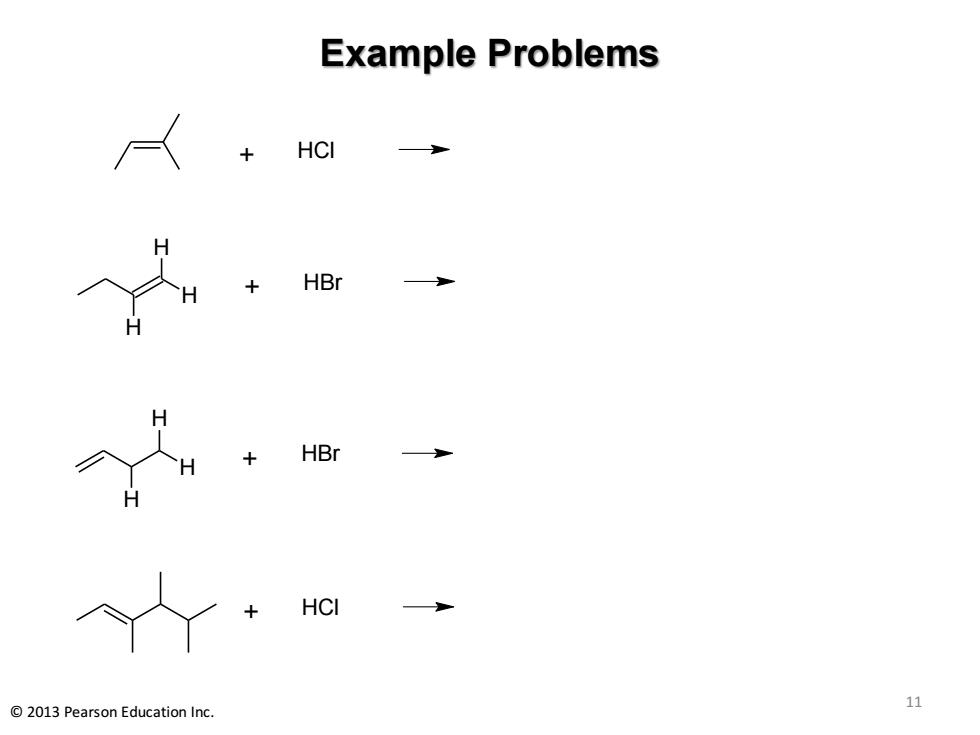
Example Problems HCI HBr HBr HC 2013 Pearson Education Inc 11
Example Problems 11 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc. + HCl + HBr H H H + HBr H H H + HCl

Free-Radical Addition of HBr In the presence of peroxides,HBr adds to an alkene to form the "anti-Markovnikov"product. Peroxides produce free radicals. 。 Only HBr has just the right reactivity for each step of the free-radical chain reaction to take place. The peroxide effect is not seen with HCl or HI because the reaction of an alkyl radical with HCl or HI is strongly endothermic. 12 2013 Pearson Education Inc
Free-Radical Addition of HBr • In the presence of peroxides, HBr adds to an alkene to form the “anti-Markovnikov” product. • Peroxides produce free radicals. • Only HBr has just the right reactivity for each step of the free-radical chain reaction to take place. • The peroxide effect is not seen with HCl or HI because the reaction of an alkyl radical with HCl or HI is strongly endothermic. 12 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc

Free-Radical Addition of HBr The peroxide bond breaks homolytically to form the first radical R-R D6at.RO R-O The alkoxy radical attacks proton,forming alcohol and bromide radical R-O R-OH Br Bromine adds to the double bond,forming the most stable radical possible Br CHz H -C CH3 H CH3 Carbon radical attack proton,regenerates bromide radical Br CH3 Br CH2 H- H-Br H-H Br H CH3 H CH3 2013 Pearson Education Inc. 13
Free-Radical Addition of HBr • The peroxide bond breaks homolytically to form the first radical 13 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc. R R O O heat R O R + O • The alkoxy radical attacks proton, forming alcohol and bromide radical R O H Br R OH + Br Br H H CH3 CH3 H H CH3 Br CH3 C • Bromine adds to the double bond, forming the most stable radical possible • Carbon radical attack proton, regenerates bromide radical H H CH3 Br CH3 C H Br H H H CH3 Br CH3 + Br
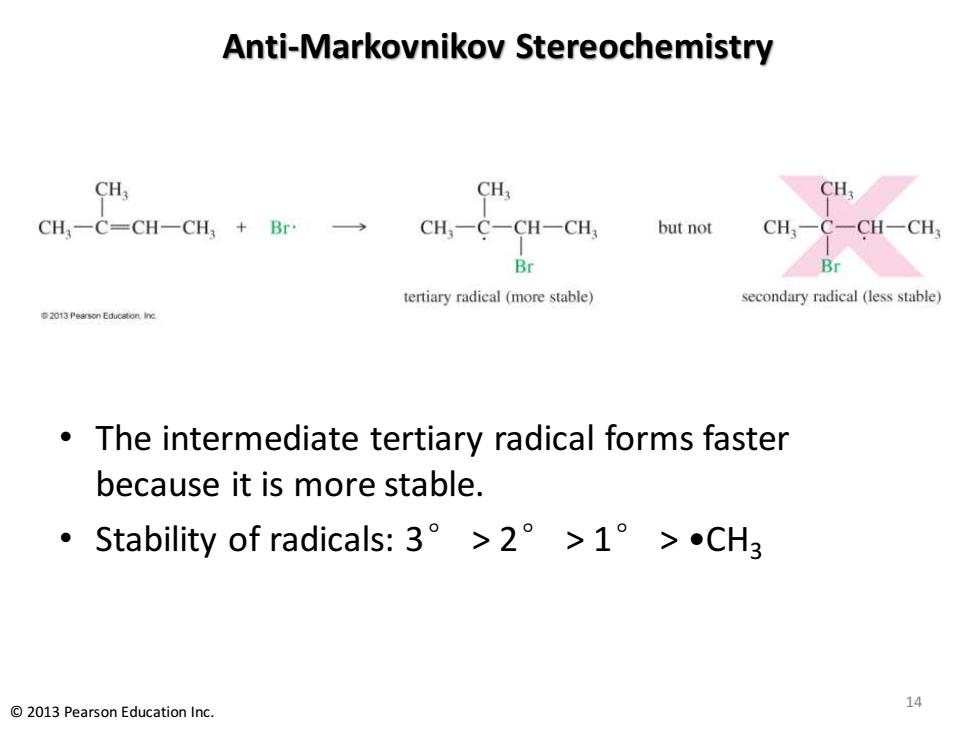
Anti-Markovnikov Stereochemistry CH3 CH CH CH,一C=CH一CH3+Br· CH,一C-CH一CH but not CH,- -CH一CH Br tertiary radical (more stable) secondary radical (less stable) 2013 Pearson Education.Iine The intermediate tertiary radical forms faster because it is more stable. ·Stability of radicals:3°>2°>1°>CH3 14 2013 Pearson Education Inc
Anti-Markovnikov Stereochemistry • The intermediate tertiary radical forms faster because it is more stable. • Stability of radicals: 3° > 2° > 1° > •CH3 14 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc
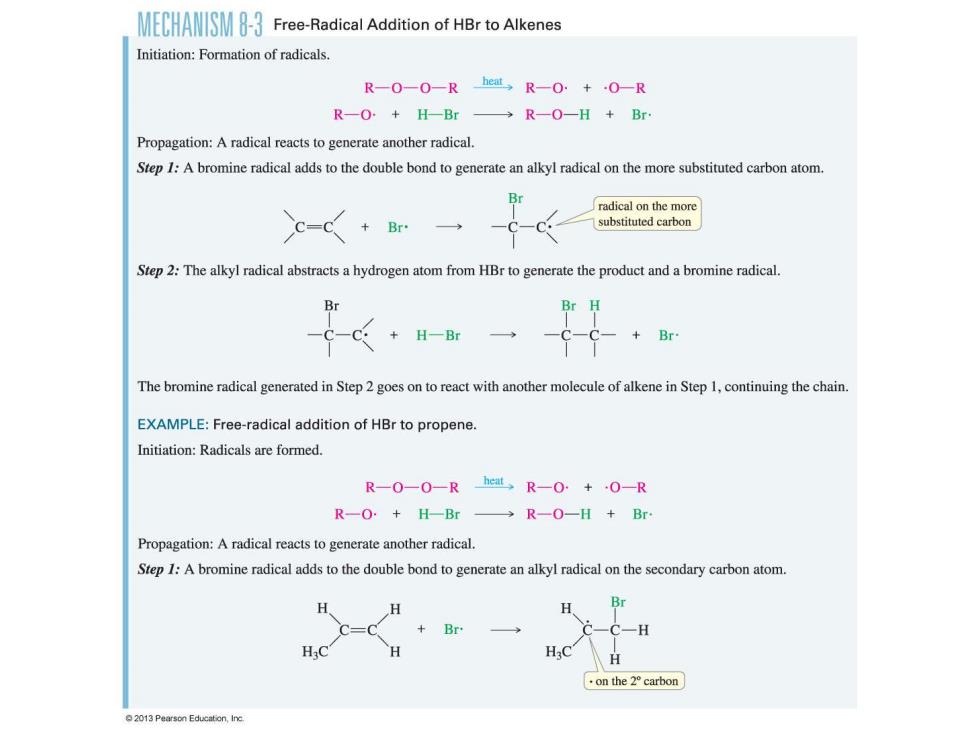
CHANSFree-Radical Addition of HBr to Alkenes Initiation:Formation of radicals. R-O-O-R heat,R-0+·O0-R R-O+H-Br→R-O-H+Br Propagation:A radical reacts to generate another radical. Step I:A bromine radical adds to the double bond to generate an alkyl radical on the more substituted carbon atom. Br radical on the more -C<+r一 substituted carbon Step 2:The alkyl radical abstracts a hydrogen atom from HBr to generate the product and a bromine radical Br H -C-C+H-Br -C-C- +Br The bromine radical generated in Step 2 goes on to react with another molecule of alkene in Step 1,continuing the chain. EXAMPLE:Free-radical addition of HBr to propene. Initiation:Radicals are formed. R-0-0-Rheat,R-0.+0-R R-O+H-Br→R-O-H+Br Propagation:A radical reacts to generate another radical. Step I:A bromine radical adds to the double bond to generate an alkyl radical on the secondary carbon atom. H、 C=C +Br on the2°carbon 2013 Pearson Education,Inc