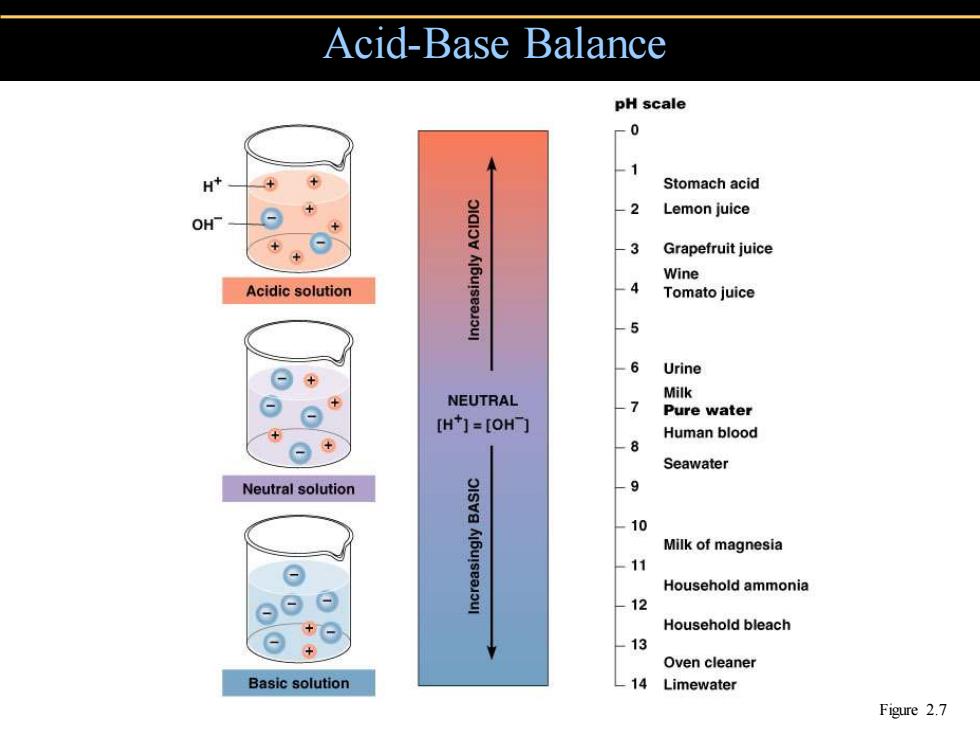
Acid-Base Balance pH scale -0 -1 H Stomach acid 2 Lemon juice OH -3 Grapefruit juice Wine Acidic solution -4 Tomato juice -5 -6 Urine NEUTRAL Milk 人7 Pure water [H1=[OH门 Human blood ⊙+ -8 Seawater Neutral solution 9 -10 Milk of magnesia -11 Household ammonia 12 Household bleach 13 Oven cleaner Basic solution -14 Limewater Figure 2.7
Acid-Base Balance Figure 2.7
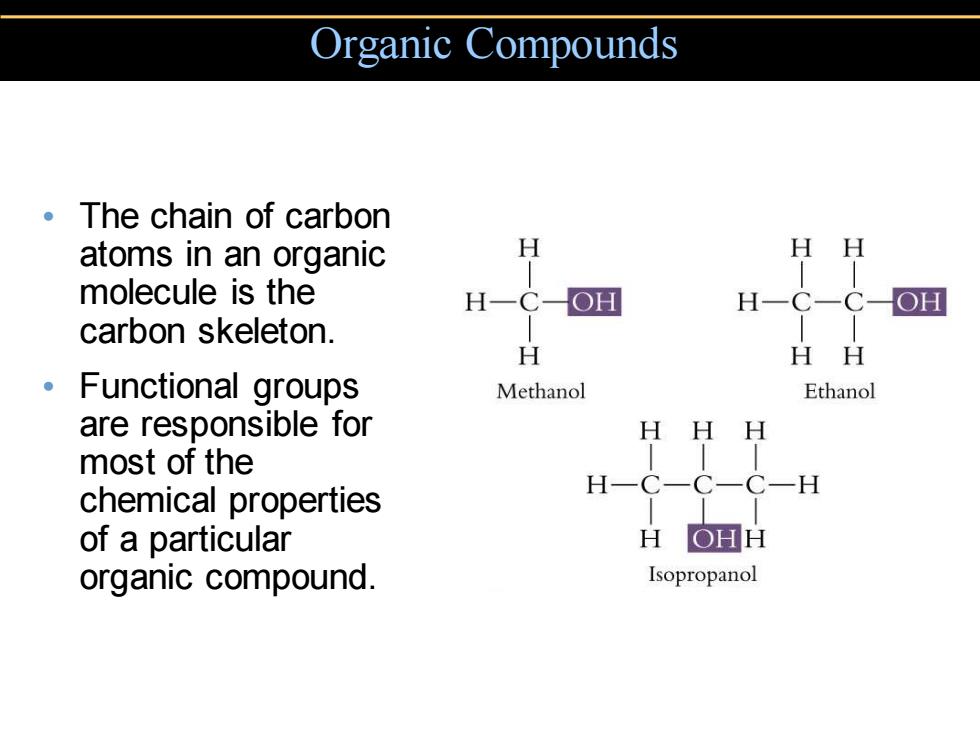
Organic Compounds ·The chain of carbon atoms in an organic H HH molecule is the H-C-OH H-C-C-OH carbon skeleton. H HH 。Functional groups Methanol Ethanol are responsible for HH H most of the H一C C一C-H chemical properties of a particular H OHH organic compound. Isopropanol
• The chain of carbon atoms in an organic molecule is the carbon skeleton. • Functional groups are responsible for most of the chemical properties of a particular organic compound. Organic Compounds
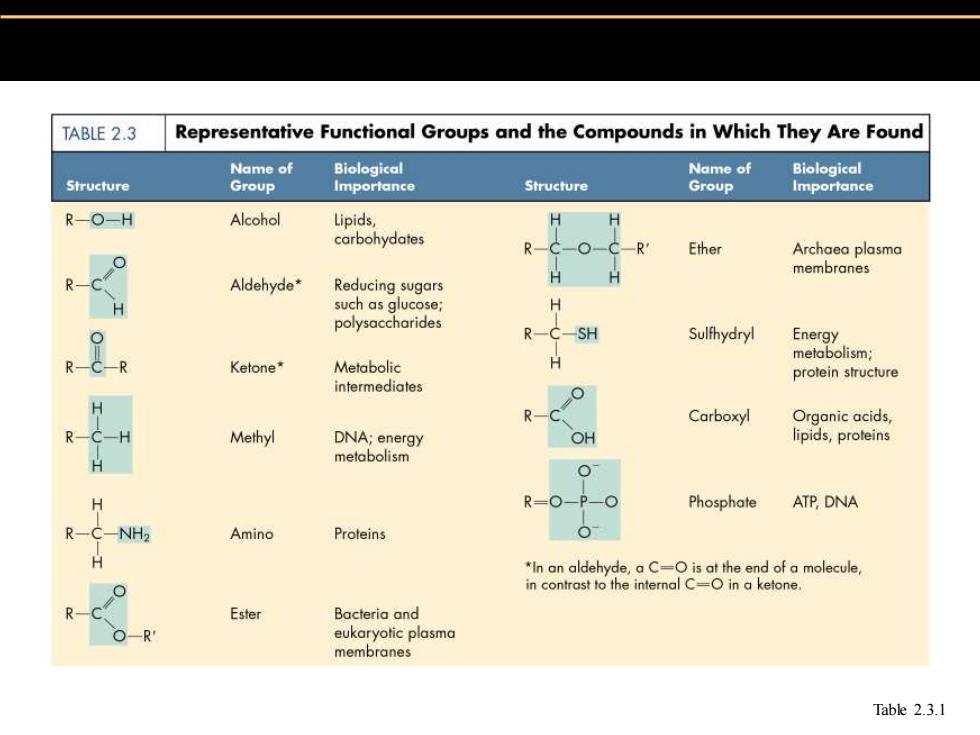
TABLE 2.3 Representative Functional Groups and the Compounds in Which They Are Found Name of Biological Name of Biological Structure Group Importance Structure Group Importance R-O-H Alcohol Lipids, carbohydates Ether Archaea plasma membranes Aldehyde* Reducing sugars such as glucose; polysaccharides Sulfhydryl Energy metabolism; Ketone* Metabolic protein structure intermediates Carboxyl Organic acids, Methyl DNA;energy OH lipids,proteins metabolism R=O-P-O Phosphate ATP DNA -NH2 Amino Proteins *In an aldehyde,a C-O is at the end of a molecule, in contrast to the internal C=O in a ketone. Ester Bacteria and eukaryotic plasma membranes Table 2.3.1
Table 2.3.1