
Chapter 10,part B Classification of Microorganisms
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 10, part B Classification of Microorganisms
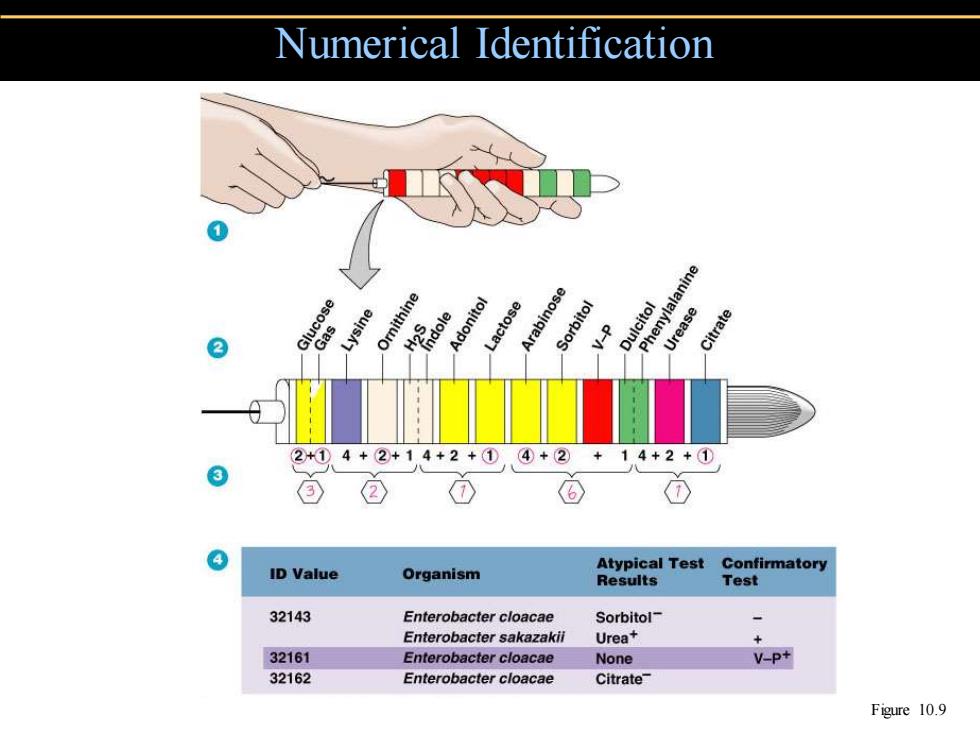
Numerical Identification ose Lysine Ornithine Adonitol ctose rabinose V enylalanine Dulcitol 2 Urease Citrate 2+①4+②+14+2+① ④+② 14+2+① ② ID Value Atypical Test Confirmatory Organism Results Test 32143 Enterobacter cloacae Sorbitol- Enterobacter sakazakii Urea+ + 32161 Enterobacter cloacae None V-P+ 32162 Enterobacter cloacae Citrate Figure 10.9
Numerical Identification Figure 10.9
Serology 。Combine known antiserum unknown bacterium 。Slide agglutination 。ELISA Western blot Figure 10.10
• Combine known antiserum + unknown bacterium • Slide agglutination • ELISA • Western blot Serology Figure 10.10
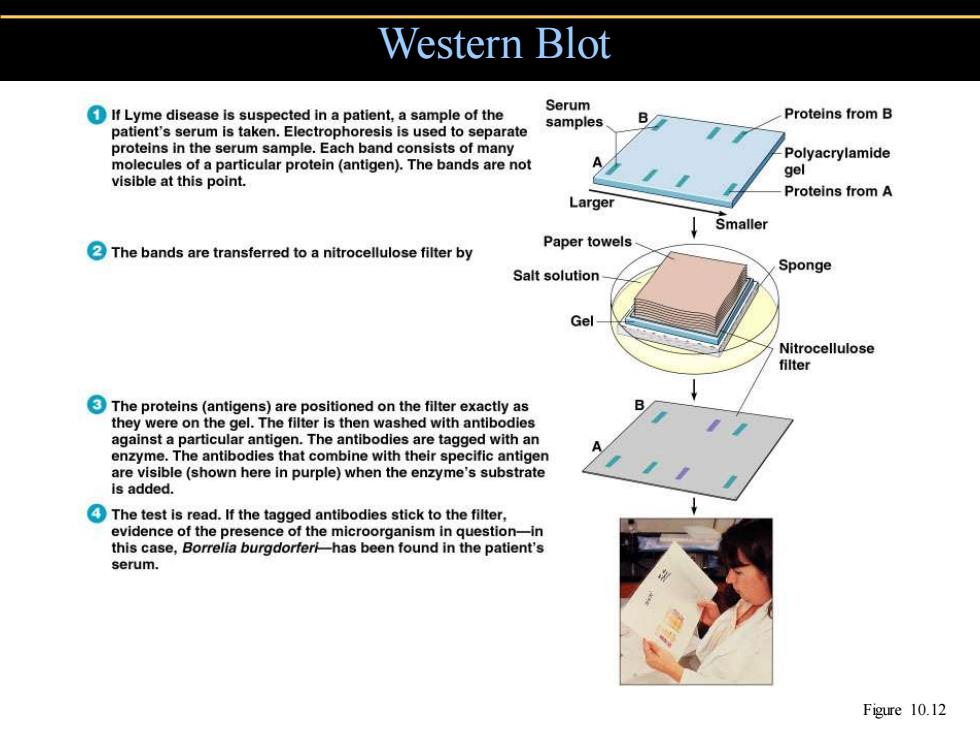
Western Blot If Lyme disease is suspected in a patient,a sample of the Serum Proteins from B samples patient's serum is taken.Electrophoresis is used to separate B/ proteins in the serum sample.Each band consists of many -Polyacrylamide molecules of a particular protein (antigen).The bands are not A 9e1 visible at this point. Proteins from A Larger Smaller The bands are transferred to a nitrocellulose filter by Paper towels- Salt solution Sponge Gel Nitrocellulose filter The proteins(antigens)are positioned on the filter exactly as they were on the gel.The filter is then washed with antibodies against a particular antigen.The antibodies are tagged with an enzyme.The antibodies that combine with their specific antigen are visible(shown here in purple)when the enzyme's substrate is added. The test is read.If the tagged antibodies stick to the filter, evidence of the presence of the microorganism in question-in this case,Borrelia burgdorferi-has been found in the patient's serum. Figure 10.12
Western Blot Figure 10.12
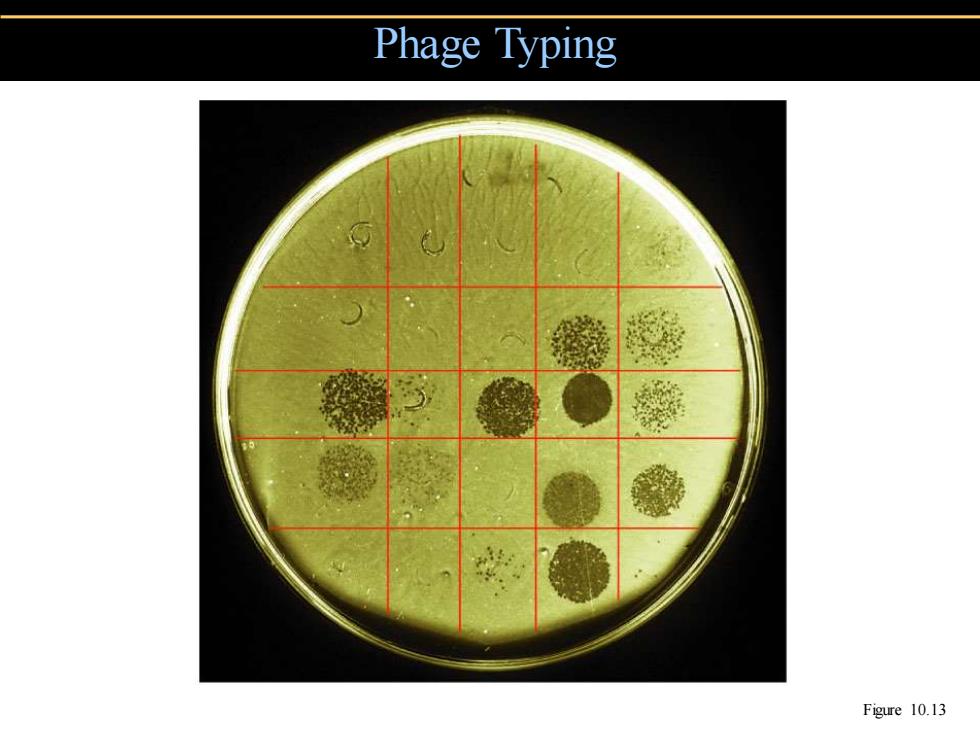
Phage Typing Figure 10.13
Phage Typing Figure 10.13