PLEURAL EFFUSION An increase in hydrostatic pressure or decrease in oncotic pressure will result in a low-protein collection of pleural fluid characterized as transudates(漏出液).For example,heart failure can produce transudates by increasing hydrostatic pressure in the pulmonary venous system,atelectasis(肺不张)_can promote transudates by making pleural pressure more subatmospheric,and occasionally, oncotic pressure may be suffciently reduced to cause transudates (hypoalbuminemia低白蛋白血症). Changes in pleural membrane permeability can produce high-protein effusions,which are characterized as exudates(渗出液)and can be seen in inflammatory states such as pneumonia,tuberculosis 痼),or rheumatoid arthritis(类风湿关节炎) Tumors can disrupt the integrity of the mesothelial layer or the integrity of the capillary epithelium,thereby resulting in exudative effusions,or they may block lymphatic drainage
第 一 部 分 An increase in hydrostatic pressure or decrease in oncotic pressure will result in a low-protein collection of pleural fluid characterized as transudates(漏出液). For example, heart failure can produce transudates by increasing hydrostatic pressure in the pulmonary venous system, atelectasis(肺不张) can promote transudates by making pleural pressure more subatmospheric, and occasionally, oncotic pressure may be suffciently reduced to cause transudates (hypoalbuminemia低白蛋白血症). Changes in pleural membrane permeability can produce high-protein effusions, which are characterized as exudates(渗出液) and can be seen in inflammatory states such as pneumonia, tuberculosis(结核 病), or rheumatoid arthritis(类风湿关节炎). Tumors can disrupt the integrity of the mesothelial layer or the integrity of the capillary epithelium, thereby resulting in exudative effusions, or they may block lymphatic drainage. PLEURAL EFFUSION

PLEURAL EFFUSION CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS Patients with pleural effusions may be asymptomatic 状)or may experience dyspnea(呼吸困难).When the parietal pleura is actively inflamed,pain can be present, and it is generally unilateral(单侧),sharp,and worsens with inspiration. At times,effusions may be suffciently large to contribute to respiratory failure(呼吸衰竭).Physical findings include dullness to percussion(叩诊浊音)in the area of the effusion,along with diminished breath sounds(呼吸音减弱) and absent tactile fremitus(触觉语颤)
第 一 部 分 CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS Patients with pleural effusions may be asymptomatic(无症 状) or may experience dyspnea(呼吸困难). When the parietal pleura is actively inflamed, pain can be present, and it is generally unilateral(单侧), sharp, and worsens with inspiration. At times, effusions may be suffciently large to contribute to respiratory failure(呼吸衰竭). Physical findings include dullness to percussion (叩诊浊音)in the area of the effusion, along with diminished breath sounds(呼吸音减弱) and absent tactile fremitus(触觉语颤). PLEURAL EFFUSION
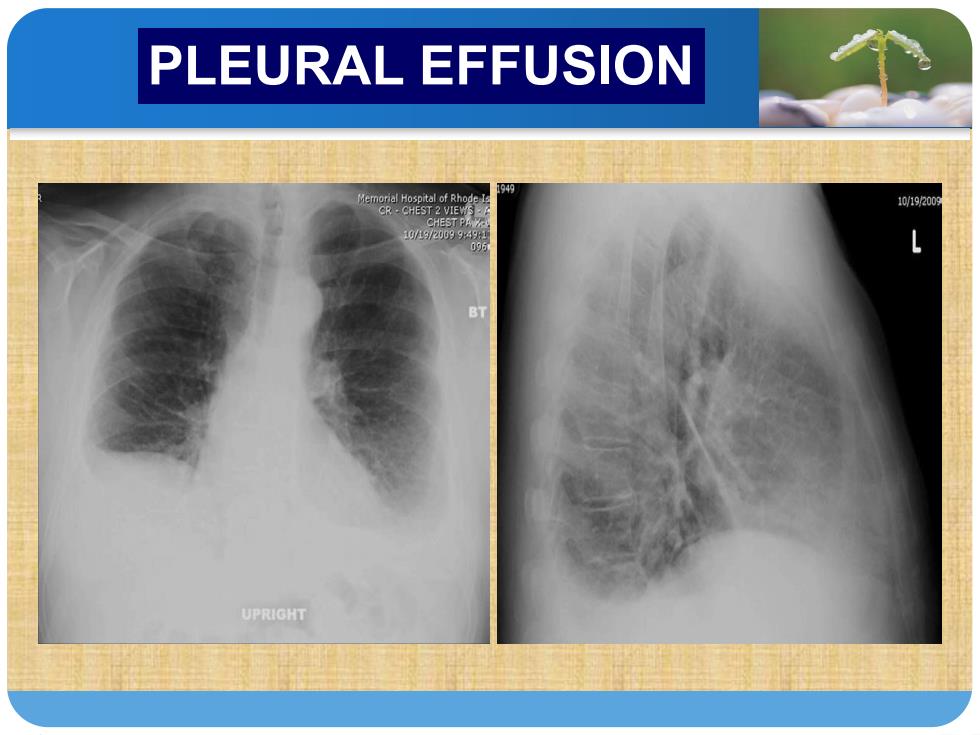
PLEURAL EFFUSION DIAGNOSIS Chest radiography is often the first imaging method used to detect an effusion.The volume of fluid in the pleural space needs to exceed 250 mL to be visualized on the chest radiograph.When an effusion is present,there is blunting of the costophrenic angle(肋膈角)on the posteroanterior chest radiograph,and a meniscus(新月液面) can be seen posteriorly on the lateral chest radiograph. Fluid may also collect in either the minor or major fissures
第 一 部 分 DIAGNOSIS Chest radiography is often the first imaging method used to detect an effusion. The volume of fluid in the pleural space needs to exceed 250 mL to be visualized on the chest radiograph. When an effusion is present, there is blunting of the costophrenic angle(肋膈角) on the posteroanterior chest radiograph, and a meniscus(新月液面) can be seen posteriorly on the lateral chest radiograph. Fluid may also collect in either the minor or major fissures. PLEURAL EFFUSION

PLEURAL EFFUSION Occasionally,pleural fluid collections in the major or minor fissures may appear as a pulmonary mass(肺部团块) and are referred to as pseudotumors ()A lateral Decubitus(侧卧位)chest radiograph can be obtained to determine whether fluid is free flowing or loculated 的). Chest CT provides better characterization of pleural and parenchymal abnormalities by better defining loculated effusions,distinguishing between atelectasis (and effusion,and distinguishing loculated effusion from lung abscess(肺脓肿)
第 一 部 分 Occasionally, pleural fluid collections in the major or minor fissures may appear as a pulmonary mass(肺部团块) and are referred to as pseudotumors(假瘤). A lateral Decubitus(侧卧位) chest radiograph can be obtained to determine whether fluid is free flowing or loculated(包裹 的). Chest CT provides better characterization of pleural and parenchymal abnormalities by better defining loculated effusions, distinguishing between atelectasis(不张) and effusion, and distinguishing loculated effusion from lung abscess(肺脓肿) PLEURAL EFFUSION
PLEURAL EFFUSION 101920 CHEST PAW 1g/19/209994982 95 UPRIGHT
PLE第URA一L E部FF分USION