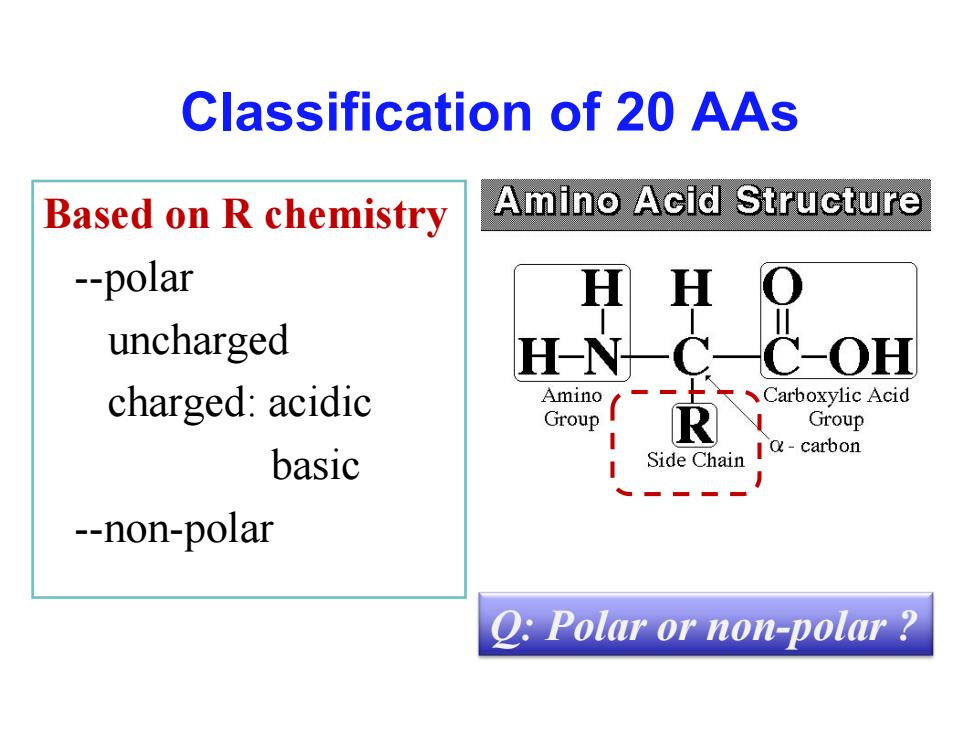
Classification of 20 AAs Based on R chemistry Amino Acid Structure --polar uncharged H N OH charged:acidic Amino Carboxylic Acid Group R Group basic Side Chain Ia-carbon --non-polar Q:Polar or non-polar
Classification of 20 AAs Based on R chemistry --polar uncharged charged: acidic basic --non-polar Q: Polar or non-polar ?

Relevant concepts Substances that dissolve well in the water are referred to as polar or hydrophilic Molecules that dissolve sparingly in water are non-polar or hydrophobic
Relevant concepts • Substances that dissolve well in the water are referred to as polar or hydrophilic • Molecules that dissolve sparingly in water are non-polar or hydrophobic
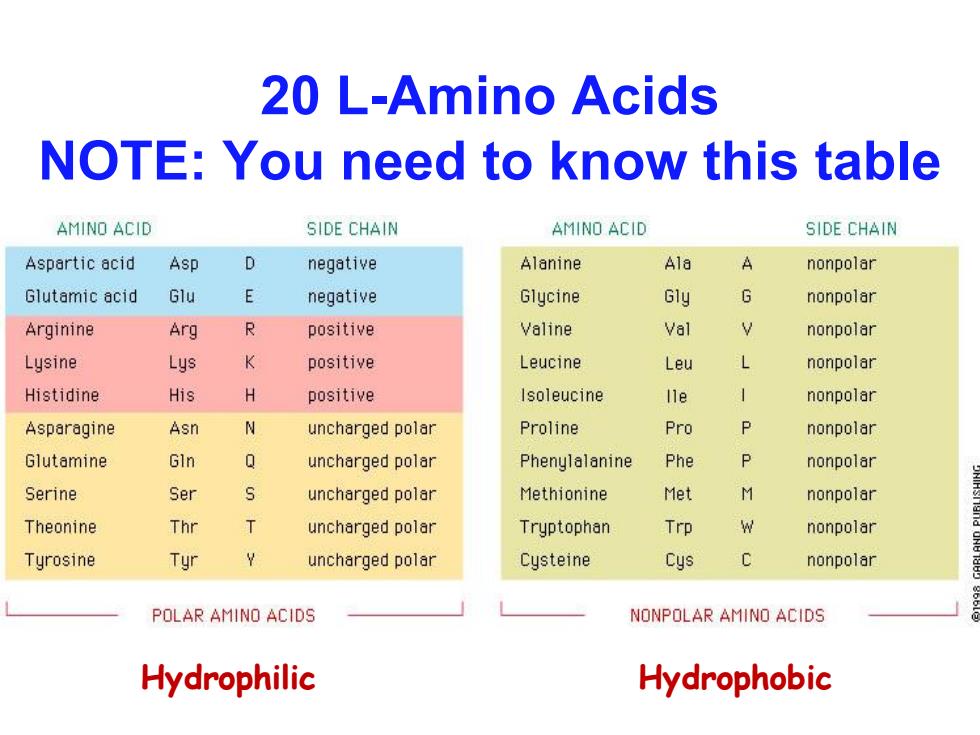
20 L-Amino Acids NOTE:You need to know this table AMINO ACID SIDE CHAIN AMINO ACID SIDE CHAIN Aspartic acid Asp D negative Alanine Ala nonpolar Glutamic acid Glu E negative Glycine Gly G nonpolar Arginine Arg R positive Valine Val nonpolar Lysine Lys K positive Leucine Leu L nonpolar Histidine His H positive Isoleucine lle nonpolar Asparagine Asn N uncharged polar Proline Pro P nonpolar Glutamine GIn Q uncharged polar Phenylalanine Phe P nonpolar Serine Ser uncharged polar Methionine Met M nonpolar Theonine Thr T uncharged polar Tryptophan Trp W nonpolar Tyrosine Tyr uncharged polar Cysteine Cys nonpolar POLAR AMINO ACIDS NONPOLAR AMINO ACIDS Hydrophilic Hydrophobic
20 L-Amino Acids NOTE: You need to know this table Hydrophilic Hydrophobic
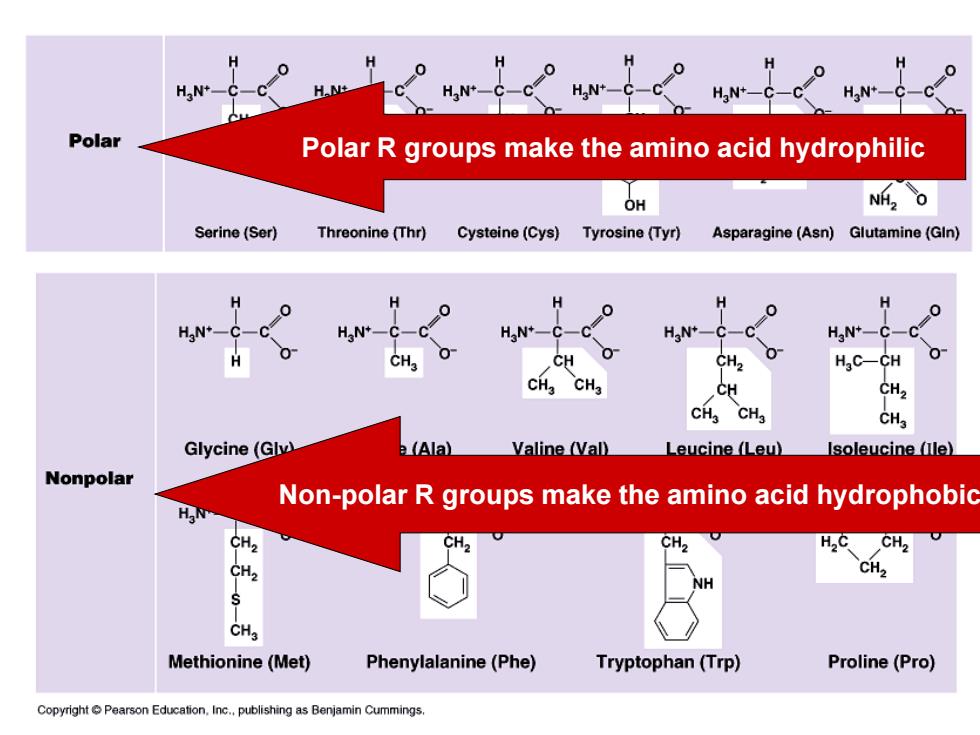
HN+- H.N+ HaN+-C-C HaN+-C-C Polar Polar R groups make the amino acid hydrophilic OH NHZO Serine(Ser) Threonine(Thr) Cysteine(Cys)Tyrosine(Tyr) Asparagine(Asn)Glutamine(GIn) H H 0 0 H H H 0 HaN*-C-C HaN+-C-C HaN+-C-C HaN+-C- HaN+-C-C CH CH2 HaC-CH 0 CHg CHa CH CH2 CH3 CHa CHa Glycine(Glv) e (Ala) Valine (Val) Leucine (Leu) Isoleucine alle) Nonpolar Non-polar R groups make the amino acid hydrophobic HN CH2 CH2 CH2 H2C CH2 CH2 CH2 NH CH3 Methionine(Met) Phenylalanine(Phe) Tryptophan(Trp) Proline(Pro) CopyrightPearson Education.Inc..publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Polar R groups make the amino acid hydrophilic Non-polar R groups make the amino acid hydrophobic
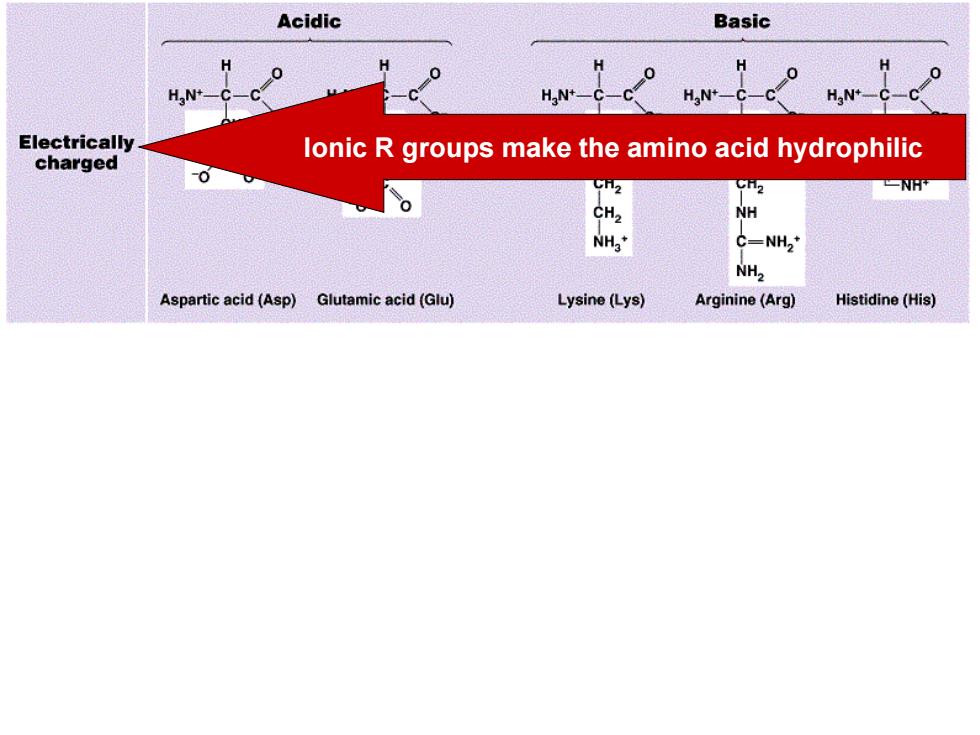
Acidic Basic H N+- Electrically charged lonic R groups make the amino acid hydrophilic -0 -NH NH C=NH,* NH2 Aspartic acid(Asp)Glutamic acid(Glu) Lysine(Lys) Arginine (Arg) Histidine(His)
Ionic R groups make the amino acid hydrophilic