CHAPTER 1 Proteins Overview Amino acid structures Four levels of organization in proteins -02 binding proteins:myoglobin and hemoglobin 2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate function in RBC protein physical-chemical properties and purifications methods Clinical correlations:Prion disease,Scurvy, Methemoglobinemia
CHAPTER 1 Proteins – Amino acid structures – Four levels of organization in proteins – O2 binding proteins: myoglobin and hemoglobin – 2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate function in RBC – protein physical-chemical properties and purifications methods – Clinical correlations: Prion disease, Scurvy, Methemoglobinemia Overview

Section Molecular Composition of Proteins life is maintained by molecular network system Protein make up about 15%of the cell Proteins play key roles in a living system Enzymes,Structural,Transport,Motor Storage,Signaling,Receptors,Gene regulation Special functions (antibody)
• life is maintained by molecular network system • Protein make up about 15% of the cell • Proteins play key roles in a living system Enzymes, Structural, Transport, Motor Storage, Signaling, Receptors, Gene regulation Special functions (antibody) ………. ……….. ………… Molecular Composition of Proteins Section 1
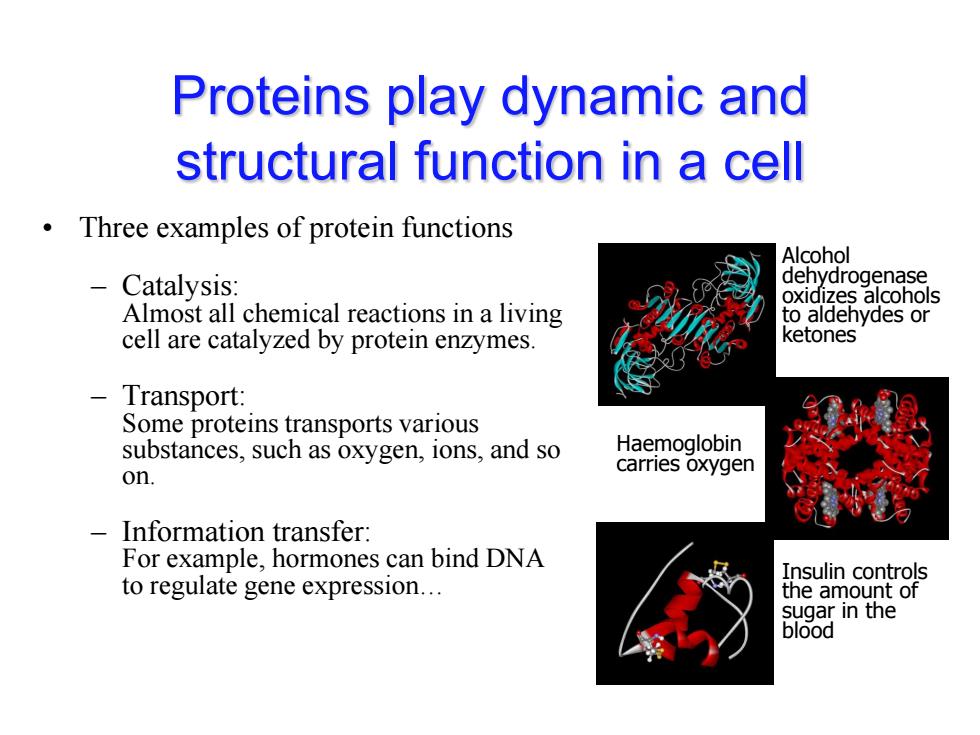
Proteins play dynamic and structural function in a cell Three examples of protein functions Alcohol Catalysis: dehydrogenase oxidizes alcohols Almost all chemical reactions in a living to aldehydes or cell are catalyzed by protein enzymes. ketones -Transport: Some proteins transports various substances,such as oxygen,ions,and so Haemoglobin on. carries oxygen Information transfer: For example,hormones can bind DNA Insulin controls to regulate gene expression... the amount of sugar in the blood
Proteins play dynamic and structural function in a cell • Three examples of protein functions – Catalysis: Almost all chemical reactions in a living cell are catalyzed by protein enzymes. – Transport: Some proteins transports various substances, such as oxygen, ions, and so on. – Information transfer: For example, hormones can bind DNA to regulate gene expression… Alcohol dehydrogenase oxidizes alcohols to aldehydes or ketones Haemoglobin carries oxygen Insulin controls the amount of sugar in the blood

Alcohol acts as a central nervous system depressant alcohol abuse

The Chemical Breakdown of Alcohol CH CH,OH_ADH>CHaCHO ALDH>CH COO- Acetaldehyde Acetate The chemical name for alcohol is ethanol(CH3CH2OH).The body processes and eliminates ethanol in separate steps.Chemicals called enzymes help to break apart the ethanol molecule into other compounds (or metabolites),which can be processed more easily by the body.Some of these intermediate metabolites can have harmful effects on the body. Most of the ethanol in the body is broken down in the liver by an enzyme called alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH),which transforms ethanol into a toxic compound called acetaldehyde(CH3CHO),a known carcinogen.However,acetaldehyde is generally short-lived; it is quickly broken down to a less toxic compound called acetate (CHaCOO)by another enzyme called aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH).Acetate then is broken down to carbon dioxide and water. mainly in tissues other than the liver