
Special attentions to some AAs ● The aromatic AA,phenylalanine,tyrosine and tryptophan,have ring structures and are non-polar with exception of the hydroxyl group of tyrosine Serine and threonine are small polar AA that have hydroxyl group The sulfur-containing AAs are Cys and Met The amide of carboxylic AA,asparagine and glutamine,are uncharged and polar Proline is unique,it is imino acid because its side chain loops back to form-membered ring with its amino group,which cause proline to produce kinks in the polypeptide backbone
Special attentions to some AAs • The aromatic AA, phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan, have ring structures and are non-polar with exception of the hydroxyl group of tyrosine • Serine and threonine are small polar AA that have hydroxyl group • The sulfur-containing AAs are Cys and Met • The amide of carboxylic AA, asparagine and glutamine, are uncharged and polar • Proline is unique, it is imino acid because its side chain loops back to form-membered ring with its amino group, which cause proline to produce kinks in the polypeptide backbone
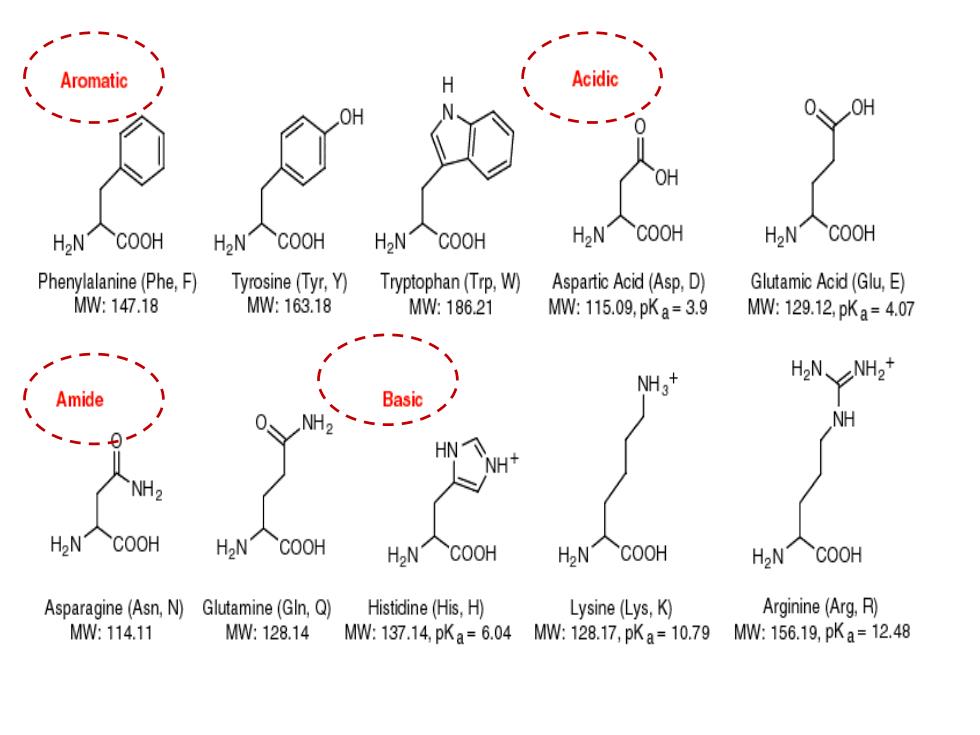
Aromatic Acidic OH OH H2NCOOH H2NCOOH H2NCOOH H2NCOOH H2N COOH Phenylalanine(Phe,F) Tyrosine(Tyr,Y) Tryptophan(Trp,W) Aspartic Acid (Asp,D) Glutamic Acid(Glu,E) MW:147.18 MW:163.18 MW:186.21 MW:115.09,pKa=3.9 MW:129.12,pKa=4.07 NH3+ H2N、NH2 Amide Basic NH2 H H2NCOOH H2NCOOH H2N COOH H2NCOOH H2N COOH Asparagine(Asn,N)Glutamine(GIn,Q) Histidine(His,H) Lysine (Lys,K) Arginine(Arg,R) MW:114.11 MW:128.14MW:137.14,pKa=6.04MW:128.17,pKa=10.79 MW:156.19,pKa=12.48

Smal Nucleophilic OH SH CH3 H2N COOH H2N COOH H2N COOH H2N COOH H2N COOH Glycine(Gly,G) Alanine(Ala,A) Serine(Ser,S) Threonine(Thr,T) Cysteine(Cys,C) MW:57.05 MW:71.09 MW:87.08,pKa~16 MW101.11,pKaw16 MW:103.15,pKa=8.35 Hydrophobic Branched-chain AA H2N COOH H2N COOH H2N COOH H2N COOH COOH Valine (Val,V) Leucine(Leu,L) Isoleucine(lle,I) Methionine(Met,M) Proline(Pro,P) MW:99.14 MW:113.16 MW:113.16 MW:131.19 MW:97.12 The nitrogen in Pro tied into a ring structure as a secondary imino group.Being stiff and angled,it is often found at the bend of polypeptides. H
The nitrogen in Pro tied into a ring structure as a secondary imino group. Being stiff and angled, it is often found at the bend of polypeptides. Branched-chain AA

20 common AAs are found in proteins alanine-ala-A 。leucine-leu-L ·arginine-arg-R ·lysine-ys-K asparagine-asn-N methionine-met-M aspartic acid-asp-D phenylalanine-phe-F cysteine-cys-C proline-pro-P ·glutamine-gln-Q serine-ser-S ·glutamic acid-glu-E threonine-thr-T ·glycine-gly-G tryptophan-trp-W histidine-his-H tyrosine-tyr-Y isoleucine-ile-I valine -val -V “Essential Amino Acids” are those that must be ingested in the diet (our body can't make them)
20 common AAs are found in proteins • alanine - ala - A • arginine - arg - R • asparagine - asn - N • aspartic acid - asp - D • cysteine - cys - C • glutamine - gln - Q • glutamic acid - glu - E • glycine - gly - G • histidine - his - H • isoleucine - ile - I • leucine - leu - L • lysine - lys - K • methionine - met - M • phenylalanine - phe - F • proline - pro - P • serine - ser - S • threonine - thr - T • tryptophan - trp - W • tyrosine - tyr - Y • valine - val - V “Essential Amino Acids” are those that must be ingested in the diet (our body can’t make them)

Summary Both D-AAs and L-AAs occur in nature,only L-AAs are present in protein L-AAs are zwitterion The pKa values of all functional groups of an AA dictate its net charge at a given pH at which an AA bear no net charge and thus does not move in a direct current electrical field The R group of AA determine their unique biochemical functions
Summary • Both D-AAs and L-AAs occur in nature, only L-AAs are present in protein • L-AAs are zwitterion • The pKa values of all functional groups of an AA dictate its net charge at a given pH at which an AA bear no net charge and thus does not move in a direct current electrical field • The R group of AA determine their unique biochemical functions