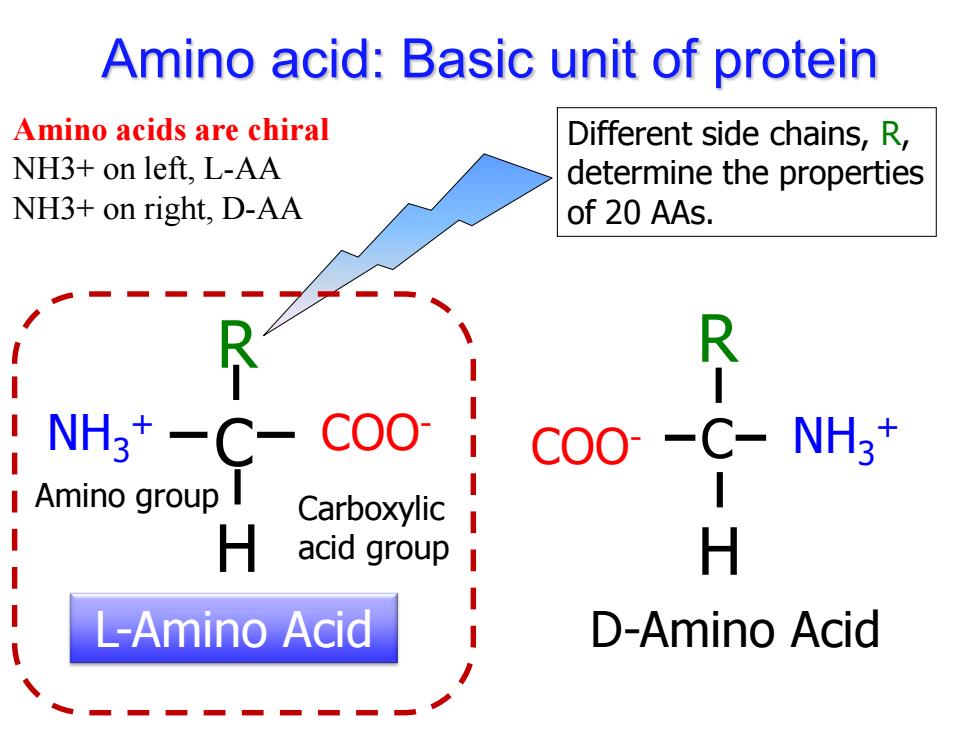
Amino acid:Basic unit of protein Amino acids are chiral Different side chains,R, NH3+on left.L-AA determine the properties NH3+on right,D-AA of 20 AAs. C- NH虜*一C- C00 COO--C-NH3+ I Amino group I Carboxylic H acid group H L-Amino Acid D-Amino Acid
Amino acid: Basic unit of protein NH COO- 3 + C R H L-Amino Acid Different side chains, R, determine the properties of 20 AAs. Amino group Carboxylic acid group Amino acids are chiral NH3+ on left, L-AA NH3+ on right, D-AA COO- NH3 + C R H D-Amino Acid

Amino acids are zwitterion The protonation state of alanine pk of COO-close to 2.34 pk of NH3+near 9.69 Alanine 14.0 12.0h pK2=9.69 10.0 H2N-H CH3 8.0 8.0- pH>10 pH<2 or pH>9 02 6.0 =601 6.0- HgN-H cation?anion? 4.0 4.0 CH3 pH between 2 to 9? pKg1=2.34 pH≈6 2.0 2.0 9C02H H3N-H CH3 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 <2 Equivalents of OH" pl=1/2(pkaCOOH+pkaNH3+) The zwitterion of alanine is the predominant form in the pH range from 2.3 to 9.9
Amino acids are zwitterion The zwitterion of alanine is the predominant form in the pH range from 2.3 to 9.9 pk of COO- close to 2.34 pk of NH3+ near 9.69 pH<2 or pH> 9 cation? anion? pH between 2 to 9? The protonation state of alanine pI=1/2(pkaCOOH+pkaNH3+)
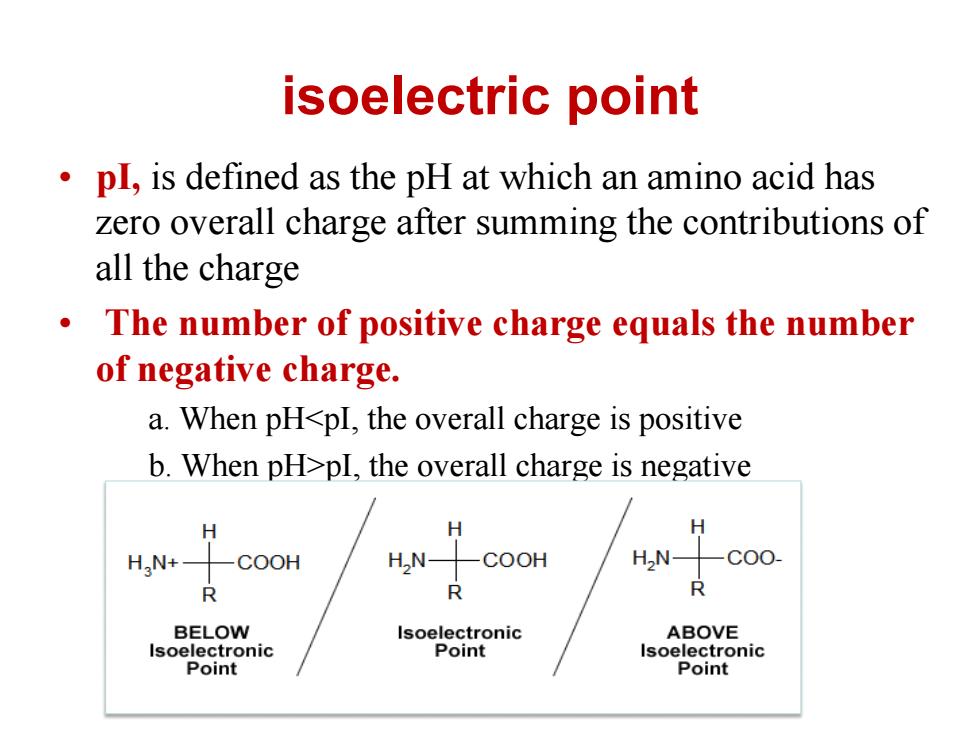
isoelectric point pl,is defined as the pH at which an amino acid has zero overall charge after summing the contributions of all the charge 。 The number of positive charge equals the number of negative charge. a.When pH<pI,the overall charge is positive b.When pH>pI,the overall charge is negative H HaN+- COOH H,N COOH HN- -C00- R R R BELOW Isoelectronic ABOVE Isoelectronic Point Isoelectronic Point Point
isoelectric point • pI, is defined as the pH at which an amino acid has zero overall charge after summing the contributions of all the charge • The number of positive charge equals the number of negative charge. a. When pH<pI, the overall charge is positive b. When pH>pI, the overall charge is negative c. When pH=pI, there is no overall charge
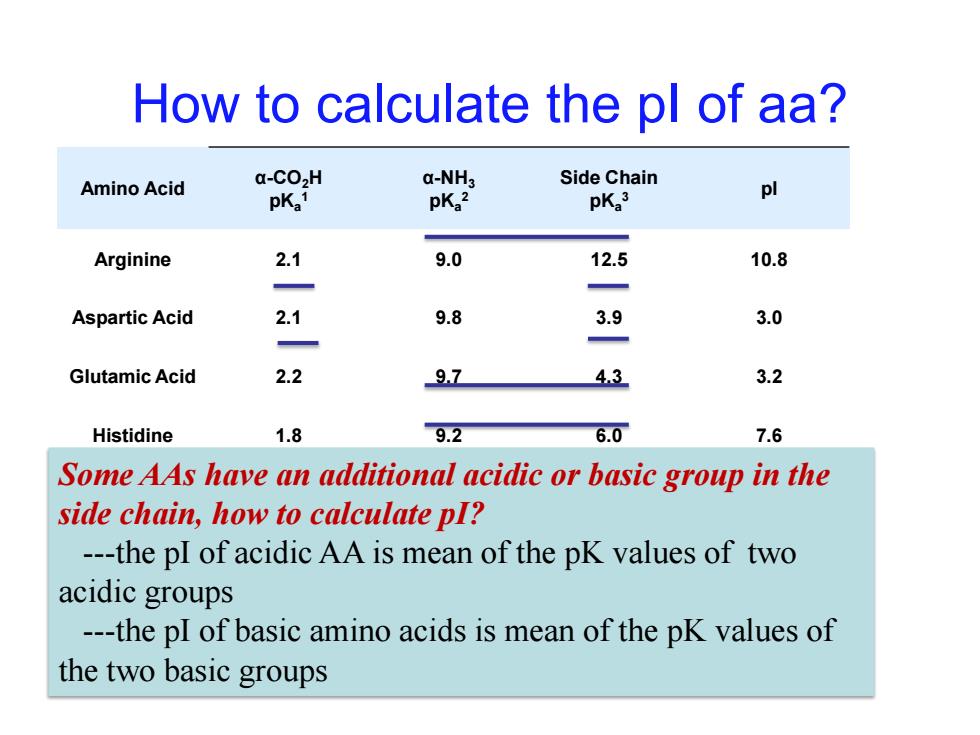
How to calculate the pl of aa? Amino Acid a-CO>H a-NH3 Side Chain pKa1 pKa2 pKa3 pl Arginine 2.1 9.0 12.5 10.8 Aspartic Acid 2.1 9.8 3.9 3.0 Glutamic Acid 2.2 97 43 3.2 Histidine 1.8 9.2 6.0 7.6 Some AAs have an additional acidic or basic group in the side chain,how to calculate pI? ---the pI of acidic AA is mean of the pK values of two acidic groups ---the pI of basic amino acids is mean of the pK values of the two basic groups
How to calculate the pI of aa? Amino Acid α-CO2H pKa 1 α-NH3 pKa 2 Side Chain pKa 3 pI Arginine 2.1 9.0 12.5 10.8 Aspartic Acid 2.1 9.8 3.9 3.0 Glutamic Acid 2.2 9.7 4.3 3.2 Histidine 1.8 9.2 6.0 7.6 Some AAs have an additional acidic or basic group in the Lysine 2.2 9.0 10.5 9.8 side chain, how to calculate pI? ---the pI of acidic AA is mean of the pK values of two acidic groups ---the pI of basic amino acids is mean of the pK values of the two basic groups

What's the significance of zwitterion property? Ionizable groups stabilize the pH value of the solution against external disturbances. Any ionizable group buffers the pH of the solution at pH value close to its pK. The buffering capacity of ionizable groups helps human maintain a constant in body fluid. A contribution to homeostatsis
What’s the significance of zwitterion property? • Ionizable groups stabilize the pH value of the solution against external disturbances. • Any ionizable group buffers the pH of the solution at pH value close to its pK. • The buffering capacity of ionizable groups helps human maintain a constant in body fluid. A contribution to homeostatsis