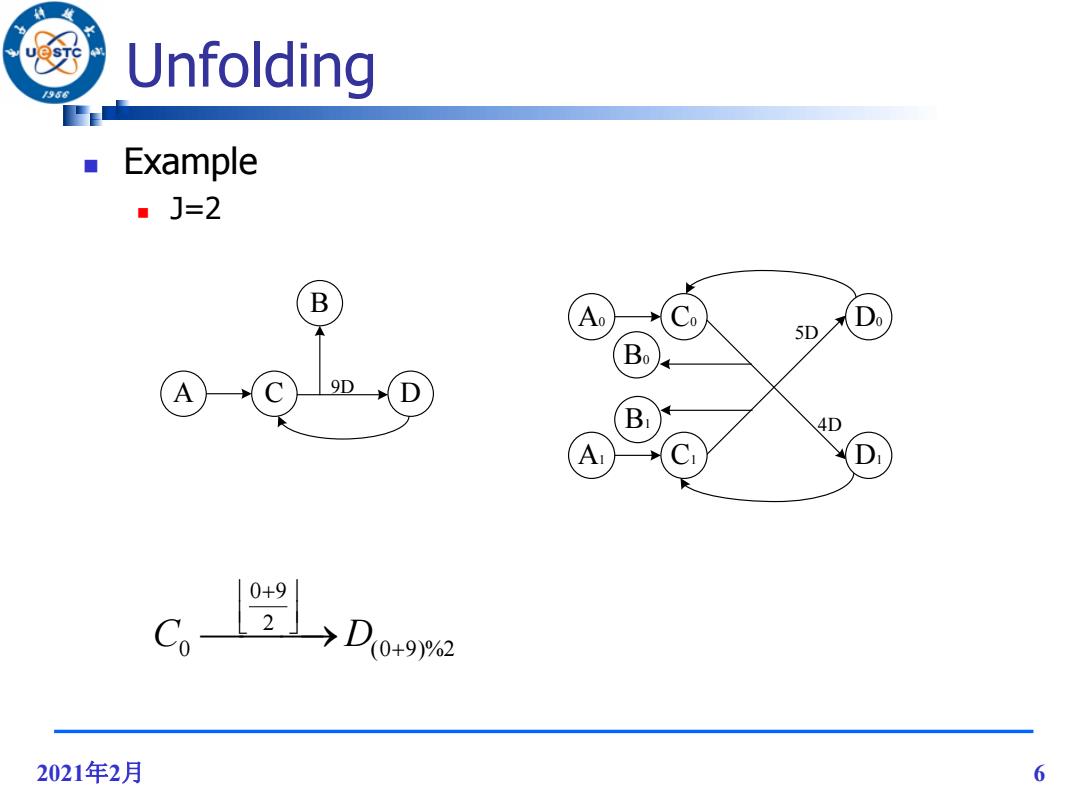
U Unfolding Example ■J=2 B Ao Co Do 5D Bo A 9D Br 4D A D 0+9 L2→D0+92 2021年2月 6
2021年2月 6 Unfolding Example J=2 C 9D D B A C0 4D 5D C1 D0 D1 B1 B0 A1 A0 0 9 2 C D 0 (0 9)%2
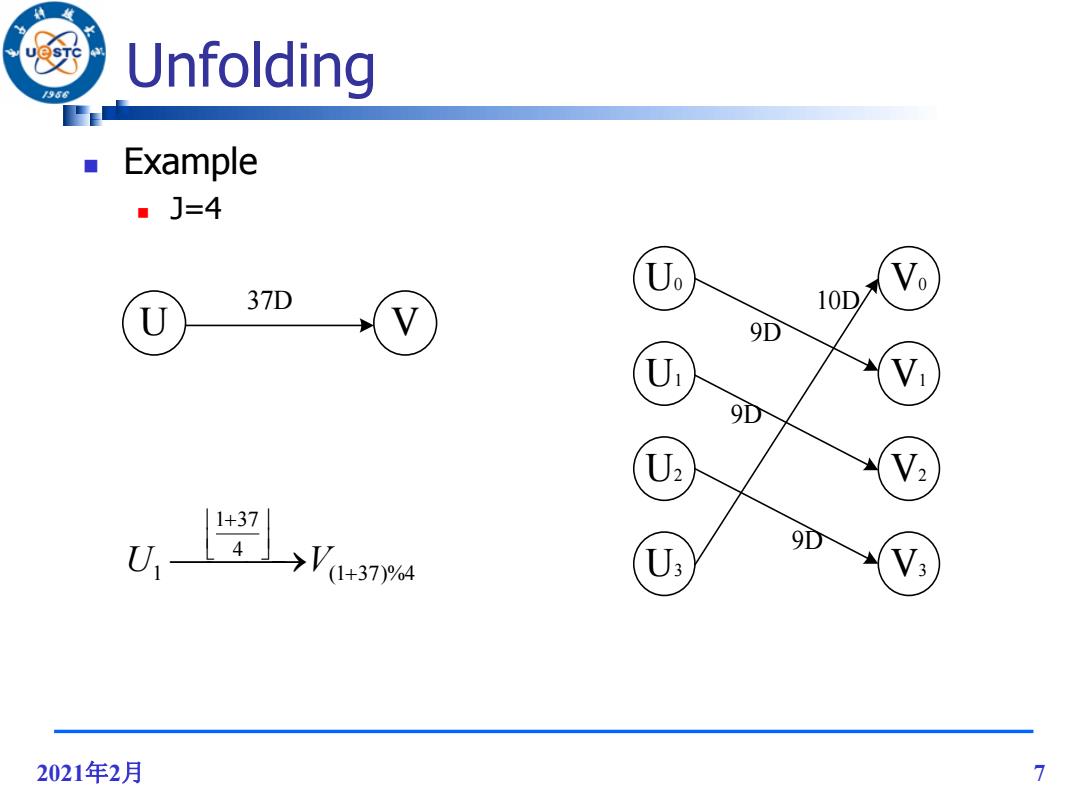
U Unfolding Example ■J=4 Uo 37D 10D U V 9D U 9D U2 1+37 9D U: 2021年2月 7
2021年2月 7 Unfolding Example J=4 U V 37D U0 V3 V2 V1 V0 U3 U2 U1 9D 10D 9D 9D 1 37 4 U V 1 (1 37)%4
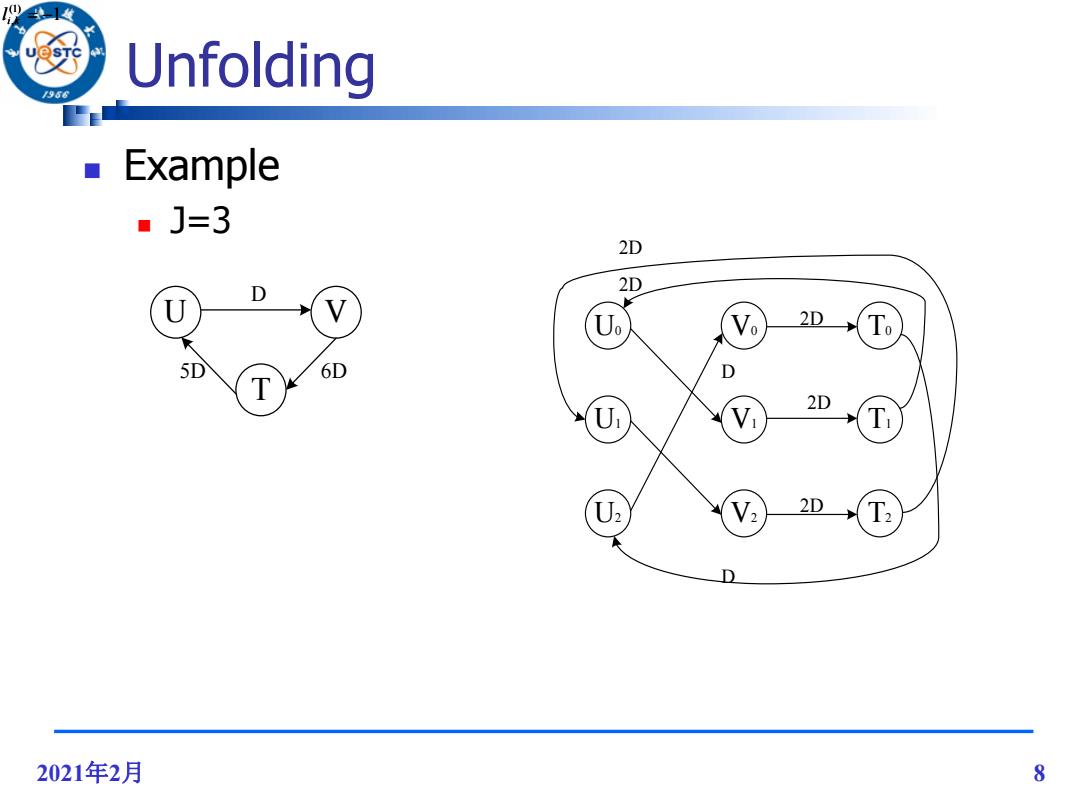
Unfolding Example ■]=3 2D D 2D U Uo 2D 5D 6D D T 2D U U: 2D D 2021年2月 8
2021年2月 8 Unfolding Example J=3 U V T 5D 6D D U0 U2 U1 V0 V2 V1 T0 T2 T1 2D 2D 2D 2D 2D D D 1 (1) l i,k 1 (1) l i,k
Unfolding algorithm proof 295 The unfolding algorithm described here indeed creates an unfolded DFG with the same precedence constraints as the original DFG. The edges UV(i+w)%with delays in the unfolded DFG corresponds to the edge U>V with w delay in the original DFG. The k-th iteration of the node U:in the J-unfolded DFG executes the (Jk+i)-th iteration of the node U in the original DFG. The output of the k-th iteration of the node U is consumed by the iteration of the node V in the unfolded DFG. 2021年2月 9
2021年2月 9 Unfolding algorithm proof The unfolding algorithm described here indeed creates an unfolded DFG with the same precedence constraints as the original DFG. The edges UiV(i+w)%J with delays in the unfolded DFG corresponds to the edge UV with w delay in the original DFG. The k-th iteration of the node Ui in the J-unfolded DFG executes the (Jk+i)-th iteration of the node U in the original DFG. The output of the k-th iteration of the node Ui is consumed by the iteration of the node V(i+w)%J in the unfolded DFG. J i w th J i w k ( )
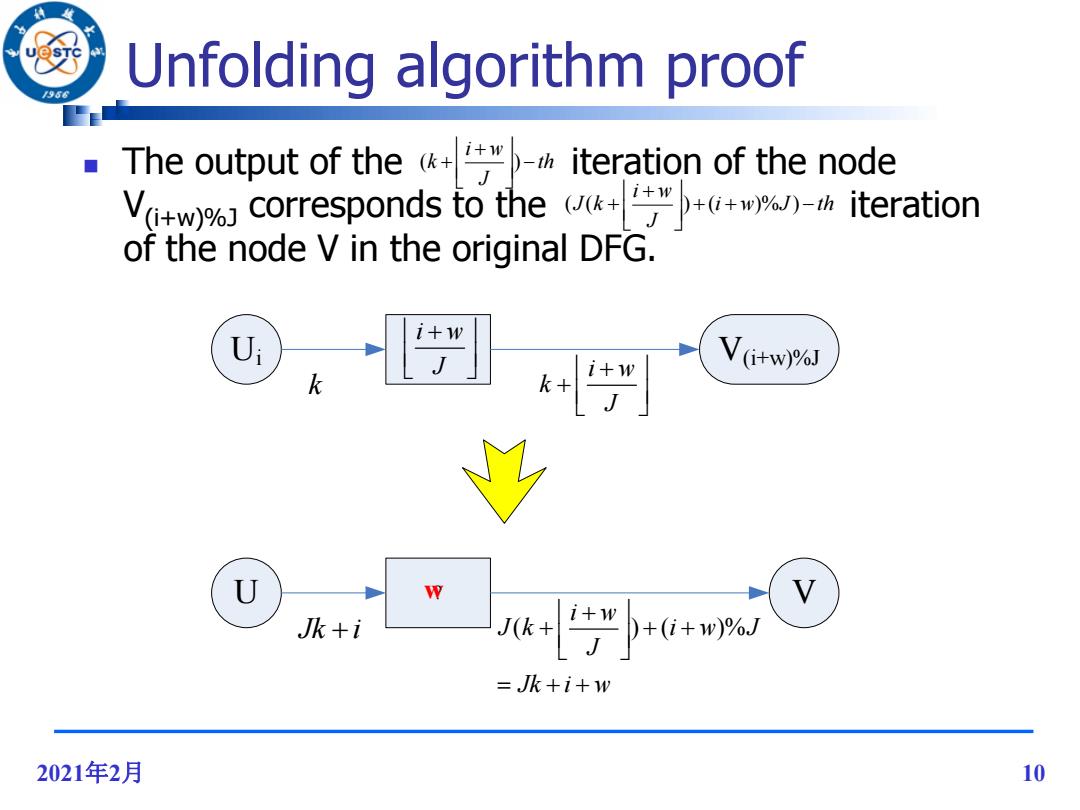
Unfolding algorithm proof The output of the iteration of the node Vw corresponds to the iteration of the node V in the original DFG. U: i+w V(itw)J k k+ U V Jk+i J++6+m% =Jk+i+w 2021年2月 10
2021年2月 10 Unfolding algorithm proof The output of the iteration of the node V(i+w)%J corresponds to the iteration of the node V in the original DFG. th J i w k ( ) i w J th J i w J k ( ( ) ( )% ) Ui U V(i+w)%J i w J k i w k J ? Jk i ( ) ( )% i w J k i w J J Jk i w w V