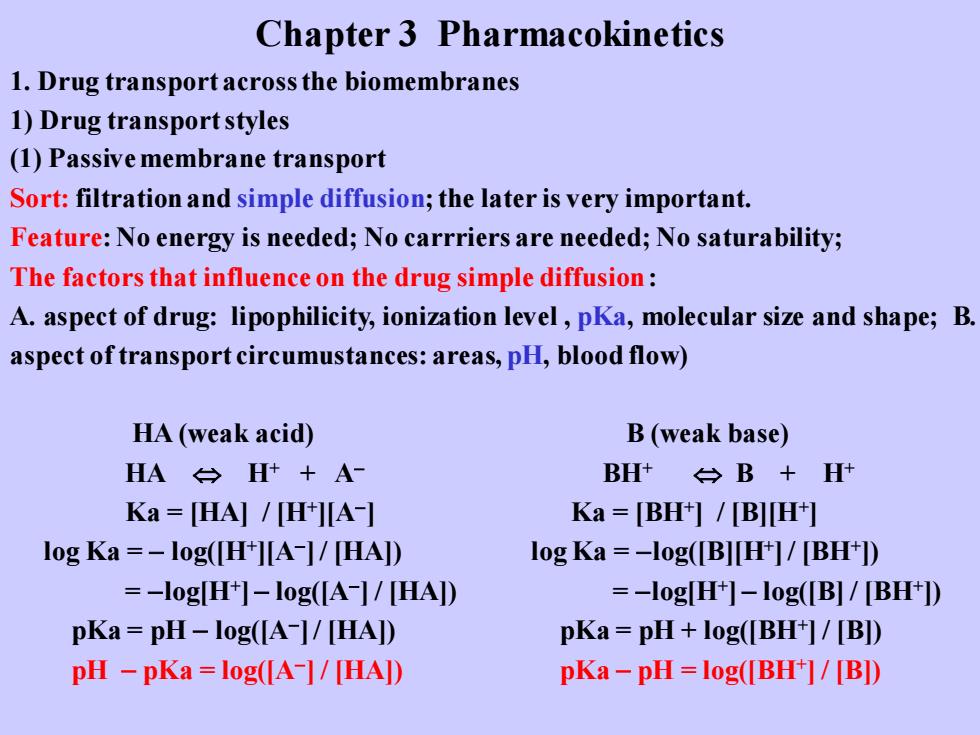
Chapter 3 Pharmacokinetics 1.Drug transport across the biomembranes 1)Drug transport styles (1)Passive membrane transport Sort:filtration and simple diffusion;the later is very important. Feature:No energy is needed;No carrriers are needed;No saturability; The factors that influence on the drug simple diffusion: A.aspect of drug:lipophilicity,ionization level,pKa,molecular size and shape;B. aspect of transport circumustances:areas,pH,blood flow) HA(weak acid) B(weak base) HA台H++A BH+台B+H Ka=[HA]/[H+][A-] Ka=BH/BH剀 log Ka=-l0g([H+][A-]/[HA]) log Ka=-log([B][H+]/[BH+]) =-log[H+]-log([A-]/[HA]) =-log[H+]-log([B]/[BH+]) pKa=pH-log([A-]/[HA]) pKa=pH+log(BH中/[B) pH -pKa=log([A-]/[HA]) pKa-pH=log([BH+]/[BD)
Chapter 3 Pharmacokinetics 1. Drug transport across the biomembranes 1) Drug transport styles (1) Passive membrane transport Sort: filtration and simple diffusion; the later is very important. Feature: No energy is needed; No carrriers are needed; No saturability; The factors that influence on the drug simple diffusion: A. aspect of drug: lipophilicity, ionization level , pKa, molecular size and shape; B. aspect of transport circumustances: areas, pH, blood flow) HA (weak acid) B (weak base) HA H+ + A− BH+ B + H+ Ka = [HA] / [H+ ][A− ] Ka = [BH+ ] / [B][H+ ] log Ka = − log([H+ ][A− ]/ [HA]) log Ka = −log([B][H+ ]/ [BH+ ]) = −log[H+ ] − log([A− ] / [HA]) = −log[H+ ] − log([B] / [BH+ ]) pKa = pH − log([A− ]/ [HA]) pKa = pH + log([BH+ ] / [B]) pH − pKa = log([A− ] / [HA]) pKa − pH = log([BH+ ] / [B])
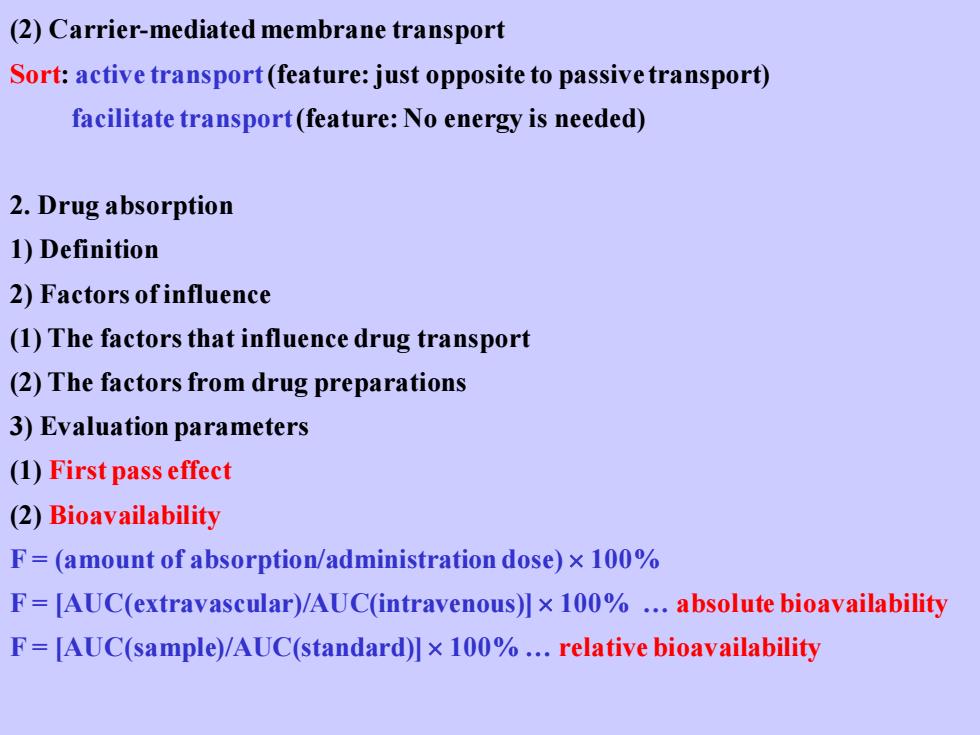
(2)Carrier-mediated membrane transport Sort:active transport(feature:just opposite to passive transport) facilitate transport(feature:No energy is needed) 2.Drug absorption 1)Definition 2)Factors ofinfluence (1)The factors that influence drug transport (2)The factors from drug preparations 3)Evaluation parameters (1)First pass effect (2)Bioavailability F=(amount of absorption/administration dose)x 100% F=[AUC(extravascular)/AUC(intravenous)]x 100%.absolute bioavailability F=[AUC(sample)/AUC(standard)]x 100%.relative bioavailability
(2) Carrier-mediated membrane transport Sort: active transport(feature: just opposite to passive transport) facilitate transport(feature: No energy is needed) 2. Drug absorption 1) Definition 2) Factors of influence (1) The factors that influence drug transport (2) The factors from drug preparations 3) Evaluation parameters (1) First pass effect (2) Bioavailability F = (amount of absorption/administration dose) 100% F = [AUC(extravascular)/AUC(intravenous)] 100% . absolute bioavailability F = [AUC(sample)/AUC(standard)] 100% . relative bioavailability