
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs 。Broad-spectrum 。Superinfection 。Bactericidal Bacteriostatic
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs • Broad-spectrum • Superinfection • Bactericidal • Bacteriostatic
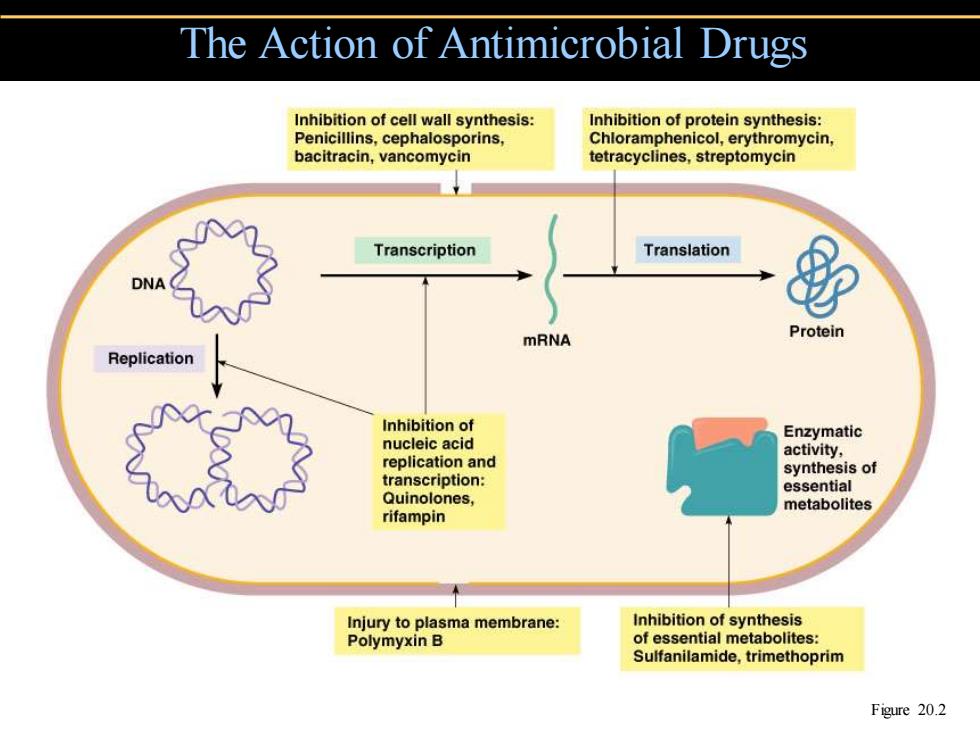
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs Inhibition of cell wall synthesis: Inhibition of protein synthesis: Penicillins,cephalosporins, Chloramphenicol,erythromycin, bacitracin,vancomycin tetracyclines,streptomycin Transcription Translation mRNA Protein Replication Inhibition of Enzymatic nucleic acid activity, replication and synthesis of transcription: essential Quinolones, metabolites rifampin Injury to plasma membrane: Inhibition of synthesis Polymyxin B of essential metabolites: Sulfanilamide,trimethoprim Figure 20.2
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs Figure 20.2
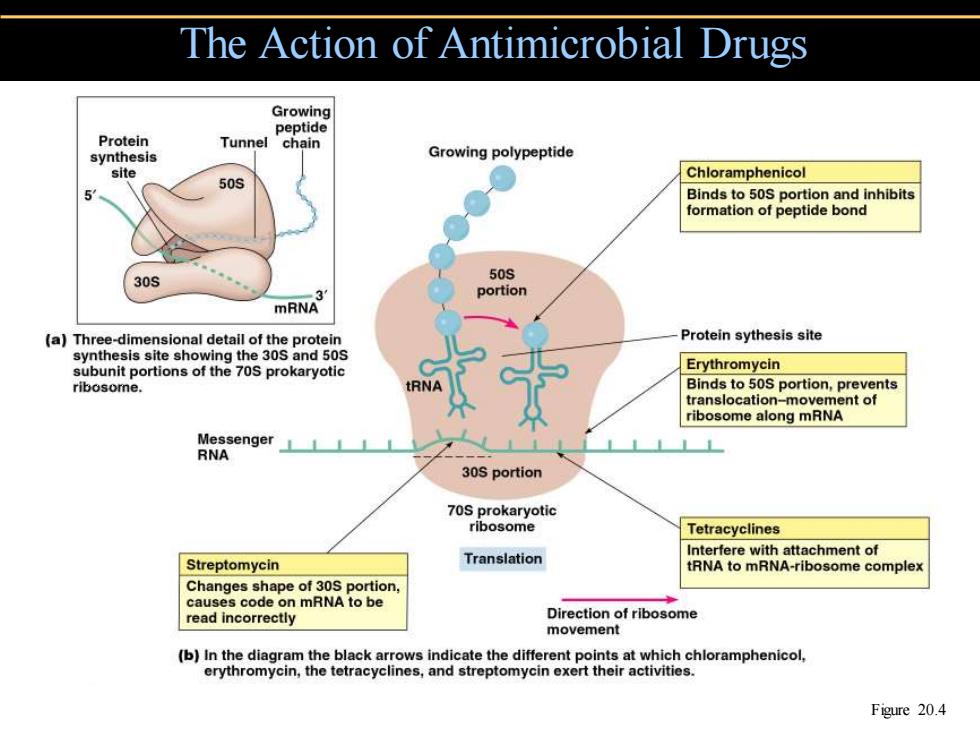
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs Growing peptide Protein Tunnel chain synthesis Growing polypeptide site Chloramphenicol 50S Binds to 50S portion and inhibits formation of peptide bond 30S 50S portion mRNA (a)Three-dimensional detail of the protein Protein sythesis site synthesis site showing the 30S and 50S subunit portions of the 70S prokaryotic Erythromycin ribosome. RNA Binds to 50S portion,prevents translocation-movement of ribosome along mRNA Messenger RNA 30S portion 70S prokaryotic ribosome Tetracyclines Interfere with attachment of Streptomycin Translation tRNA to mRNA-ribosome complex Changes shape of 30S portion. causes code on mRNA to be read incorrectly Direction of ribosome movement (b)In the diagram the black arrows indicate the different points at which chloramphenicol, erythromycin,the tetracyclines,and streptomycin exert their activities. Figure 20.4
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs Figure 20.4