
Enzymes commonly employ one or more of the following strategies to catalyze specific reactions: 1.Covalent Catalysis共价催化:the active site contains a reactive group,usually a powerful nucleophile,that becomes temporarily covalently attached to a part of the substrate in the course of catalysis.The proteolytic enzyme provides an excellent example of this strategy 共价催化的活性位点有活泼基团,通常是很强的亲核基团。 在酶促过程中亲核基团能暂时性共价连接底物。 2.General Acid-Base Catalysis酸碱催化.In general acid- base catalysis,a molecule other than water plays the role of a proton donor or acceptor. 酸碱催化中,水分子之外的物质提供质子或接受质子
1. Covalent Catalysis共价催化: the active site contains a reactive group, usually a powerful nucleophile, that becomes temporarily covalently attached to a part of the substrate in the course of catalysis. The proteolytic enzyme provides an excellent example of this strategy . 共价催化的活性位点有活泼基团,通常是很强的亲核基团。 在酶促过程中亲核基团能暂时性共价连接底物。 2. General Acid–Base Catalysis酸碱催化. In general acid– base catalysis, a molecule other than water plays the role of a proton donor or acceptor. 酸碱催化中,水分子之外的物质提供质子或接受质子 Enzymes commonly employ one or more of the following strategies to catalyze specific reactions:

3.( Catalysis by Approximation邻近催化.Many reactions include two distinct substrates.The reaction rate may be considerably enhanced by bringing the two substrates together along a single binding surface on an enzyme. 很多酶有两个不同的底物。将两种底物置于一个酶分 子的同一结合面能显著增加反应速度 4.Metal lon Catalysist金属离子催化.Metal ions can function catalytically in several ways,ie. Nucleophiles and an electrophile 金属离子起催化作用的方式有几种。配位作用、亲电 作用或亲核作用等
3. Catalysis by Approximation邻近催化. Many reactions include two distinct substrates. The reaction rate may be considerably enhanced by bringing the two substrates together along a single binding surface on an enzyme. 很多酶有两个不同的底物。将两种底物置于一个酶分 子的同一结合面能显著增加反应速度 4. Metal Ion Catalysis金属离子催化. Metal ions can function catalytically in several ways, ie. Nucleophiles and an electrophile 金属离子起催化作用的方式有几种。配位作用、亲电 作用或亲核作用等

Cases -Serine proteases:to promote a reaction that is almost immeasurably slow at neutral pH in the absence of a catalyst.将pH7.0几乎不发生 的反应(蛋白质水解)进行下去 -Carbonic anhydrases:to achieve a high absolute rate of reaction,suitable for integration with other rapid physiological processes.加速以与其他快速生理过程融合 -Restriction endonucleases,to attain a high degree of specificity. 酶切反应的高度特异性 NMP kinases:to transfer a phosphoryl group from AT P to a nucleotide and not to water.磷酸基团从ATP转移给另一个核苷酸(而不 会转移到水分子)
-Serine proteases : to promote a reaction that is almost immeasurably slow at neutral pH in the absence of a catalyst. 将pH 7.0几乎不发生 的反应(蛋白质水解)进行下去 -Carbonic anhydrases: to achieve a high absolute rate of reaction,suitable for integration with other rapid physiological processes. 加速以与其他快速生理过程融合 -Restriction endonucleases, to attain a high degree of specificity.实现 酶切反应的高度特异性 - NMP kinases: to transfer a phosphoryl group from AT P to a nucleotide and not to water.磷酸基团从ATP转移给另一个核苷酸(而不 会转移到水分子) Cases
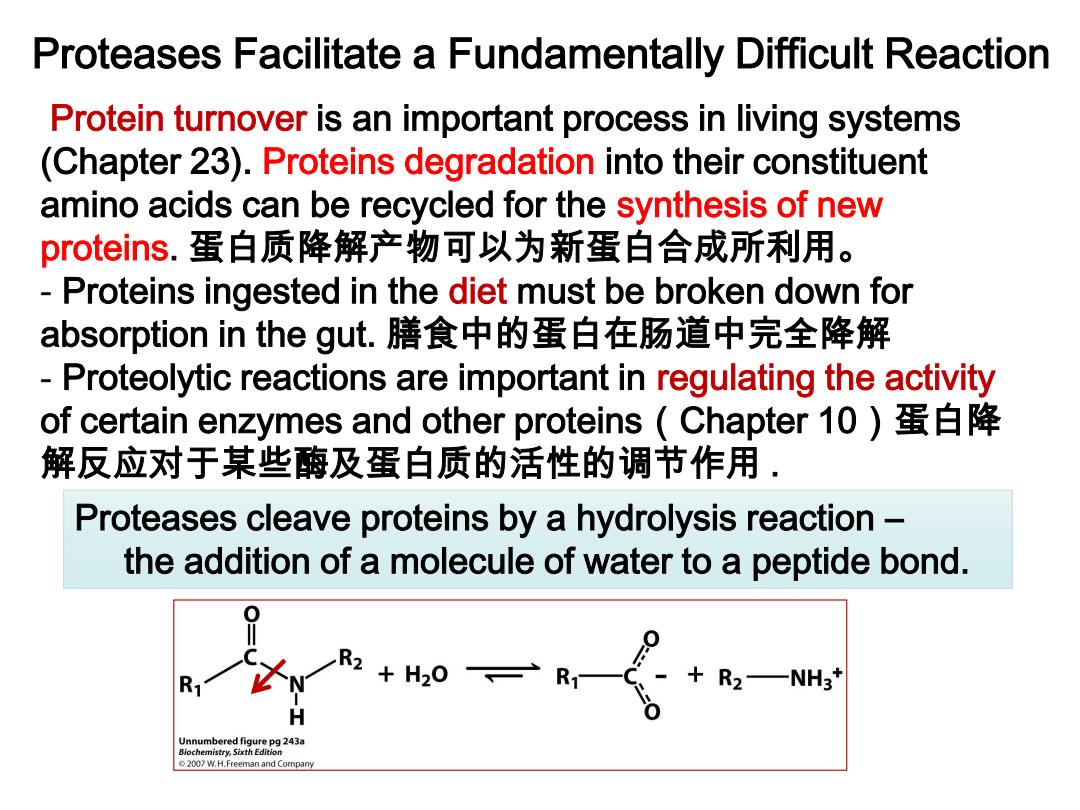
Proteases Facilitate a Fundamentally Difficult Reaction Protein turnover is an important process in living systems (Chapter 23).Proteins degradation into their constituent amino acids can be recycled for the synthesis of new proteins.蛋白质降解产物可以为新蛋白合成所利用。 Proteins ingested in the diet must be broken down for absorption in the gut.膳食中的蛋白在肠道中完全降解 Proteolytic reactions are important in regulating the activity of certain enzymes and other proteins(Chapter10)蛋白降 解反应对于某些酶及蛋白质的活性的调节作用 Proteases cleave proteins by a hydrolysis reaction- the addition of a molecule of water to a peptide bond. R ,+R2一NH Unnumbered figure pg 243a Biochemistry,Sixth Edition 2007 W.H.Freeman and Company
Proteases Facilitate a Fundamentally Difficult Reaction Protein turnover is an important process in living systems (Chapter 23). Proteins degradation into their constituent amino acids can be recycled for the synthesis of new proteins. 蛋白质降解产物可以为新蛋白合成所利用。 - Proteins ingested in the diet must be broken down for absorption in the gut. 膳食中的蛋白在肠道中完全降解 - Proteolytic reactions are important in regulating the activity of certain enzymes and other proteins(Chapter 10)蛋白降 解反应对于某些酶及蛋白质的活性的调节作用 . Proteases cleave proteins by a hydrolysis reaction – the addition of a molecule of water to a peptide bond

The half-life for the hydrolysis of a typical peptide at neutral pH is estimated to be between 10 and 1000 years. The resonance structure endows the peptide bond with partial double bond character,that accounts for the planarity of a peptide bond also makes such bonds resistant to hydrolysis.肽键共振赋予其平面结构,因此抗水解。 R H duP924h The carbonyl carbon atom is less electrophilic and less susceptible to nucleophilic attack than are the carbonyl carbon atoms in compounds such as carboxylate esters. Yet,peptide bonds must be hydrolyzed within milliseconds in some biochemical processes
The half-life for the hydrolysis of a typical peptide at neutral pH is estimated to be between 10 and 1000 years. The resonance structure endows the peptide bond with partial double bond character, that accounts for the planarity of a peptide bond also makes such bonds resistant to hydrolysis. 肽键共振赋予其平面结构,因此抗水解。 The carbonyl carbon atom is less electrophilic and less susceptible to nucleophilic attack than are the carbonyl carbon atoms in compounds such as carboxylate esters. Yet, peptide bonds must be hydrolyzed within milliseconds in some biochemical processes