3,Transforms 1
3. Transforms 1

Overview We will introduce the most useful transforms which are similar to Fourier transform in signal processing,including: ▣Stieltjes transform ▣Shannon transform ▣R transform ▣S transform ▣n-transform These transforms will form a strong basis to be able to understand the extensions discussed in the subsequent Chapters 2
Overview 2 We will introduce the most useful transforms which are similar to Fourier transform in signal processing, including: Stieltjes transform Shannon transform R transform S transform η-transform These transforms will form a strong basis to be able to understand the extensions discussed in the subsequent Chapters
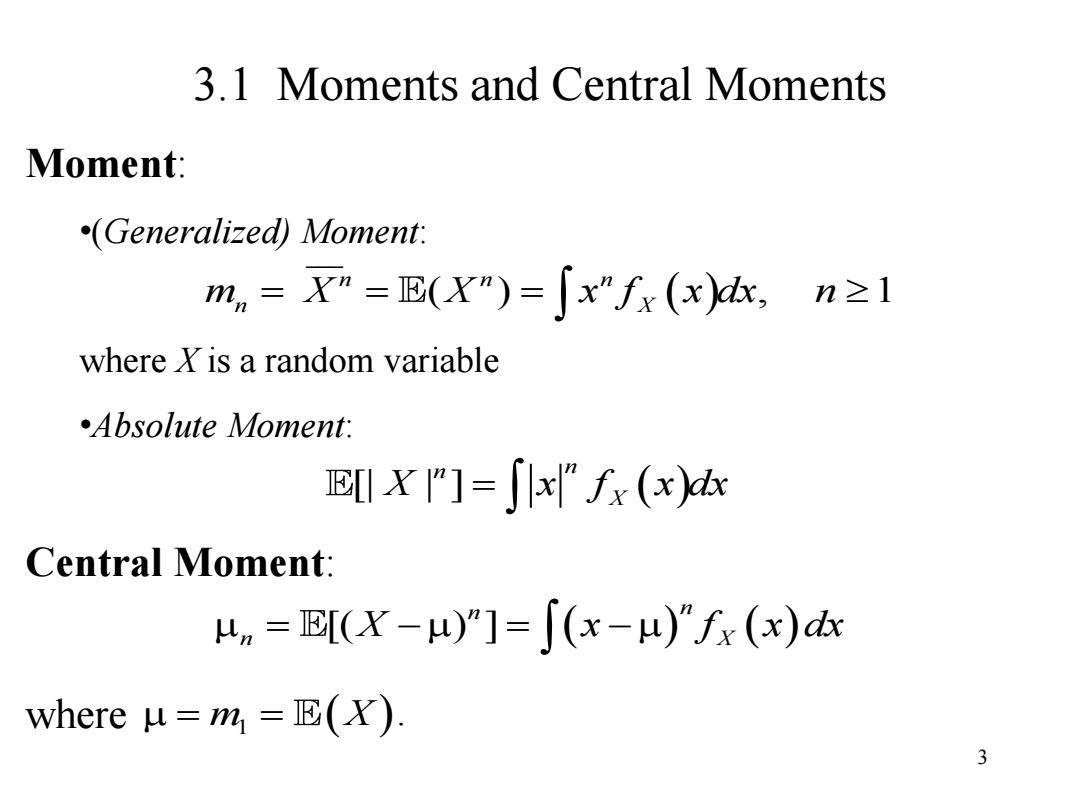
3.1 Moments and Central Moments Moment: (Generalized)Moment: mn=X”=E(X")=∫x”fx(x),n≥1 where X is a random variable Absolute Moment: EX]=Jlx”fx(x) Central Moment: un=E(X-)”]=J(x-u)”fx(x)d where u=m=(). 3
3 3.1 Moments and Central Moments Moment: •(Generalized) Moment: where X is a random variable •Absolute Moment: Central Moment: where ___ ( ) , 1 n n n m X X x f x dx n n X [| | ] n n X x f x dx X [( ) ] n n n X X x f x dx m X 1
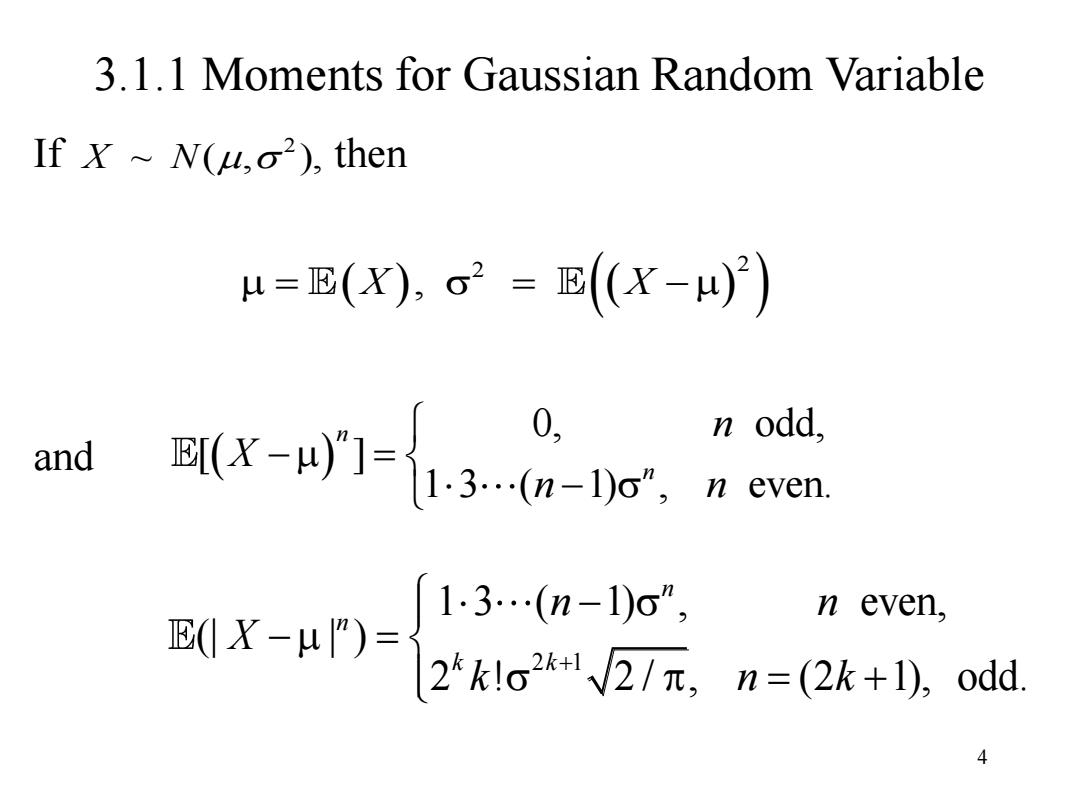
3.1.1 Moments for Gaussian Random Variable If X N(u,o2),then u=E(X),o2=E(X-)) and 现x-1-h9w.日n n odd, 13…(n-1)o”, n even, X-u)F2k1o2元,n=(2k+0,odd 4
4 3.1.1 Moments for Gaussian Random Variable If then and ~ ( , ), 2 X N 2 2 X X , 0, odd, [ ] 1 3 ( 1) , even. n n n X n n 2 1 1 3 ( 1) , even, (| | ) 2 ! 2 / , (2 1), odd. n n k k n n X k n k

3.2 Characteristic Function 3.2 Definition: Φx(o)=E(eo)=∫ehof(x) For diserete r. Φx(o)=∑eoP(X=k) Properties: (iΦx(o)=1andΦx(o≤1. mm.=129(x)1-2m m-(-o (n≥1) 0=0 5
5 3.2 Characteristic Function 3.2 Definition: For discrete r.v., Properties: (i) and (ii) ( ) ( ) . jX jx X X e e f x dx k jk X ( ) e P(X k). X (0) 1 () 1. X 1 1 0 ( ) 1 1 ! ! 1 ( ) ( 1) n n n X n n n n n X n n n j j X m n n d m X n j d