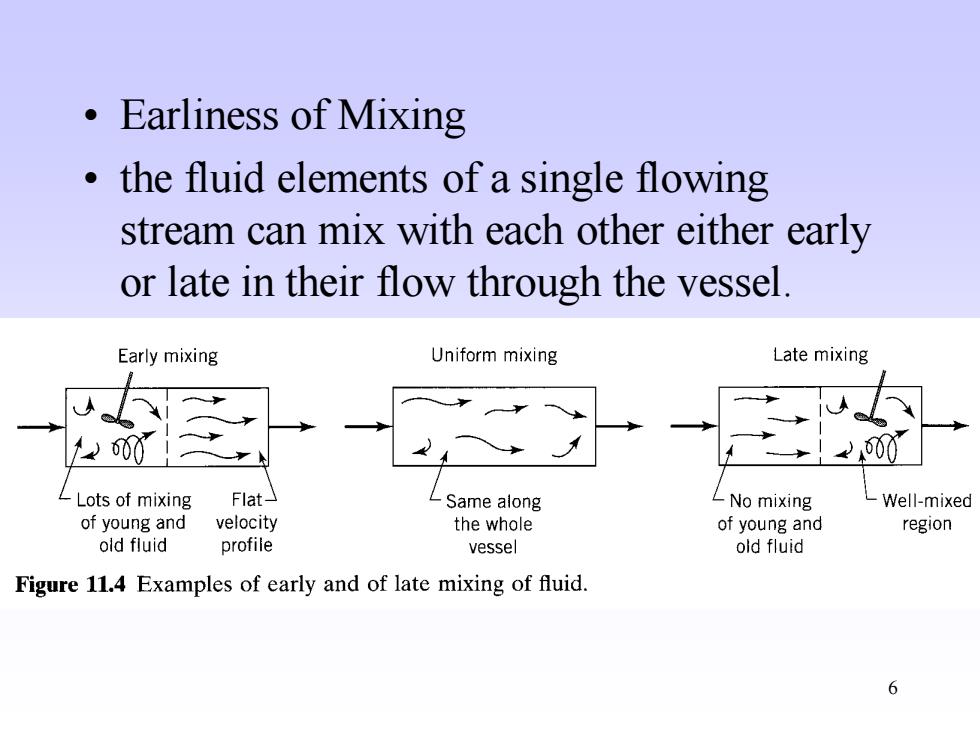
。Earliness of Mixing the fluid elements of a single flowing stream can mix with each other either early or late in their flow through the vessel Early mixing Uniform mixing Late mixing 00 00 Lots of mixing Flat- Same along LNo mixing Well-mixed of young and velocity the whole of young and region old fluid profile vessel old fluid Figure 11.4 Examples of early and of late mixing of fluid. 6
6 • Earliness of Mixing • the fluid elements of a single flowing stream can mix with each other either early or late in their flow through the vessel
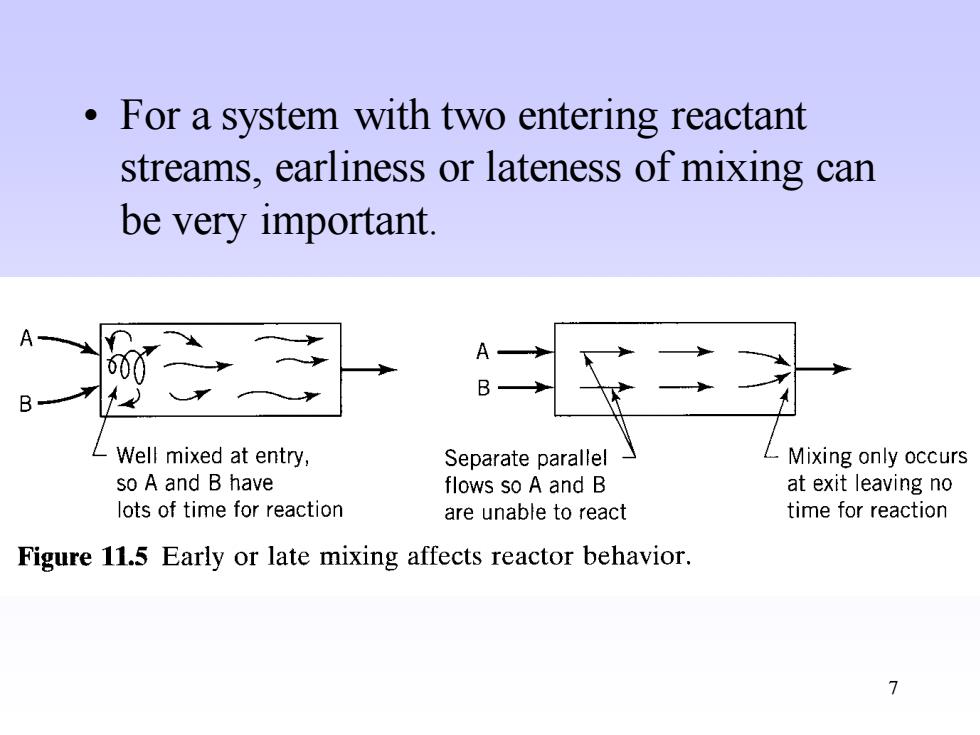
For a system with two entering reactant streams,earliness or lateness of mixing can be very important. A 60 B LWell mixed at entry, Separate parallel LMixing only occurs so A and B have flows so A and B at exit leaving no lots of time for reaction are unable to react time for reaction Figure 11.5 Early or late mixing affects reactor behavior. 7
7 • For a system with two entering reactant streams, earliness or lateness of mixing can be very important

Role of RTD,State of Aggregation,and Earliness of Mixing in Determining Reactor Behavior In some situations one of these three factors can be ignored,in others it can become crucial.Often,much depends on the time for reaction t,the time for mixingtmix,and the time for stay in the vessel tsty.In many casests has a meaning somewhat like but somewhat broader. 8
8 • Role of RTD, State of Aggregation, and Earliness of Mixing in Determining Reactor Behavior • In some situations one of these three factors can be ignored, in others it can become crucial. Often, much depends on the time for reaction , the time for mixing , and the time for stay in the vessel . In many cases has a meaning somewhat like but somewhat broader. trx t mix t stay t stay t mix

11.1 E,The Age Distribution of Fluid,the RTD In this section,we do not consider any reaction It is evident that elements of fluid taking different routs through the reactor may take different lengths of time to pass through the vessel.The distribution of these times for the stream of fluid leaving the vessel is called the exit age distribution E,or the residence time distribution RTD of the fluid. E has the units of time-1. 9
9 11.1 E, The Age Distribution of Fluid, the RTD • It is evident that elements of fluid taking different routs through the reactor may take different lengths of time to pass through the vessel. The distribution of these times for the stream of fluid leaving the vessel is called the exit age distribution E, or the residence time distribution RTD of the fluid. E has the units of time -1 . In this section, we do not consider any reaction

As a beginning,we have a review of ideal flow reactor MFR (CSTR)in which fluid has maximum back-mixing PFR in which there isn't any back-mixing Non-ideal reactor:it's back-mixing between CSTR and PFR back-mixing The mix of fluid with different stay time 10
10 • As a beginning, we have a review of ideal flow reactor • MFR(CSTR) in which fluid has maximum back-mixing • PFR in which there isn’t any back-mixing • Non-ideal reactor: it’s back-mixing between CSTR and PFR • back-mixing The mix of fluid with different stay time