
国 上海文通大学 Vector manipulations TON Vector Magnitude Head Magnitude (terminus) Direction Tail (origin) Vector can be represented Graphically R=Ri+Ryj R=R+jRy ◆ Analytically R=[R.RT R=Rei=R(cos0+jsine) 国上泽支大半 Vector manipulations Vector addition: A=Aeio A B=Beia C=A+B C=A+B=Aei+Bei0a =B+A 0 =(Acos0,+Bcoseg)+ (a) j(Asin+Bsineg) A=C-B Vector substraction: A=C-B=Ceic-Beio =(Ccosec-Bcos0g)+ j(Csinec-Bsine) Figure(Vee 6
6 Vector manipulations Vector Magnitude Direction Vector can be represented Graphically Analytically Head Magnitude (terminus) Tail (origin) R R jR x y R e (cos sin ) j R j R [ ]T R R x y R R Ri R j x y Vector manipulations Figure (a) Vector addition and (b) vector subtraction. B A B C A j Ae A B j Be B =( cos cos )+ j( sin sin ) A B j j A B A B Ae Be A B A B CAB =( cos cos )+ j( sin sin ) C B j j C B C B Ce Be C B C B A CB Vector addition: Vector substraction:
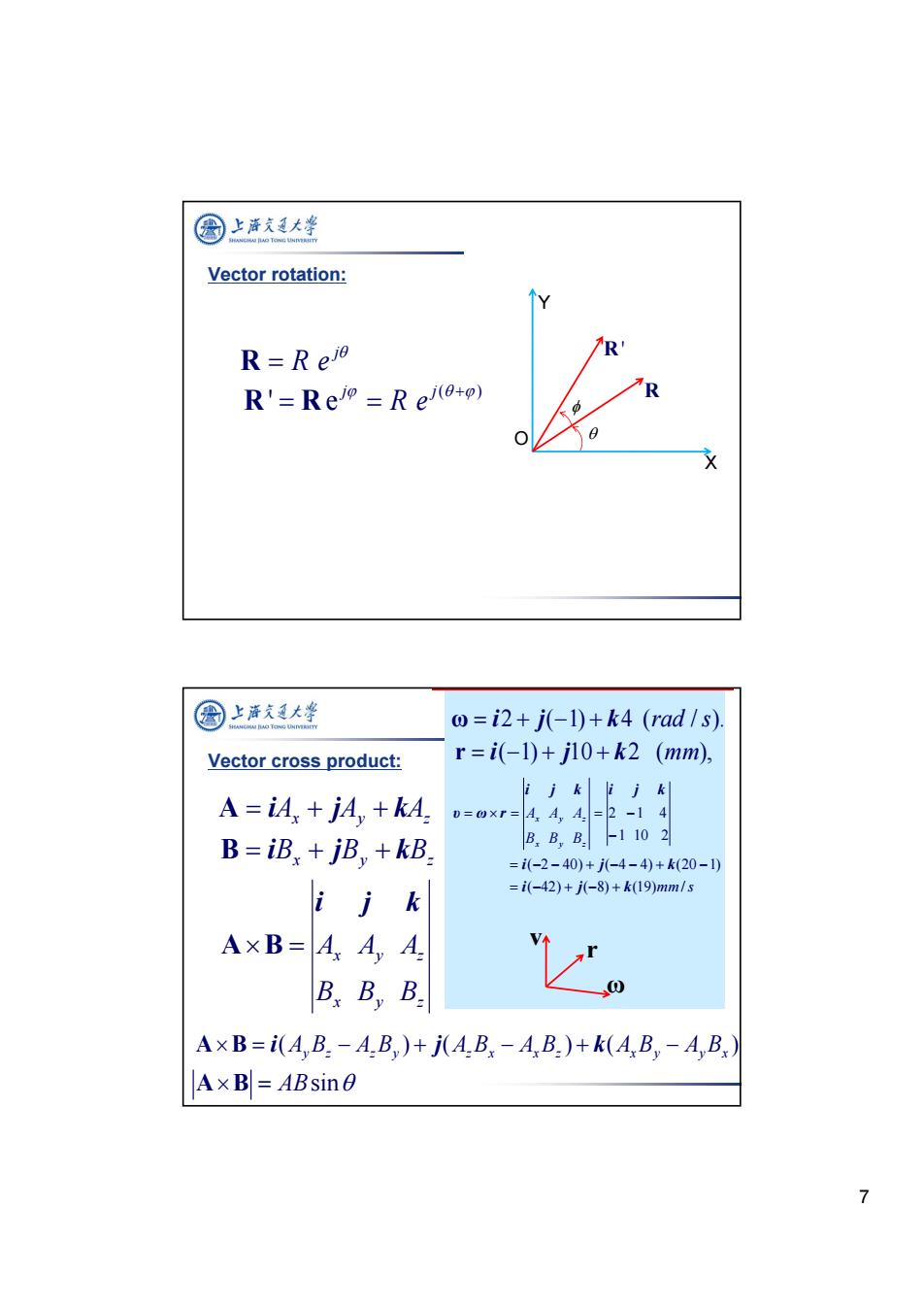
圈上游文大学 Vector rotation: R=Reio R R'=Reio=Rei(o+o) 国上泽支大半 o=i2+j-1)+k4(rad1s). Vector cross product: r=i(-1)+j10+k2(mm), A=iA,jA,+kA. ii i j k D=@xr= B=iB:jBy+kB. -1102 =i(-2-40)+j-4-4)+k(20-1) i jk =i(-42)+j(-8)+k(19)mm/s A×B=AA,A B.B,B. AxB=i(A,B.-A.B)+j(A.B-A B.)+k(A,B-A,B. A×Bl=ABsin0 7
7 Vector rotation: j R e R ( ) 'e j j R e R R X Y O R R ' ω i2 j(1) k4 (rad / s). r i(1) j10 k2 (mm), mm s B B B A A A x y z x y z ( 42) ( 8) (19) / ( 2 40) ( 4 4) (20 1) 1 10 2 2 1 4 i j k i j k i j k i j k υ ω r ω r v Ax Ay Az A i j k Bx By Bz B i j k Vector cross product: x y z x y z B B B A A A i j k AB ( ) ( ) ( ) AyBz AzBy AzBx AxBz AxBy AyBx A B i j k A B ABsin

国上泽夫通大学 i Vector dot product: A-B=ABcos0 ixj=k jxi=-k jxk=i k×j=-i kxi=j ixk=-j i×i=j×j=k×k=0 i.i=j.j=k.k=1 i.j=j.k=k.i=0 ixi=-k j=k 国 上海文通大学 Some useful trigonometric identities: COS0=eten 2 .sing=-jen-em 2 1-tan2(3) 2tan() cos0 sin= 1+a3 cos(0±)=cos(0)cos(p)干sin(0)sin(p) sin(0±)=sin(g)cos()±cos(0)sin() 8
8 Vector dot product: A B ABcos 0 k i j i k j i i j j k k i j k j i k j k i k j i i.i j.j k.k 1 i.j j.k k.i 0 Some useful trigonometric identities: 2 2 2 cos ,sin 2 2 1 tan ( ) 2 tan( ) 2 2 cos ,sin 1 tan ( ) 1 tan ( ) 2 2 cos( ) cos( )cos( ) sin( )sin( ) sin( ) sin( )cos( ) cos( )sin( ) jj jj ee ee j

图上泽通大学 Differentiation of complex polar vectors: Let R=R ei represent the position of a point with respect to a fixed reference origin,then First order: d(RRe+R(j)-ke+Roje" Second order: (Re=Re+Rdje+(Ra+0je+RaUe°7间 d -Re0+20Rj er+Rj e-ROelo =(R-R02)ei0+(20R+0R)j ei 上潘久大学 Second order: (R)-Re(Re d' =e+20Re+8Re°-R0e° =(R-RO)e+(20R+0R)j e 20Rj e Rj e hen R ROe 0 9
9 Differentiation of complex polar vectors: j R e Let repres R ent the position of a point with respect to a fixed reference origin, then First order: ( ) ( )= d j jj j j R e Re R e j Re R j e dt 2 2 2 2 Second order: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) = 2 =( ) +(2 ) jj j j j j j jj j d R e Re R j e R R j e R je j dt Re Rj e Rj e R e RR e R R j j e X Y O R j j e j Re j R j e j e j Re 2 j R e 2 j Rj e j Rj e P 2 2 2 2 Second order: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) = 2 =( ) +(2 ) jj j j j j j jj j d R e Re R j e RR j e R je j dt Re Rj e Rj e R e RR e R R j j e
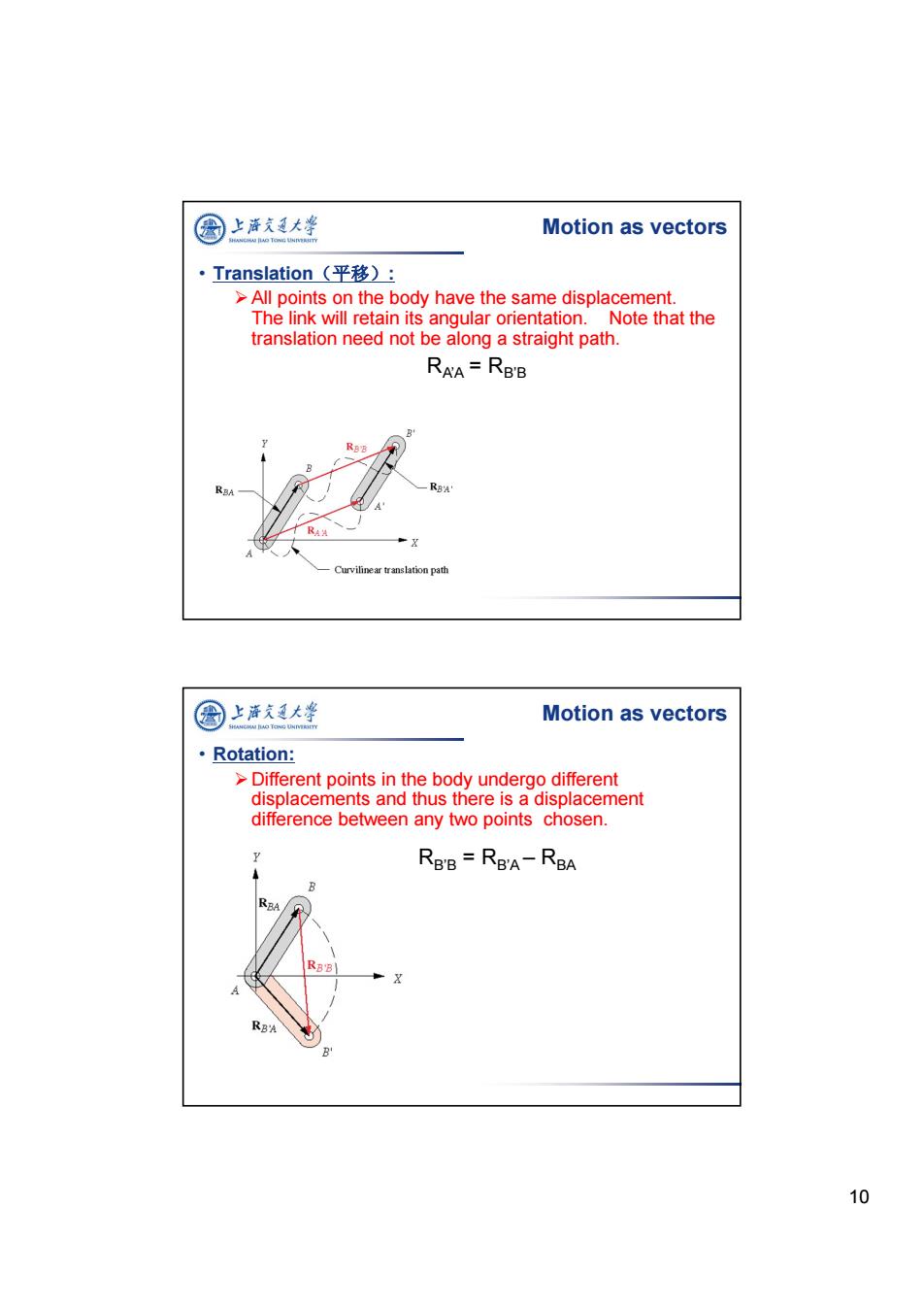
图 上海文通大¥ Motion as vectors ·Translation(平移): >All points on the body have the same displacement. The link will retain its angular orientation.Note that the translation need not be along a straight path. RAA=RBB R RBB RBA RBA RA Curvilinear translation path 国上泽支大半 Motion as vectors ·Rotation: >Different points in the body undergo different displacements and thus there is a displacement difference between any two points chosen. RBB=RBA-RBA RBA RB'B RBA 10
10 • Translation(平移): All points on the body have the same displacement. The link will retain its angular orientation. Note that the translation need not be along a straight path. RA’A = RB’B Motion as vectors • Rotation: Different points in the body undergo different displacements and thus there is a displacement difference between any two points chosen. RB’B = RB’A – RBA Motion as vectors