LECTURE 4 ME371/ME337 DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Electric Motors Principles and Applications Covered:Ch2-in Design of Machinery 国上大峰 Lectures Power/Energy Conversion (Electric Motors) Power/Energy ransmission (Gears Belt Drives, Power Screws) Joints Transmission (Fasteners Support Structural Connectors) (Bearings) Support Shafts Axles Spindles) Tools Stress Analysis, Failure Theories Dynamics,Statics,Etc.... 2
1 Electric Motors ——Principles and Applications LECTURE 4 ME371/ME337 DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Covered:Ch2- in Design of Machinery 2 Lectures Power/Energy Conversion (Electric Motors) Power/Energy Transmission (Gears, Belt Drives, Power Screws) Transmission Support (Bearings) Joints (Fasteners, Connectors) Structural Support (Frames Shafts Axles Spindles) Tools Stress Analysis, Failure Theories Dynamics, Statics, Etc…

圈上再我大峰 Objectives of this Lecture Describe the factors that must be specified to select a suitable motor Describe the principles of operation of DC motors. Describe four basic designs of DC motors,and describe their performance curves. Describe the general form of a motor performance curve. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of DC motors compared with AC motors. OUTLINE Actuators introduction Principles of operation ▣Torque-.speed curves Performance parameters 4
3 Objectives of this Lecture • Describe the factors that must be specified to select a suitable motor • Describe the principles of operation of DC motors. • Describe four basic designs of DC motors, and describe their performance curves. • Describe the general form of a motor performance curve. • Describe the advantages and disadvantages of DC motors compared with AC motors. 4 OUTLINE Actuators introduction Principles of operation Torque-speed curves Performance parameters

圈上大峰 Motor Selection What are the various kinds of actuators out there? What are the various kinds of 'electromagnetic' motors? What are their relative advantages disadvantages? How do these different kinds of motors work? Actuators ■What? Converts Energy from one domain to another Energy conversion to mechanical domain is most relevant to us ! ■Why? To change the state of a system(position,velocity,acceleration) How?Actuator Specifications Range Mechanical parameters(mass, ·Resolution inertia,stiffness etc.) Accuracy/Repeatability Electrical parameters(resistance, Force/Torque Capability inductance,capacitance) Power Rating Losses:Internal resistance, Mounting and Size friction,damping Internal Bearing Specs Max Ratings(e.g.voltage,current 。 Drivers(e.g.drive amplifier torque,speed,flow rate..) for motors,pump for hydraulic cylinder) 6
5 Motor Selection • What are the various kinds of actuators out there? • What are the various kinds of ‘electromagnetic’ motors? • What are their relative advantages / disadvantages? • How do these different kinds of motors work? 6 Actuators What? - Converts Energy from one domain to another - Energy conversion to mechanical domain is most relevant to us !! Why? - To change the state of a system (position, velocity, acceleration) How? Actuator Specifications • Range • Resolution • Accuracy/Repeatability • Force/Torque Capability • Power Rating • Mounting and Size • Internal Bearing Specs • Drivers (e.g. drive amplifier for motors, pump for hydraulic cylinder) • Mechanical parameters (mass, inertia, stiffness etc.) • Electrical parameters (resistance, inductance, capacitance) • Losses: Internal resistance, friction, damping • Max Ratings (e.g. voltage, current, torque, speed, flow rate..)
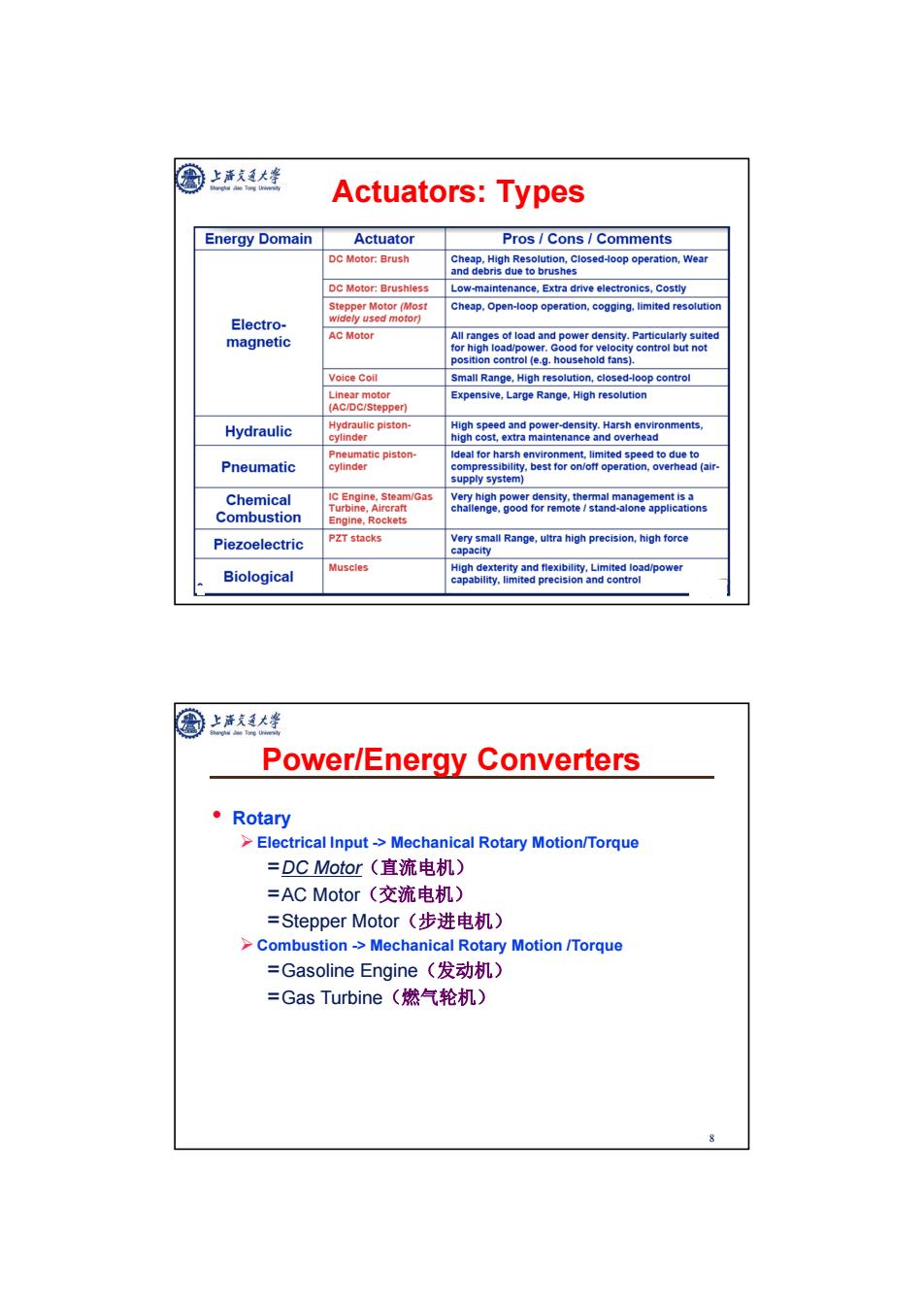
圈上话衣大峰 Actuators:Types Energy Domain Actuator Pros Cons Comments DC Motor:Brush Cheap,High Resolution,Closed-oop operation,Wear and debris due to brushes DC Motor:Brushless Low-maintenance,Extra drive electronics,Costly Stepper Motor (Most Cheap,Open-loop operation,cogging.limited resolution Electro- widely used motor) magnetic AC Motor All ranges of load and power density.Particularly suited for high load/power.Good for velocity control but not position control (e.g.household fans). Voice Coil Small Range,High resolution,closed-loop control Linear motor Expensive,Large Range,High resolution (AC/DC/Stepper) Hydraulic Hydraulic piston- High speed and power-density.Harsh environments, cylinder high cost,extra maintenance and overhead Pneumatic piston- Ideal for harsh environment,limited speed to due to Pneumatic cylinder compressibility,best for on/off operation,overhead(air. supply system) Chemical IC Engine,Steam/Gas Very high power density.thermal management is a Turbine,Aircraft Combustion challenge,good for remote /stand-alone applications Engine,Rockets Piezoelectric PZT stacks Very small Range,ultra high precision,high force capacity Biological Muscles High dexterity and flexibility,Limited load/power capability,limited precision and control Power/Energy Converters ·Rotary >Electrical Input->Mechanical Rotary Motion/Torque =DC Motor(直流电机) =AC Motor(交流电机) =Stepper Motor(步进电机) >Combustion->Mechanical Rotary Motion /Torque =Gasoline Engine(发动机) =Gas Turbine(燃气轮机) 8
7 Actuators: Types 8 Power/Energy Converters • Rotary Electrical Input -> Mechanical Rotary Motion/Torque =DC Motor(直流电机) =AC Motor(交流电机) =Stepper Motor(步进电机) Combustion -> Mechanical Rotary Motion /Torque =Gasoline Engine(发动机) =Gas Turbine(燃气轮机)

Power/Energy Converters 。Linear >Electrical Input->Mechanical Linear Motion/Torque or force =Lead screw linear actuators(丝杠线性驱动器) =Linear Motor(直线电机Ac/Dc/Stepper) >Pressure->Mechanical Linear Motion/Torque or force =Hydraulic Pumps(液压泵) =Hydraulic Actuators(液压动力装置) =Pneumatic Actuators(气动动力装置) =Compressors(压缩机) 上清发通大学 Electric Motors Electric Motors convert electrical power to mechanical power. Electrical Power Mechanical Power Electric Motor I,V F vor T,@ /Current F:Force T:Torque V:Voltage v:Velocity Angular Velocity Electrical Power=I*V Mechanical Power=F*v for linear motor =T@for rotary motor Electric motors normally mean electromagnetic motors They use the principles of electromagnetism for electrical/mechanical power conversion. 10
9 Power/Energy Converters • Linear Electrical Input -> Mechanical Linear Motion/Torque or force =Lead screw linear actuators(丝杠线性驱动器) =Linear Motor (直线电机 AC/DC/Stepper) Pressure -> Mechanical Linear Motion/Torque or force =Hydraulic Pumps(液压泵) =Hydraulic Actuators(液压动力装置) =Pneumatic Actuators(气动动力装置) =Compressors(压缩机) 10 Electric Motors • Electric Motors convert electrical power to mechanical power. Electric Motor Electrical Power I, V Mechanical Power F, v or T, I : Current V: Voltage F: Force v: Velocity T: Torque : Angular Velocity • Electric motors normally mean electromagnetic motors. They use the principles of electromagnetism for electrical/mechanical power conversion. Electrical Power = I*V Mechanical Power = F*v for linear motor = T* for rotary motor