
部分两相流的分类 Classification Diagram wet steam gas smoke flow spray dust flow droplet flow dilute particle cloud churn flow gas/ gas/ solid dense particle cloud stratified flow liquid flow flow granular flow dense bubbly flow 年ggg0里g0出生g生是0里里0目00年gf prous liquid medim dilute solid 。品想银。地 solid in motion bubbly flow flow liquid solid solid fixed fluidized bed fixed bed sedimentation solid in motion solid fixed
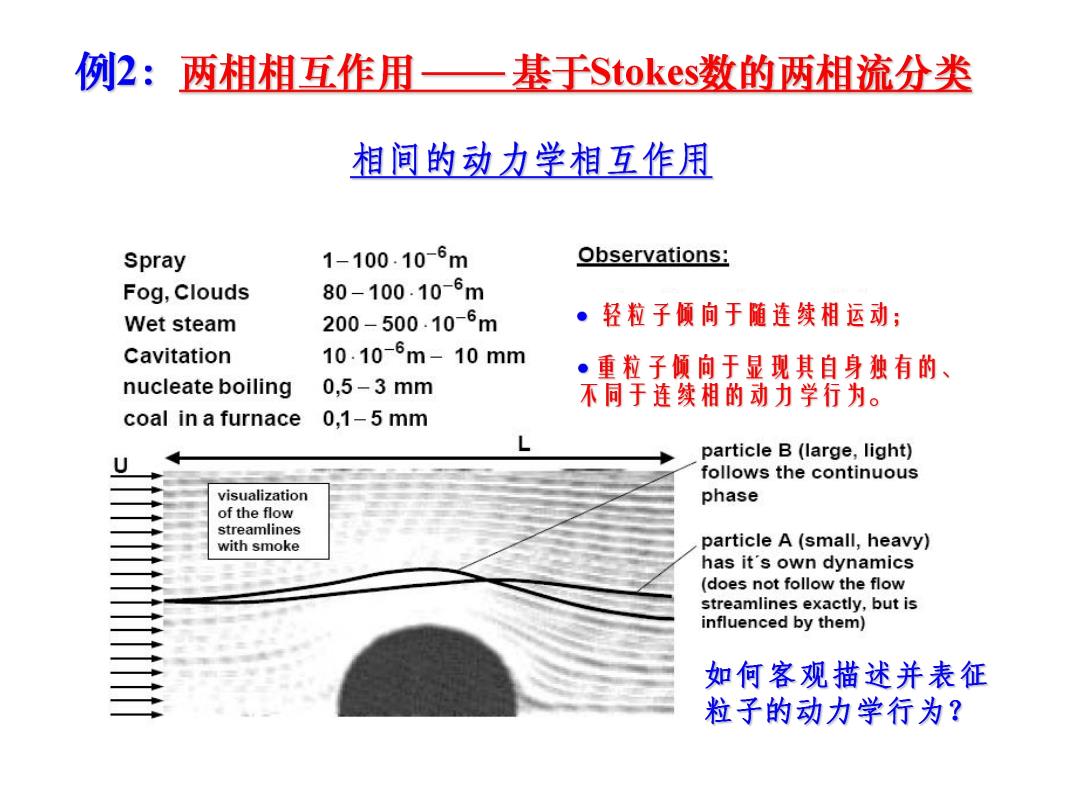
例2:两相相互作用一 基于Stokes?数的两相流分类 相间的动力学相互作用 Spray 1-100.10-6m Observations: Fog,Clouds 80-100.10-6m Wet steam 200-500.10-6m 轻粒子倾向于随连续相运动; Cavitation 10.10-6m-10mm ●重粒子倾向于显现其自身独有的、 nucleate boiling 0,5-3mm 不同于连续相的动力学行为。 coal in a furnace 0,1-5mm L particle B(large,light) follows the continuous visualization phase of the flow streamlines with smoke particle A(small,heavy) has it's own dynamics (does not follow the flow streamlines exactly,but is influenced by them) 如何客观描述并表征 粒子的动力学行为?

Stokes数的定义 连续相对粒子运动影响的量度 Idyn Stokes-number,objective measure for the St= influence of the continuous phase on the particle 粒子动态响应时间 Tflow motion 粒子在流场 Tdyn= dynamic response time 18u 中的特征停 L 留时间 characteristic residence time of a particle in a flow L:length of the flow field U:characteristic velocity flow regimes: St <1 particles move passively with the continuous phase (marker particles,,,homogeneous"flow,mechanical equilibrium) St≈1 strong interaction between particles and continuous phase(disperse two-phase flow) St >1 only little influence of the continuous phase on the particle motion(granular flow,if inter-particle collisions)
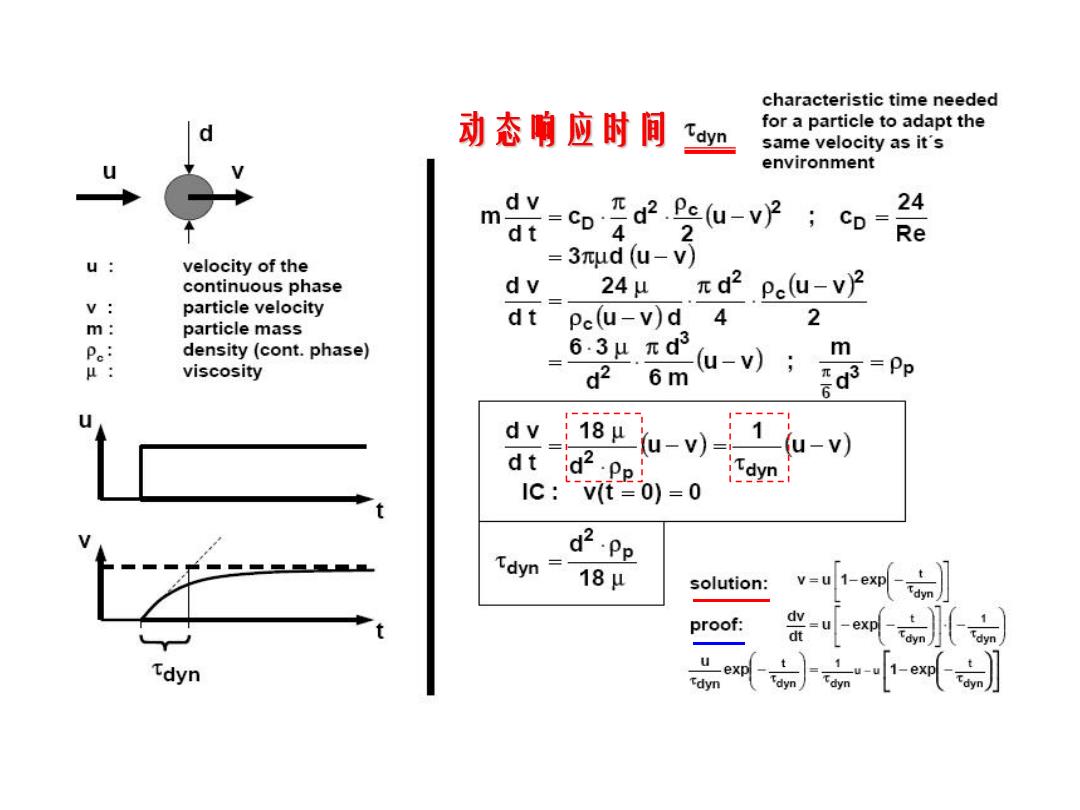
characteristic time needed 动态响应时间 Idyn for a particle to adapt the same velocity as it's environment =co4 cnd2.Pe(u-v)Co-Re 4 m dt 2 u: velocity of the =3xud (u-v) continuous phase dv 24u 元d2 Pe(u-v)2 v particle velocity dt 4 2 m: particle mass Pe(u-v)d Pe: density(cont.phase) 63μ.πd m μ: viscosity d2 6m u-); =Pp dv 18μ dt id2 u-v)= 1 (u-v) Ic:Vt=0)=0 d2.Pp 18μ solution: v-ut-x) proof: dv =u-exn月 t dt Idyn t tdyn _1u-u1-ex知

由实验测量间接确定拖曳系数CD 极限上升速度—一U (Representative Quantity) 4 equilibrium Fouoy =3πR3(pL-pG)g 3 hydrostatic 。nL-pg=co受u 2 Fbuoy buoyancy (Effect) buoyancy drag d3(pL-pg) →C=6 2PL-PG d drag (Effect) d2.PLU2 3 PL U2 Schiller-Naumann drag coefficient for bubbles Cp 24 1+0.15Re0.678 Re (Representative Quantity) 100 'Jaoo Beup 10 0,1 0,1 110100100010000 Reynolds number
极限上升速度