
Heat Pumping Processes and Systems Introduction to Thermodynamic analysis Monday June 30th 2014 Trygve M.Eikevik Professor Norwegian University of Science and Technology(NTNU) E-mail;trygve.m.eikevik@ntnu.no http://folk.ntnu.no/tme 职 ONTNU ②SINTEF shrae 2010 ASHRAE HANDE①底 http://www.ashrae.com REFRIGERATION E服证 3pps6i防A8AgR8aaeh 回NTNU SINTEF
1 Heat Pumping Processes and Systems Introduction to Thermodynamic analysis Monday June 30th 2014 Trygve M. Eikevik Professor Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) E-mail; trygve.m.eikevik@ntnu.no http://folk.ntnu.no/tme 2 http://www.ashrae.com/ http://www.ashrae.com
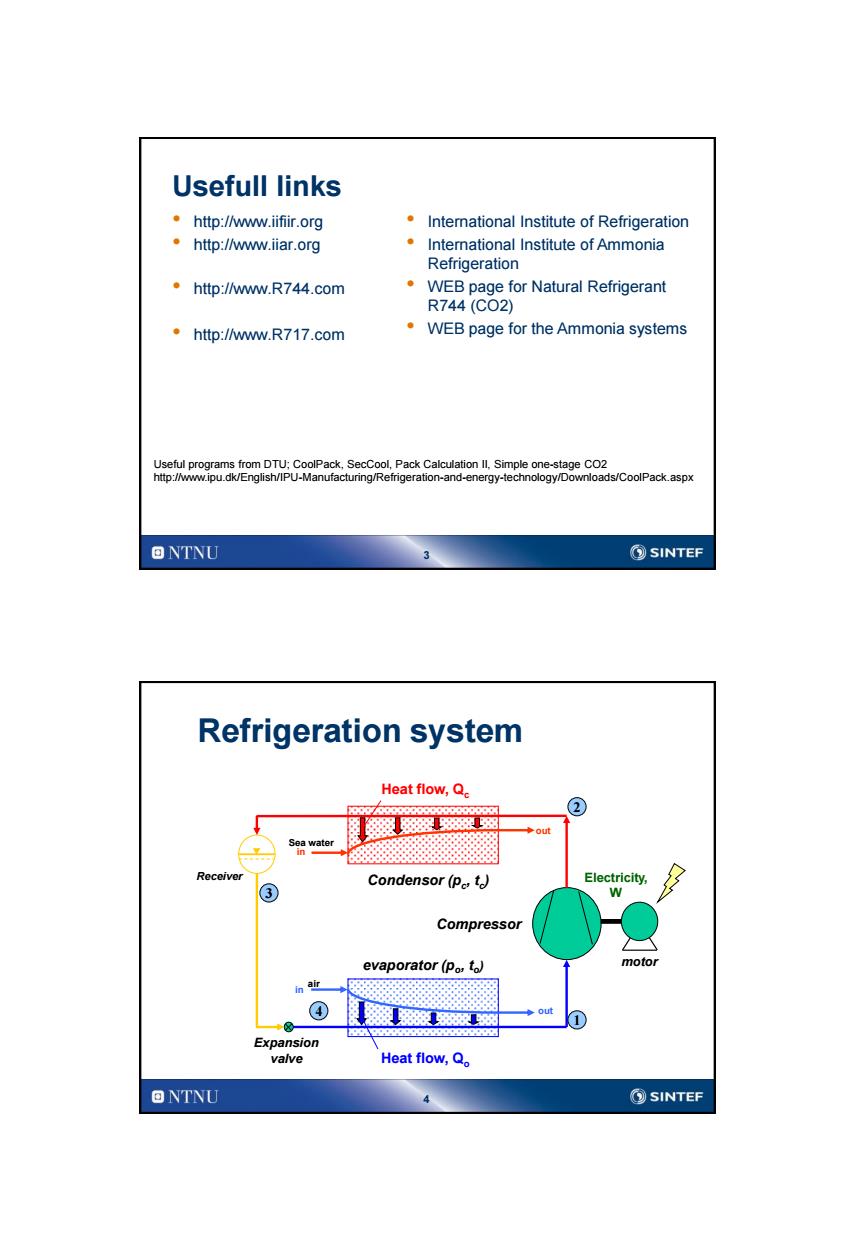
Usefull links ·http:lw.ifir.org International Institute of Refrigeration 。http:lw.iar.org International Institute of Ammonia Refrigeration ·http:lw.R744.com WEB page for Natural Refrigerant R744(CO2) ·htp:/w.R717.com WEB page for the Ammonia systems Useful programs from DTU;CoolPack,SecCool,Pack Calculation Il.Simple one-stage CO2 http://www.ipu.dk/English/IPU-Manufacturing/Refrigeration-and-energy-technology/Downloads/CoolPack.aspx ONTNU ②SINTEF Refrigeration system Heat flow,Q. 级深88避宽 out Soa water Receiver ③ Condensor(Pe,t) Electricity, W Compressor evaporator(po,to) motor in air ◆Out Expansion valve Heat flow,Q。 ONTNU SINTEF
3 Usefull links • http://www.iifiir.org • http://www.iiar.org • http://www.R744.com • http://www.R717.com • International Institute of Refrigeration • International Institute of Ammonia Refrigeration • WEB page for Natural Refrigerant R744 (CO2) • WEB page for the Ammonia systems Useful programs from DTU; CoolPack, SecCool, Pack Calculation II, Simple one-stage CO2 http://www.ipu.dk/English/IPU-Manufacturing/Refrigeration-and-energy-technology/Downloads/CoolPack.aspx 4 air in evaporator (po , to ) Condensor (pc , tc ) in out Sea water Heat flow, Qc Heat flow, Qo Compressor Expansion valve Receiver motor Electricity, W Refrigeration system out 1 4 3 2

Operation based on two important effects 1.The Pressure of the working fluid within the vapor/liquid (two phase)area is decided by the Temperature only. 2.Liquid that evaporates,takes up(absorb)heat, while vapor that condenses,release heat ONTNU ②SINTEF Propane(R290) Gas phase 医 Liquid phase ▣NTNU SINTEF
5 Operation based on two important effects 1.The Pressure of the working fluid within the vapor/liquid (two phase) area is decided by the Temperature only. 2.Liquid that evaporates, takes up (absorb) heat, while vapor that condenses, release heat 6 Propane (R290) Gas phase Liquid phase

Saturation pressure for propane 18 14 Propane saturation pressure 公 (metningstrykk) 10 'oinssold 8 vaeske 6 damp 2 0 40 20 0 20 40 6( Temperature,c ONTNU ②SINTEF Refrigeration systems Temperature-Pressures in the system tamb=+20℃ Pc Condenser Pcmin Pc.tc VExpansion valve Po.to Compressor Pomax Po Evaporator Q 4030-20-10010203040 tR=-20℃ Saturation temperature,taC] ONTNU ⑤SINTEF
7 Saturation pressure for propane 8 Refrigeration systems Temperature – Pressures in the system Condenser Evaporator pC , tC p0 , t0 𝑄 0 𝑄 𝐶 tR= -20 oC tamb= +20oC 𝑊 𝐶 Pressure, p [bar] -30 -20 -10 0 p0max Saturation temperature, tsat [ oC] -40 10 20 30 40 p0 pCmin pC Expansion valve Compressor

Working fluids Important properties of working fluids in heat pumps R404AR407C R410AR134a R7171 R2902 R7443 Molar weight 97,6 86,2 72.6 102,2 17,03 44,10 44,01 Boiling point, -46,5 43,8 -51.6 -26,2 -33,3 -42,1 -78,03 1 bar [C] Crit.temp.te[C] 74.4 87,3 72.5 101,1 132,3 96,8 31,1 Crit.Press.Pe[bar] 37,3 46,3 49,5 40.7 113,3 42,5 73.8 Paat,OC [bar] 6,0 5,7 8,0 2,9 4,3 4,8 34,9 △h.0C[kJ/kg] 169 209 221 199 1262 375 231 pn0℃[kgml 1114 1237 1171 1295 639 493 928 Pg,0℃[kg1m 30 20 31 14 4 10 98 t,5,25 bar [C] 55 60 534 77 58 68 GWP[ 3800 1700 2000 1300 0 3 0(1) Poison/flammable No No No No Yes/No No/Yes No 1)Ammonia(NHa) 2)Propane (C3Ha) 3)Carbon dioxside (CO2) 4)35 bar 5)Condensing temperature ONTNU ②SINTEF Working fluids-properties Example 2-Saturation curve for ammonia(NHa) 120 Critical point 夏w (132,2℃113,3a Linear axis- 80 60 uopeines (78.5*C,40 bar) 40 62℃,25am 20 NBP 633,3C,1013ba 0 -60 30 030 60 90 120 150 Saturation temperature,t [C] 回NTNU 10 ⑤SINTEF
9 Working fluids Important properties of working fluids in heat pumps R404A R407C R410A R134a R7171 R2902 R7443 Molar weight 97,6 86,2 72,6 102,2 17,03 44,10 44,01 Boiling point, 1 bar [°C] -46,5 -43,8 -51,6 -26,2 -33,3 -42,1 -78,03 Crit. temp. tc [°C] 74,4 87,3 72,5 101,1 132,3 96,8 31,1 Crit. Press. pc [bar] 37,3 46,3 49,5 40,7 113,3 42,5 73,8 psat, 0°C [bar] 6,0 5,7 8,0 2,9 4,3 4,8 34,9 Dhf , 0°C [kJ/kg] 169 209 221 199 1262 375 231 rv , 0°C [kg/m3 ] 1114 1237 1171 1295 639 493 928 rg , 0°C [kg/m3 ] 30 20 31 14 4 10 98 tk 5 , 25 bar [°C] 55 60 534 77 58 68 * GWP [-] 3800 1700 2000 1300 0 3 0 (1) Poison/flammable No No No No Yes/No No/Yes No 1) Ammonia (NH3 ) 2) Propane (C3H8 ) 3) Carbon dioxside (CO2 ) 4) 35 bar 5) Condensing temperature 10 Working fluids – properties Example 2 – Saturation curve for ammonia (NH3 ) Linear axis Saturation temperature, t [oC] Saturation pressure, p [bar] Critical point