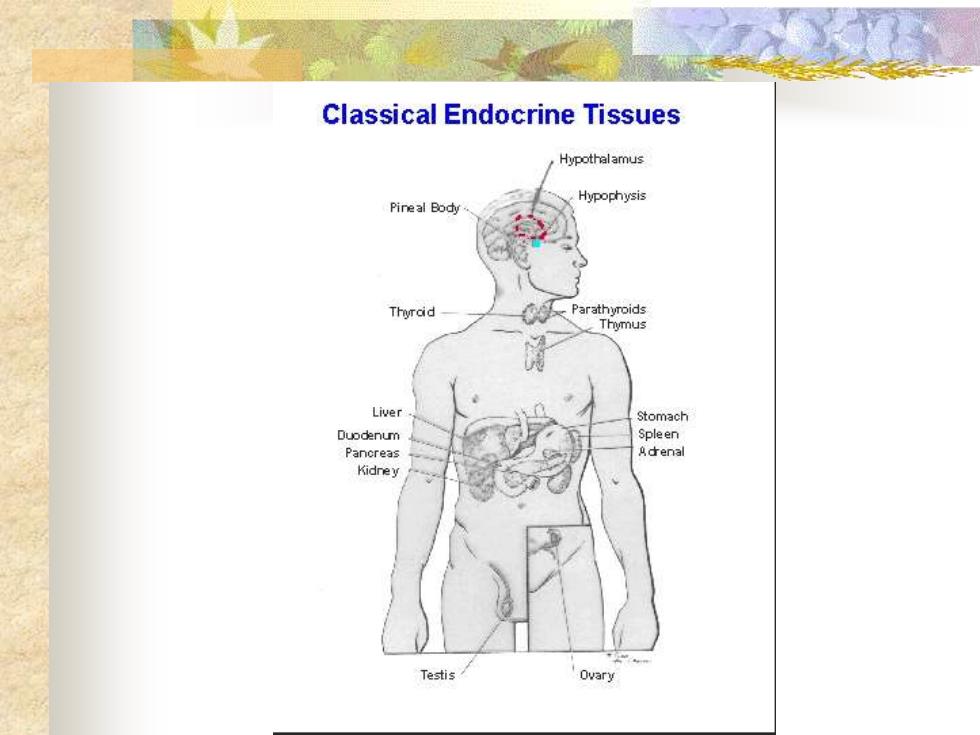
Classical Endocrine TissuesHypothalamusPineal BodyParathuroidThyraiciuerStomachDuodenumSpleenAdrenalPancreasKidreOua

Introduction to the Endocrine SystemThe term ‘hormone'(from the Greek verb ‘hormoa', to excite)1905, E.H. Starling, first defined‘the chemical messengers which,speedingfromcellto cell alongthe blood stream,may coordinatethe activities and growth of different parts of thebody
Introduction to the Endocrine System The term ‘hormone’ (from the Greek verb ‘hormoa’, to excite) 1905, E.H. Starling, first defined ‘the chemical messengers which, speeding from cell to cell along the blood stream, may coordinate the activities and growth of different parts of the body’
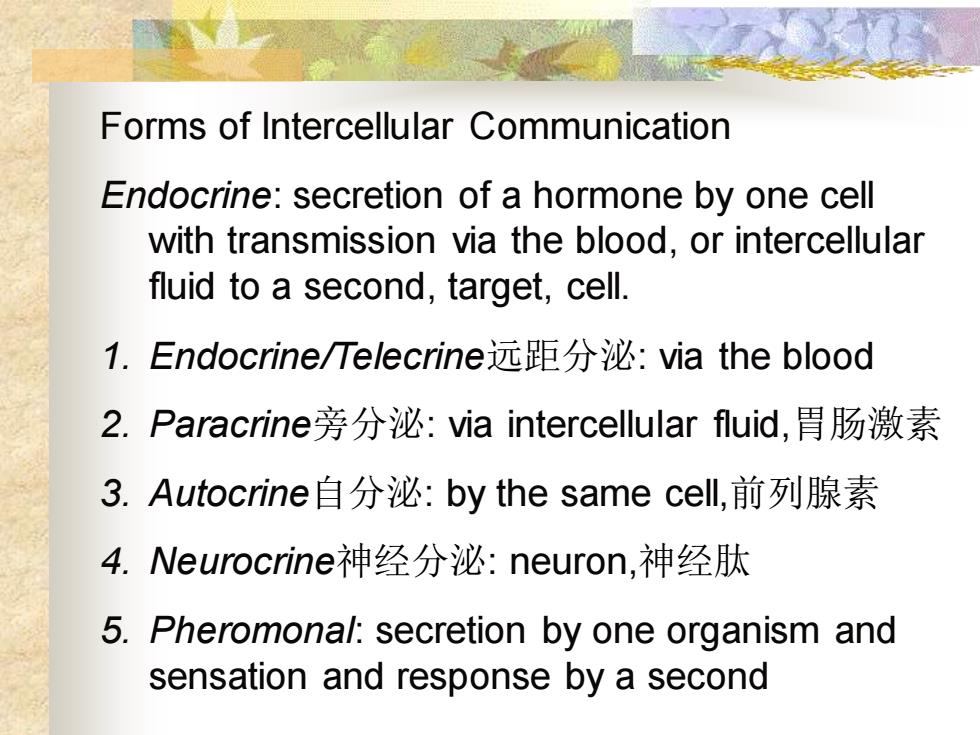
Forms of Intercellular CommunicationEndocrine: secretion of a hormone by one cellwith transmission via the blood, or intercellularfluid to a second, target, cell.1.Endocrine/Telecrine远距分泌:viatheblood2.Paracrine旁分泌:viaintercellularfluid,胃肠激素3.Autocrine自分泌:bythesamecell.前列腺素4.Neurocrine神经分泌:neuron,神经肽5. Pheromonal: secretion by one organism andsensation andresponse bya second
Forms of Intercellular Communication Endocrine: secretion of a hormone by one cell with transmission via the blood, or intercellular fluid to a second, target, cell. 1. Endocrine/Telecrine远距分泌: via the blood 2. Paracrine旁分泌: via intercellular fluid,胃肠激素 3. Autocrine自分泌: by the same cell,前列腺素 4. Neurocrine神经分泌: neuron,神经肽 5. Pheromonal: secretion by one organism and sensation and response by a second
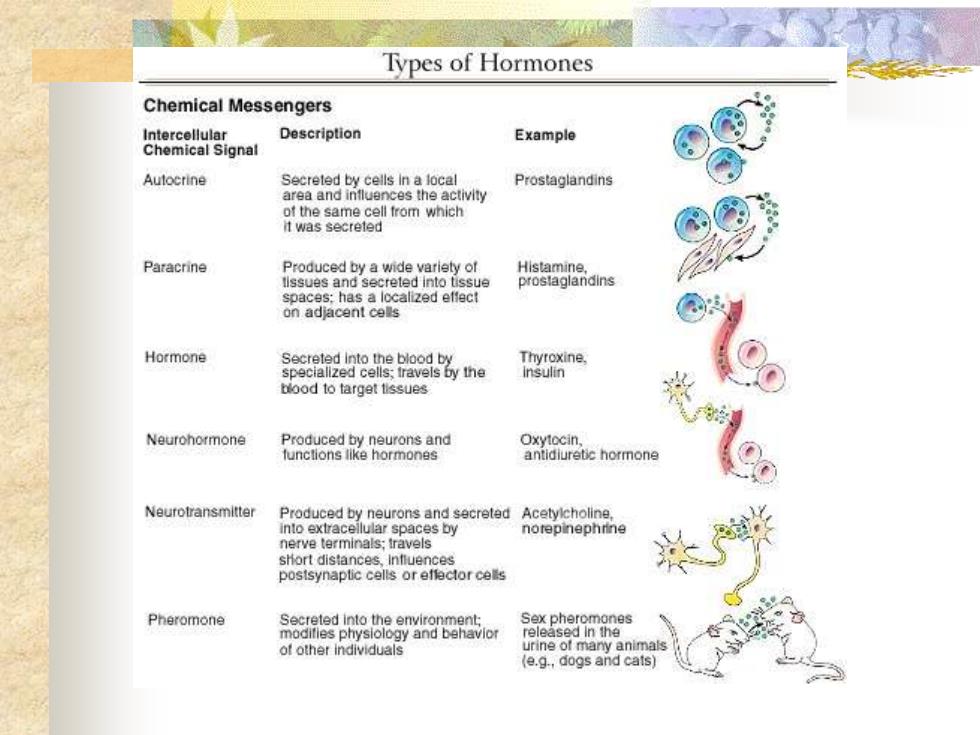
Types of HormonesChemical MessengersDescriptionIntercellularExampleChemical SignalAutocrineSecreted by cells InalocalProstaglandinsareaandintluencestheactivityofthesamecell tromwhichitwassecretedParacrineHistaminProducedbyawidevarietyofprostaglandinslissuesandseratadintotspaces:hasalocalizedetleconadjacentcellsHormoneSecreted intothebloodtThyroxine,cializedcells.fraveinsulinblood to target tissuesOxytocirNeurohormoneProducedbyneuronsandantidiuretic hormonefunclionslikehormonesNeurotransmitterProduced by neurons and secreted Acetyicholinenloextracnotepinephrinlarspacesbynerveterminals:travelsshort.distanceslntluencespostsynaptic cells oreflectorcelsPheromoneSexpheroSecreted intothe emvironmentronesmoditiesphysiologyandbehavioreleasedintheurineofmaanimaot other individuals(e.g.,dogs and cats)

Characteristics of hormoneA hormone is a chemical messenger that is:. Secreted into body fluids (usually the blood)by specialized cells, e.g endocrine ornerve cells·Effective in minute amounts· Detected only by "target" cells possessingspecial protein receptors on cell membranes.Often regulated by a second antagonistic hormone
Characteristics of hormone A hormone is a chemical messenger that is: • Secreted into body fluids (usually the blood) by specialized cells, e.g endocrine or nerve cells • Effective in minute amounts • Detected only by "target" cells possessing special protein receptors on cell membranes • Often regulated by a second antagonistic hormone