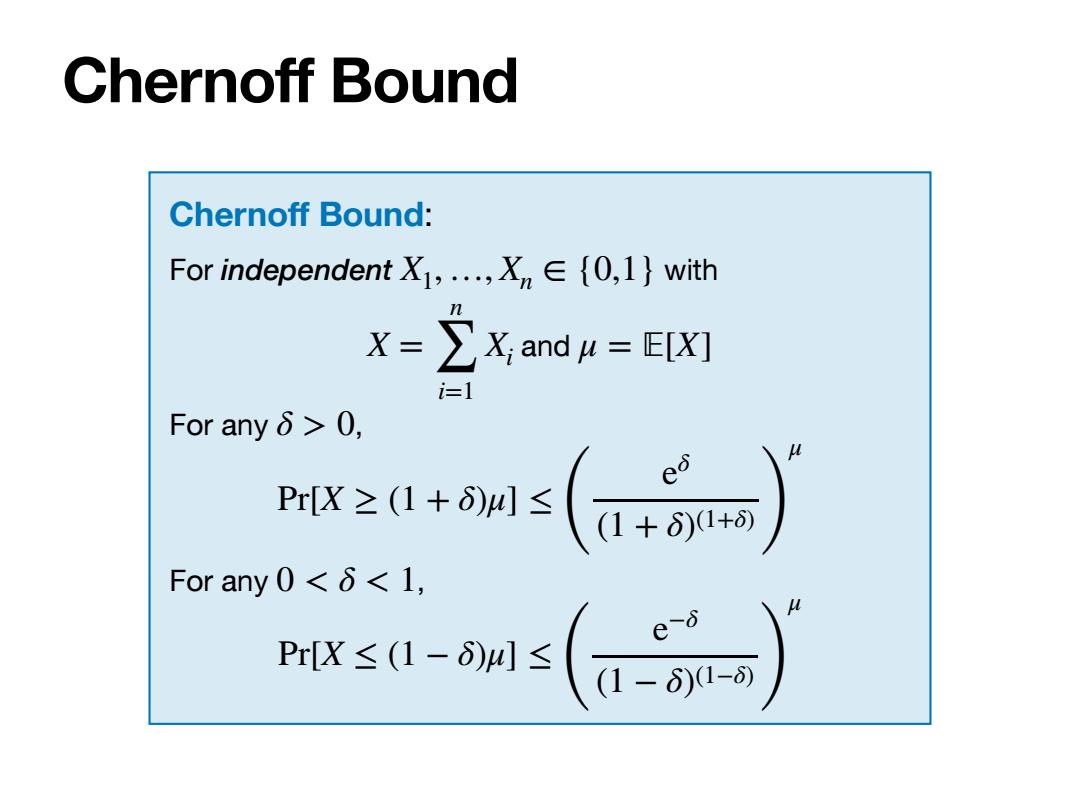
Chernoff Bound Chernoff Bound: For independent X,,Xn∈{0,l}with X=∑X,andu=E[X灯 i=1 For anyδ>0, e1os(可) For any 0<<1, Hirs0-(a-苏可》
Chernoff Bound Chernoff Bound: For independent with and For any , For any , X1, …, Xn ∈ {0,1} X = n ∑ i=1 Xi μ = 피[X] δ > 0 Pr[X ≥ (1 + δ)μ] ≤ ( eδ (1 + δ)(1+δ) ) μ 0 < δ < 1 Pr[X ≤ (1 − δ)μ] ≤ ( e−δ (1 − δ)(1−δ) ) μ
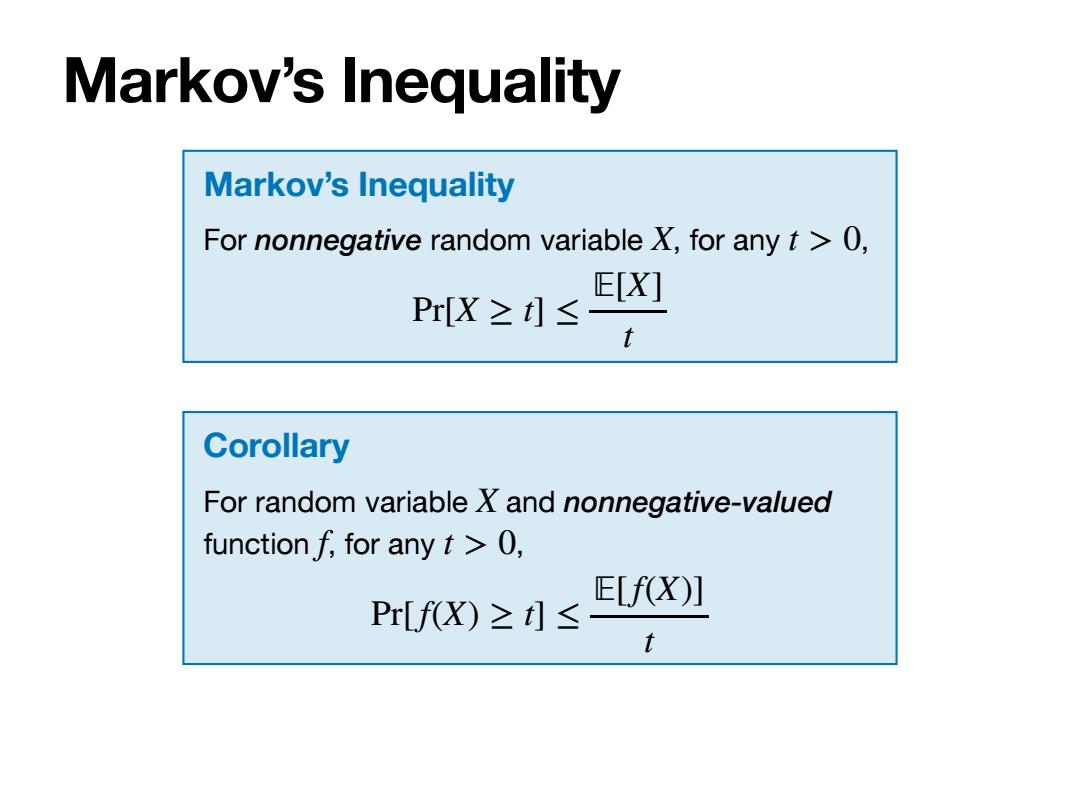
Markov's Inequality Markov's Inequality For nonnegative random variable X,for any t >0, E[X] Pr[X≥t]≤ t Corollary For random variable X and nonnegative-valued function f,for any t >0, E[f(X)] Pr[fX)≥t]≤ t
Markov’s Inequality Markov’s Inequality For nonnegative random variable , for any , X t > 0 Pr[X ≥ t] ≤ 피[X] t Corollary For random variable and nonnegative-valued function , for any , X f t > 0 Pr[f(X) ≥ t] ≤ 피[f(X)] t
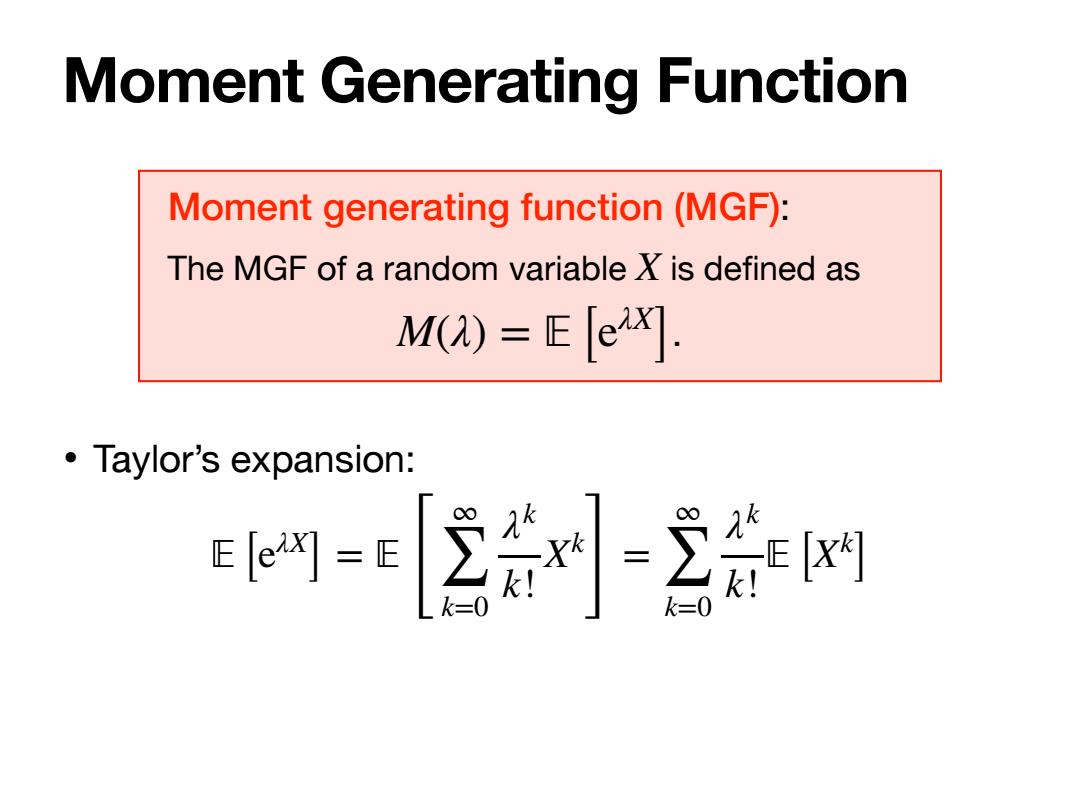
Moment Generating Function Moment generating function(MGF): The MGF of a random variable X is defined as M()=E x. 。Taylor's expansion: k=0
Moment Generating Function Moment generating function (MGF): The MGF of a random variable is defined as . X M(λ) = 피 [eλX ] • Taylor’s expansion: 피 [eλX ] = 피 [ ∞ ∑ k=0 λk k! Xk ] = ∞ ∑ k=0 λk k! 피 [Xk ]
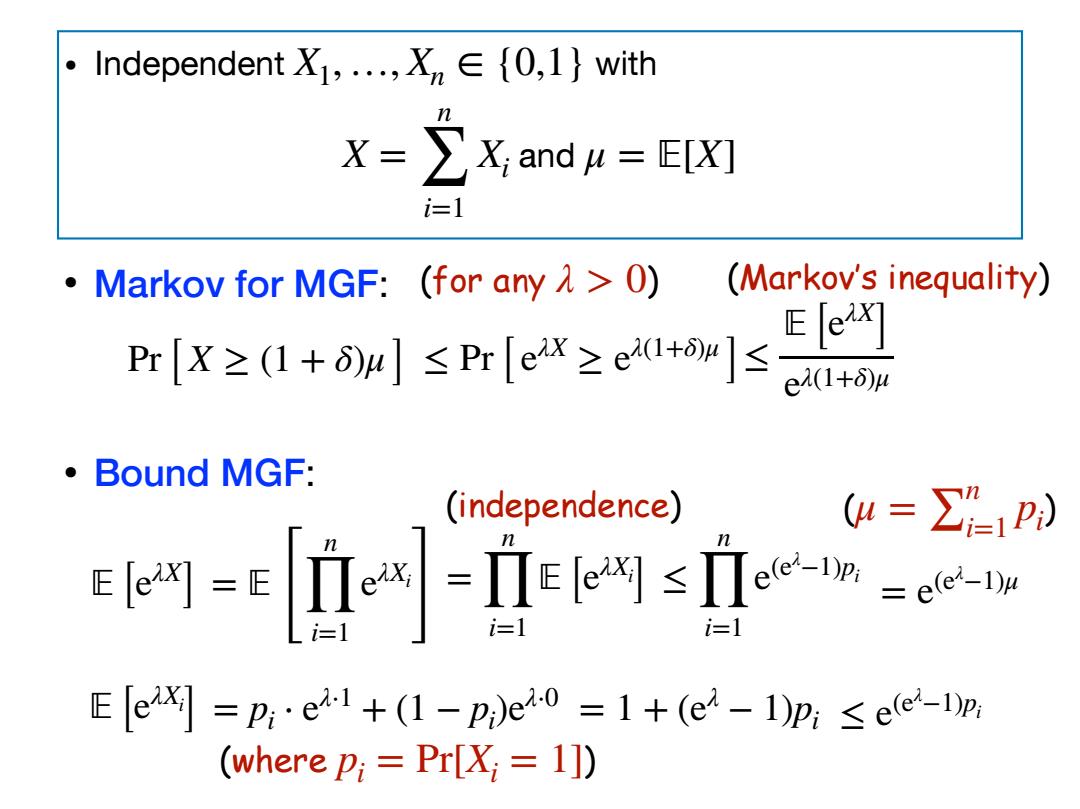
·Independent X1,.,Xn∈{0,l}with X=∑X,andu=E[X灯 =1 Markov for MGF:(for any 0) (Markov's inequality) K生+wlsrre ·Bound MGF: (independence) =∑=1P) -TEs i=1 =1 E eix=p:.e1+(1-pi)e0 =1+(e4-1)p:<ele-Dp. (where pi=Pr[X;1])
• Markov for MGF: • Bound MGF: ≤ Pr[ eλX ≥ eλ(1+δ)μ ] • Independent with and X1,…, Xn ∈ {0,1} X = n ∑ i=1 Xi μ = 피[X] Pr[ X ≥ (1 + δ)μ ] (for any λ > 0) ≤ 피 [eλX ] eλ(1+δ)μ (Markov’s inequality) 피 [eλX ] = 피 [ n ∏ i=1 eλXi ] = n ∏ i=1 피 [eλXi ] (independence) (μ = ∑ ) n i=1 pi ≤ n ∏ i=1 e(eλ −1)pi = e(eλ −1)μ 피 [eλXi ] = pi ⋅ eλ⋅1 + (1 − pi )eλ⋅0 (where p ) i = Pr[Xi = 1] = 1 + (eλ − 1)pi ≤ e(eλ −1)pi
Independent X1,,Xn∈{0,l}with X-∑;and=E[X] =1 ·Markov for MGF: (for any 1>0) Pr「X>11,11< Ee的 0.2 5)u *ou-(a+gw) 0.1 (when=ln(1+δ) 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.81.0 12 1.4 -0.11 =∏eey≤ee-1m -0.2 i=1 -0.3 Optimization: (e-1-(1+δ)achieves Min at stationary point.元=ln(1+δ)
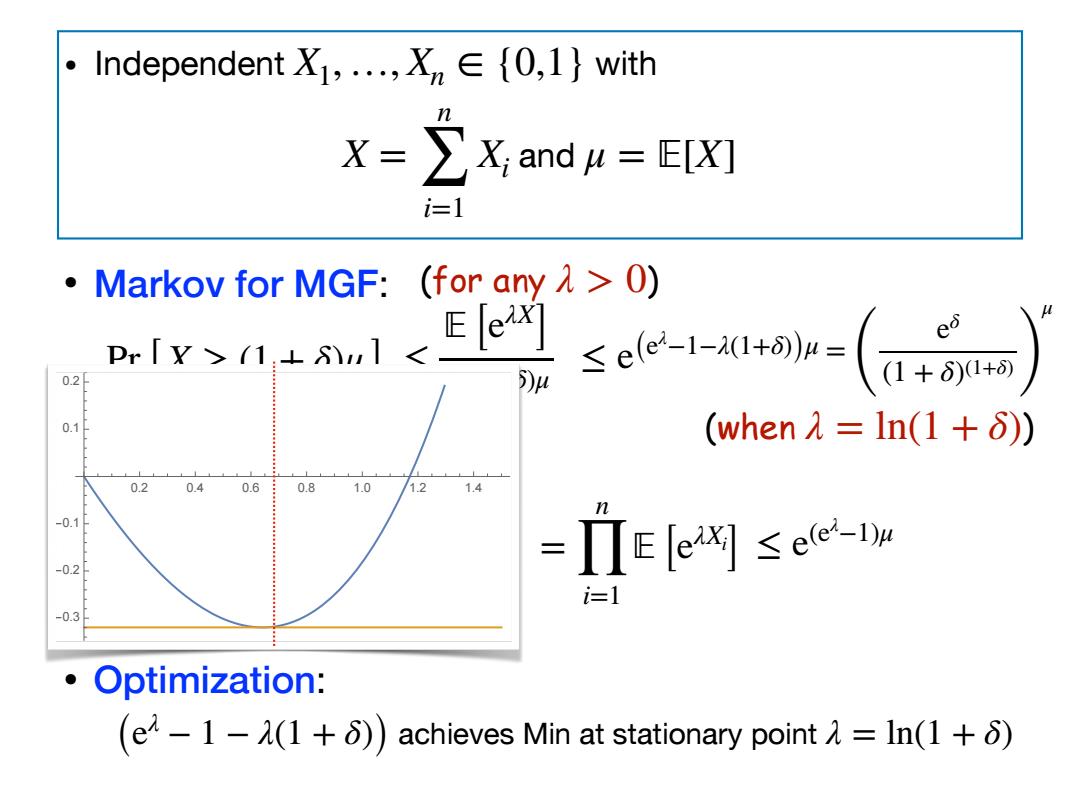
• Markov for MGF: • Bound MGF: • Independent with and X1,…, Xn ∈ {0,1} X = n ∑ i=1 Xi μ = 피[X] Pr[ X ≥ (1 + δ)μ ] (for any λ > 0) ≤ 피 [eλX ] eλ(1+δ)μ 피 [eλX ] = 피 [ n ∏ i=1 eλXi ] = n ∏ i=1 피 [eλXi ] ≤ e(eλ −1)μ ≤ e(eλ −1−λ(1+δ))μ • Optimization: (e achieves Min at stationary point λ − 1 − λ(1 + δ)) λ = ln(1 + δ) = ( eδ (1 + δ)(1+δ) ) μ (when λ = ln(1 + δ)) 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 -0.3 -0.2 -0.1 0.1 0.2