
3 Inert electrodes shall be used if no conductive ones are available,normally Pt,Au are used 4 Pure liquid,solid or gas are next to the inert electrodes seperated by the symbol“I”,“,”,or (inert electrode) e.g.(Pt|H2(g)H+ HH2(g)Pt(+) (Pt,H2(g)H or:H+H2(g),Pt (+ ()(Pt)H2(g)H or:HH2(g)(Pt)(+) Negative electrode side Positive electrode side
③ Inert electrodes shall be used if no conductive ones are available, normally Pt, Au are used. ④ Pure liquid, solid or gas are next to the inert electrodes seperated by the symbol ―︱‖ , ―,‖, or (inert electrode). H+ H2 (g) Pt (+) or:H+ |H2 (g), Pt (+) or: H+ | H2 (g) (Pt) (+) Positive electrode side e.g. (-) Pt H2 (g) H+ (-) Pt, H2 (g)H+ (-) (Pt) H2 (g) H+ Negative electrode side

Example:An electrochemical cell has been assembled with the following net reaction.Please write out the cell diagram. 2Fe2+(1.0molL)+CL,(101325P →2Fe+(0.1molL)+2CI(2.0molL) Answer: (+)C12(g)+2e→2C1(aq) (-) Fe2*(aq)-e--Fe3*(aq) (Pt,Fe2+(1.0mol-L-1),Fe3+(0.1mol-L-1)ll CI (2.0molL)|C2(101325Pa),Pt(+) Or:()Pt Fe2+(1.0mol-L-1),Fe3+(0.1mol-L-1)l Cl (2.0mol-L-)Cl2(100 kPa)Pt (+
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 3 1 1 2 2 1 2Fe 0.1mol L 2Cl 2.0mol L 2Fe 1.0mol L Cl 101325Pa + + + + Example: An electrochemical cell has been assembled with the following net reaction. Please write out the cell diagram. Answer: (+) Cl (g) 2e 2Cl (aq) 2 + (- ) Fe (aq) e Fe (aq) 2+ 3+ (-) Pt, Fe2+(1.0mol·L-1 ), Fe3+ (0.1mol·L-1 )‖ Cl- (2.0mol·L-1 ) ︱Cl2 (101325Pa), Pt (+) Or: (-) Pt︱Fe2+(1.0mol·L-1 ), Fe3+ (0.1mol·L-1 )‖ Cl- (2.0mol·L-1 ) ︱Cl2 (100 kPa) | Pt (+)
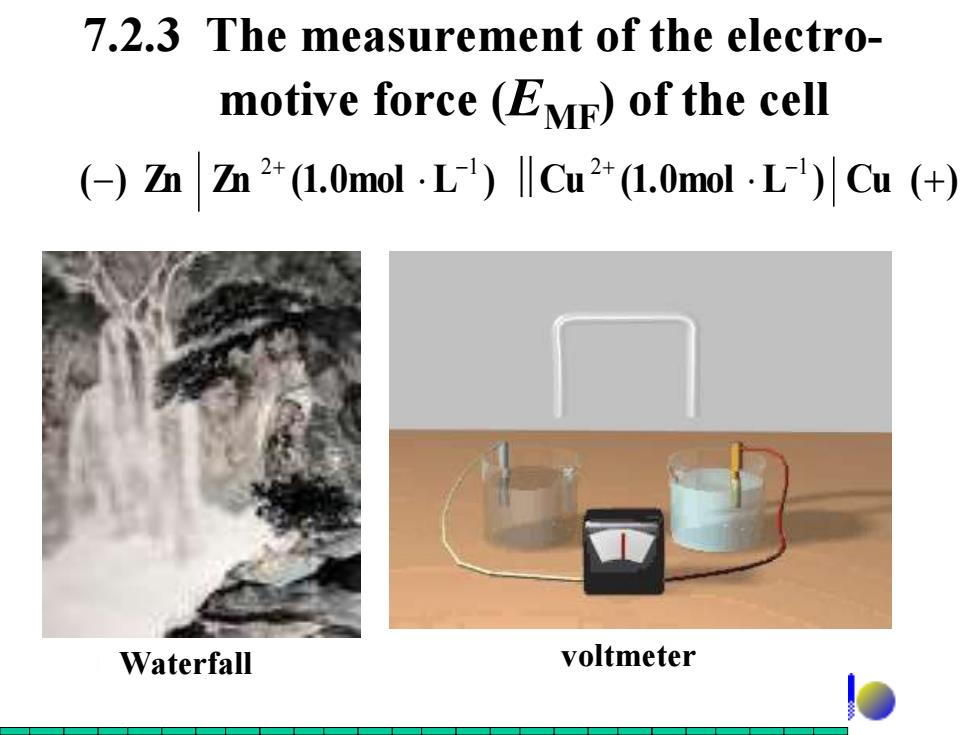
7.2.3 The measurement of the electro- motive force (EME)of the cell (-)m2+(1.0mol.L)lCu2+(1.0mol.L)Cu(+) Waterfall voltmeter
7.2.3 The measurement of the electro- motive force (EMF) of the cell () Zn Zn (1.0mol L ) Cu (1.0mol L ) Cu (+) 2+ 1 ‖ 2+ 1 Waterfall voltmeter
(-)Zn2+(1.0molL)Cu2+(1.0mol.L)Cu(+) EMF-electromotive force of the cell(the difference in electrical potential between the anode and the cathode when there is no electric current),which can be measured by a voltmeter(伏特计). Standard condition: If the concentrations of ions (e.g.:H+,Zn2+,Fe(CN)3-)are 1.0 M,RESPECTIVELY,and the pressure of gas (e.g.:H2, Cl2)is 100 kPa,The conditions specified above are called the standard conditions
EMF — electromotive force of the cell (the difference in electrical potential between the anode and the cathode when there is no electric current), which can be measured by a voltmeter(伏特计). () Zn Zn (1.0mol L ) Cu (1.0mol L ) Cu (+) 2+ 1 ‖ 2+ 1 Standard condition: If the concentrations of ions (e.g.: H+ , Zn2+, Fe(CN)6 3- ) are 1.0 M, RESPECTIVELY, and the pressure of gas (e.g.: H2 , Cl2 ) is 100 kPa, The conditions specified above are called the standard conditions

EMr-standard electromotive force. the voltage difference EMr between the two electrodes which are under standard conditions. For example,the Cu/Zn cell at standard conditions will deliver 1.10V,i.e.,EMr=1.10V
EMF standard electromotive force. the voltage difference EMF between the two electrodes which are under standard conditions. For example, the Cu/Zn cell at standard conditions will deliver 1.10V, i.e., EMF = 1.10V