
Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 19 Aldehydes and Ketones
Chapter 19 Aldehydes and Ketones Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

自成不精大好 Content 院 Carbonyl Structure Properties Preparation >Functional group transformations >Carbon-carbon bond formation >C-C Bond cleavage Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones ●C=O ●o-H,-C
Content Carbonyl Structure & Properties Preparation Functional group transformations Carbon-carbon bond formation C-C Bond cleavage Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones C=O -H, - C
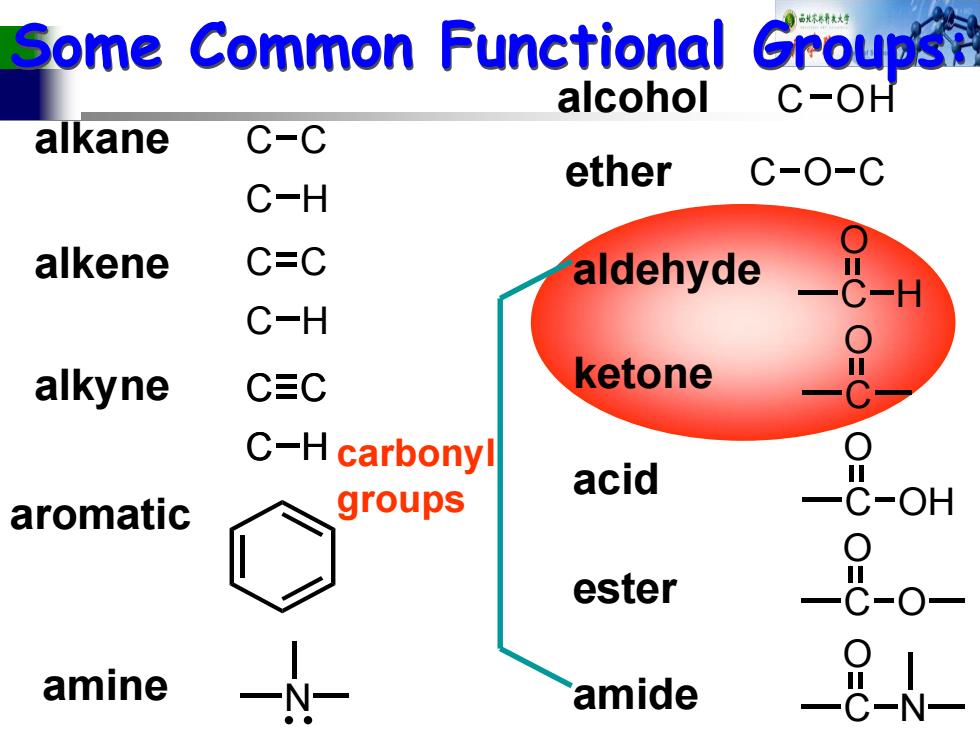
Some Common Functional Groups alcohol C-OH alkane C-C ether C-O-C C-H alkene C=C aldehyde C-H alkyne CEC ketone C-H carbonyl acid aromatic groups OH ester amine amide
Some Common Functional Groups: Some Common Functional Groups: C C C H alkane alkene C C C H alkyne C C C H aromatic alcohol C OH ether COC C O H aldehyde C O ketone C O OH acid C O ester O C O N amide N amine carbonyl groups
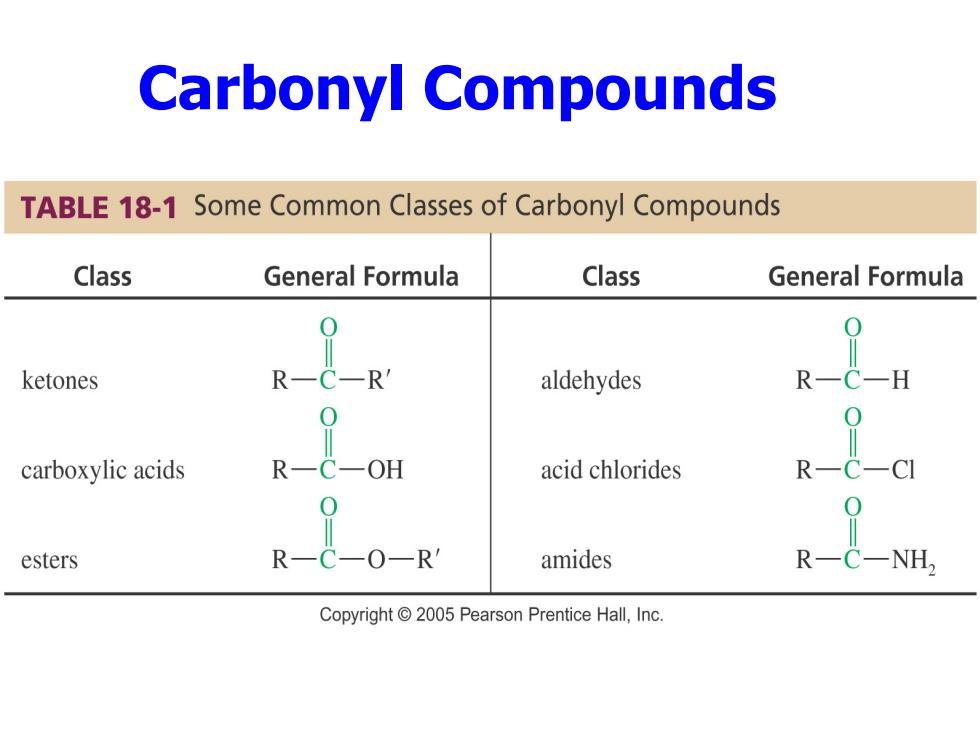
Carbonyl Compounds TABLE 18-1 Some Common Classes of Carbonyl Compounds Class General Formula Class General Formula ketones R R aldehydes R carboxylic acids OH acid chlorides esters -OR amides Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Carbonyl Compounds
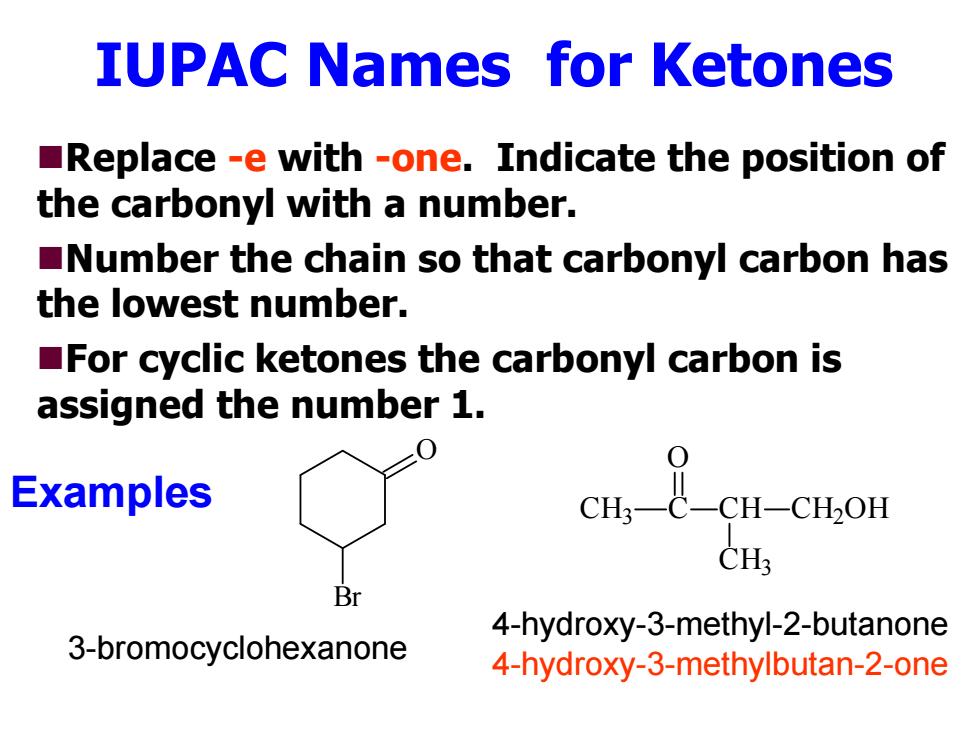
IUPAC Names for Ketones Replace -e with -one.Indicate the position of the carbonyl with a number. Number the chain so that carbonyl carbon has the lowest number. For cyclic ketones the carbonyl carbon is assigned the number 1. Examples CH: Br 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-butanone 3-bromocyclohexanone 4-hydroxy-3-methylbutan-2-one
IUPAC Names for Ketones Replace -e with -one. Indicate the position of the carbonyl with a number. Number the chain so that carbonyl carbon has the lowest number. For cyclic ketones the carbonyl carbon is assigned the number 1. O Br CH 3 C O CH CH 3 CH 2OH 3-bromocyclohexanone 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-butanone 4-hydroxy-3-methylbutan-2-one Examples