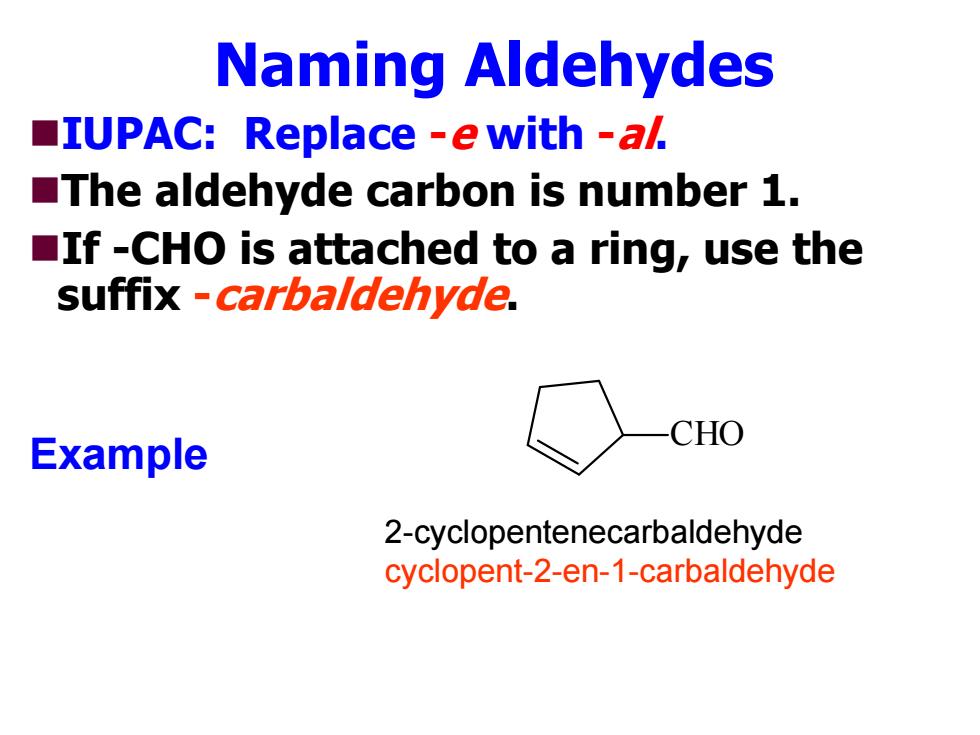
Naming Aldehydes IUPAC:Replace -e with -al The aldehyde carbon is number 1. If -CHO is attached to a ring,use the suffix -carbaldehyde. CHO Example 2-cyclopentenecarbaldehyde cyclopent-2-en-1-carbaldehyde
Naming Aldehydes IUPAC: Replace - e with -al. The aldehyde carbon is number 1. If -CHO is attached to a ring, use the suffix -carbaldehyde. Example CHO 2-cyclopentenecarbaldehyde cyclopent-2-en-1-carbaldehyde
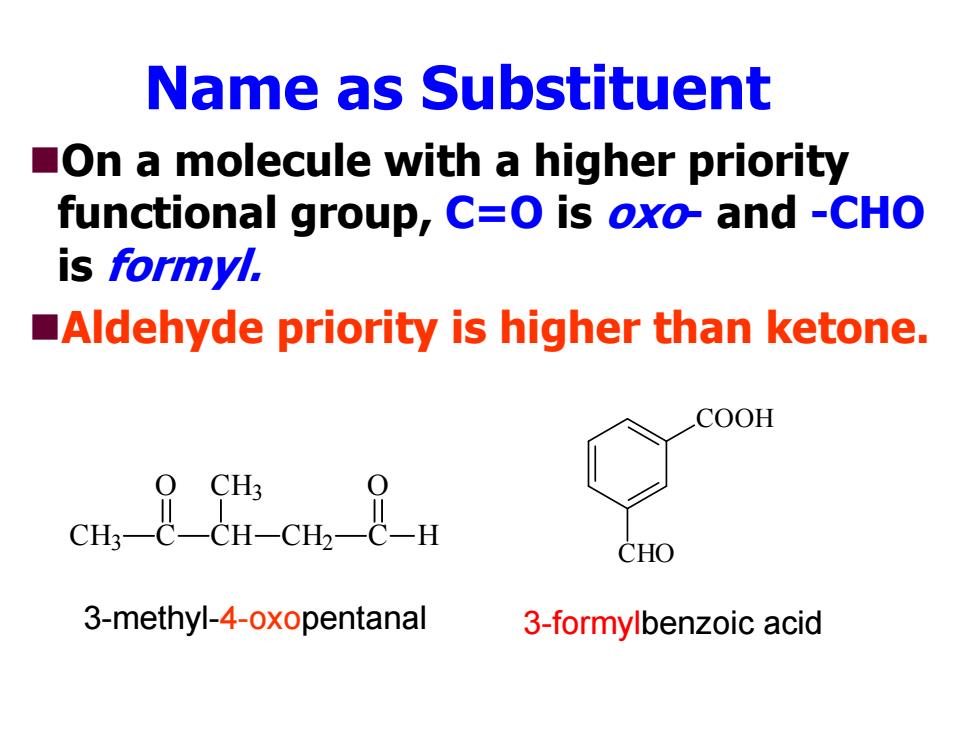
Name as Substituent On a molecule with a higher priority functional group,C=O is oxo-and -CHO is formyl. Aldehyde priority is higher than ketone. COOH CHO 3-methyl-4-oxopentanal 3-formylbenzoic acid
Name as Substituent On a molecule with a higher priority functional group, C=O is oxo- and -CHO is formyl. Aldehyde priority is higher than ketone. CH 3 C CH CH 3 CH 2 C H O O COOH CHO 3-methyl-4-oxopentanal 3-formylbenzoic acid
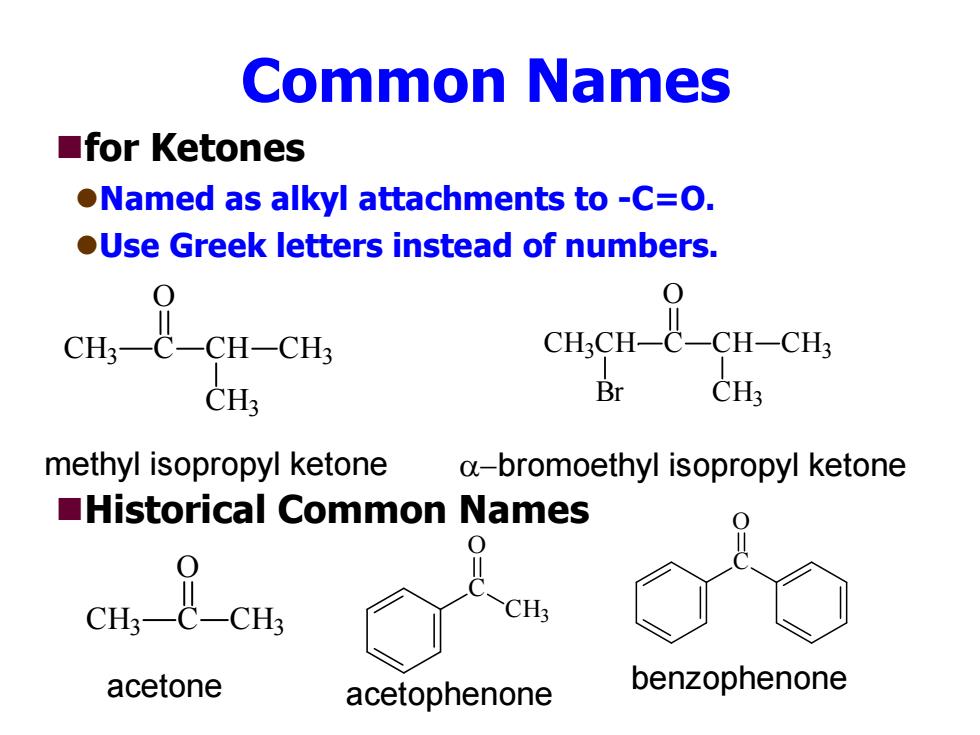
Common Names ■for Ketones Named as alkyl attachments to -C=O. OUse Greek letters instead of numbers. 0 0 CH3一C一CH-CH3 CH;CH-C-CH-CH3 CH3 Br CH: methyl isopropyl ketone a-bromoethyl isopropyl ketone Historical Common Names CH; acetone acetophenone benzophenone
Common Names for Ketones Named as alkyl attachments to -C=O. Use Greek letters instead of numbers. Historical Common Names CH 3 C O CH CH 3 CH 3 CH 3CH C O CH CH 3 CH 3 Br methyl isopropyl ketone bromoethyl isopropyl ketone CH 3 C O CH 3 C CH 3 O C O acetone acetophenone benzophenone

Aldehyde Common Names Use the common name of the acid. Drop -ic acid and add -aldehyde. 1 C:formic acid,formaldehyde 2 C's:acetic acid,acetaldehyde 3 C's:propionic acid,propionaldehyde 4 C's:butyric acid,butyraldehyde. Br B-bromobutyraldehyde 3-bromobutanal
Aldehyde Common Names Use the common name of the acid. Drop -ic acid and add -aldehyde. 1 C: formic acid, formaldehyde 2 C’s: acetic acid, acetaldehyde 3 C’s: propionic acid, propionaldehyde 4 C’s: butyric acid, butyraldehyde. CH 3 CH Br CH 2 C H O -bromobutyraldehyde 3-bromobutanal
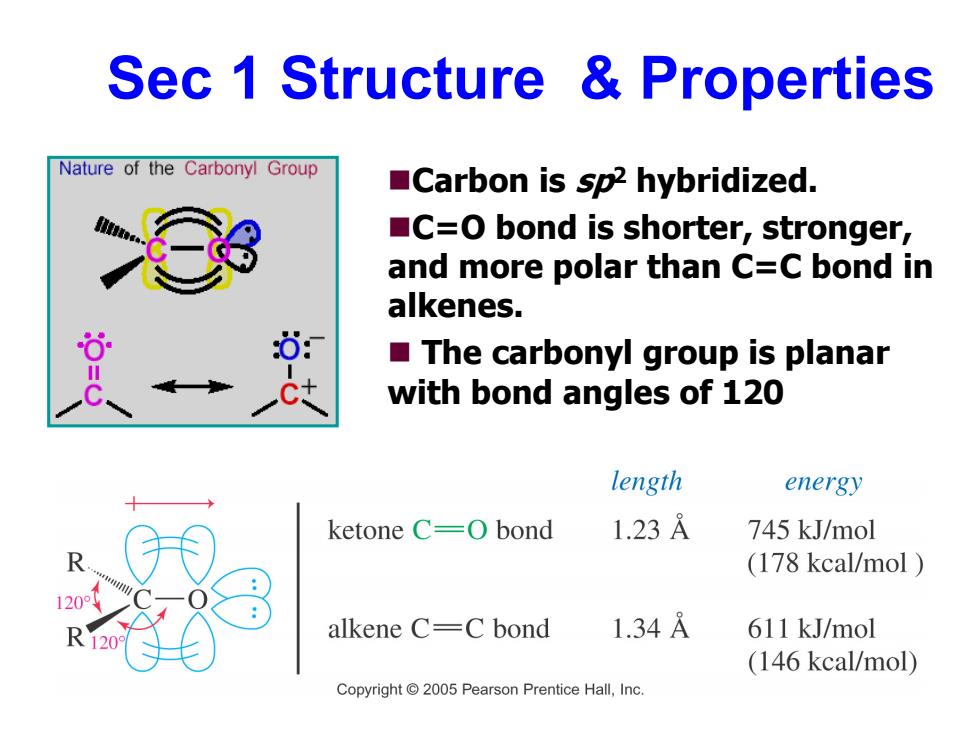
Sec 1 Structure Properties Nature of the Carbonyl Group Carbon is sp2 hybridized. C=O bond is shorter,stronger, and more polar than C=C bond in alkenes. The carbonyl group is planar with bond angles of 120 length energy ketone C=0 bond 1.23A 745 kJ/mol (178 kcal/mol alkene C=C bond 1.34A 611 kJ/mol (146 kcal/mol) Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Sec 1 Structure & Properties Carbon is sp2 hybridized. C=O bond is shorter, stronger, and more polar than C=C bond in alkenes. The carbonyl group is planar with bond angles of 120