
自秋转大材 Organic Chemistry,6h Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 7 AlRylHalides:Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Key Notes Nucleophilic Substitution,SN1/SN2,Elimination (E1/E2) Nucleophilicity,Leaving group By Junru Wang Email:wangjr07@163.com
By Junru Wang Email: wangjr07@163.com Chapter 7 Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Organic Chemistry, 6h Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Key Notes Nucleophilic Substitution, SN1/SN2, Elimination(E1/E2) Nucleophilicity, Leaving group
0诚钛对 Content 教华魔 Preparation and physical properties Nucleophilic substitution Factorsaffecting SN2 versus SN1 reactions ☐Elimination Elimination versus substitution Reactions of alkyl halides Organometallic reactions
Content ◼Preparation and physical properties ◼Nucleophilic substitution ◼Factors affecting SN2 versus SN1 reactions ◼Elimination ◼Elimination versus substitution ◼Reactions of alkyl halides ◼Organometallic reactions
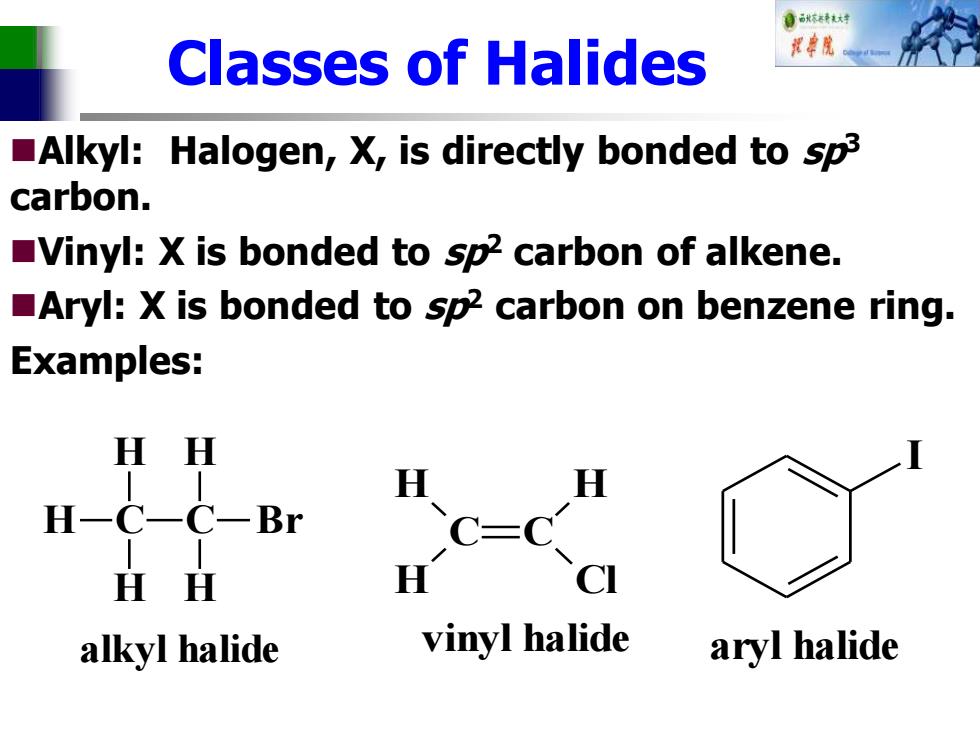
自标不有花大时 Classes of Halides Alkyl:Halogen,X,is directly bonded to sp3 carbon. Vinyl:X is bonded to sp2 carbon of alkene. Aryl:X is bonded to sp2 carbon on benzene ring. Examples: H H H H-C-C-Br .c-c H H C alkyl halide vinyl halide aryl halide
Classes of Halides ◼Alkyl: Halogen, X, is directly bonded to sp3 carbon. ◼Vinyl: X is bonded to sp2 carbon of alkene. ◼Aryl: X is bonded to sp2 carbon on benzene ring. Examples: C H H H C H H Br alkyl halide C C H H H Cl vinyl halide I aryl halide

自转达对 Classes of Alkyl Halides Methyl halides:only one C,CHaX Primary:C to which X is bonded has only one C-C bond. Secondary:C to which X is bonded has two C-C bonds. Tertiary:C to which X is bonded has three C-C bonds
Classes of Alkyl Halides ◼Methyl halides: only one C, CH3X ◼Primary: C to which X is bonded has only one C-C bond. ◼Secondary: C to which X is bonded has two C-C bonds. ◼Tertiary: C to which X is bonded has three C-C bonds
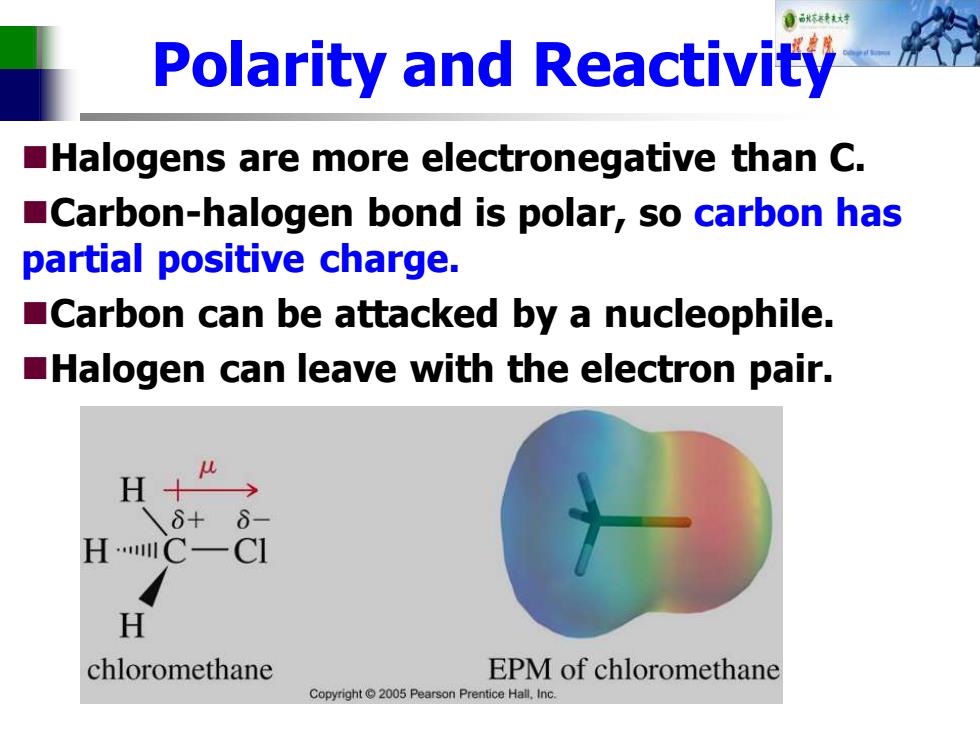
Polarity and Reactivity Halogens are more electronegative than C. Carbon-halogen bond is polar,so carbon has partial positive charge. Carbon can be attacked by a nucleophile. Halogen can leave with the electron pair. H+ 6+ HC一CI H chloromethane EPM of chloromethane Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc
Polarity and Reactivity ◼Halogens are more electronegative than C. ◼Carbon-halogen bond is polar, so carbon has partial positive charge. ◼Carbon can be attacked by a nucleophile. ◼Halogen can leave with the electron pair