糖尿病的病理生理学 THE LANCET Sap:耗竭 Search for in All Fields GO Advance Home Journals Specialties I Clinical I Global Health Audio I Conferences Information for He The Lancet,Volume 379,Issue 9833,Pages 2227-2228,16 June 2012 Previous Article I Next Artide doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60963-5?Cite0 r Link Using D0l Diabetes saps health and wealth from China's rise Ted Alcorn,Yadan Ouyang Rapid economic change in China is propelling a wave of diabetes that health professionals and the public and are only beginning to wake up to.Ted Alcorn and Yadan Ouyang report. Treatment for diabetes has changed dramatically over the past 40 years in China,and no one knows this better than Wang Wenying.Now retired from her government job but as active and gregarious as ever,the 76-year-old remembers the onset of her type 2 diabetes back in 1974,before she had been diagnosed.At that time she weighed 15 kg more than she does today,and she had begun suffering from fainting spells and often felt thirsty."There's nothing wrong with you:it's a blessing that you eat a lot and are gaining weight",she recalls the doctor saying."Now I've realised that it's a suffering,not a blessing",she says. This is the paradox of diabetes in China:the epidemic is a direct byproduct of the country's rapid increase in prosperity,and many of the factors contributing to it are luxuries the Chinese have worked a lifetime to achieve,Rising household incomes have
Sap: 耗竭 糖尿病的病理生理学
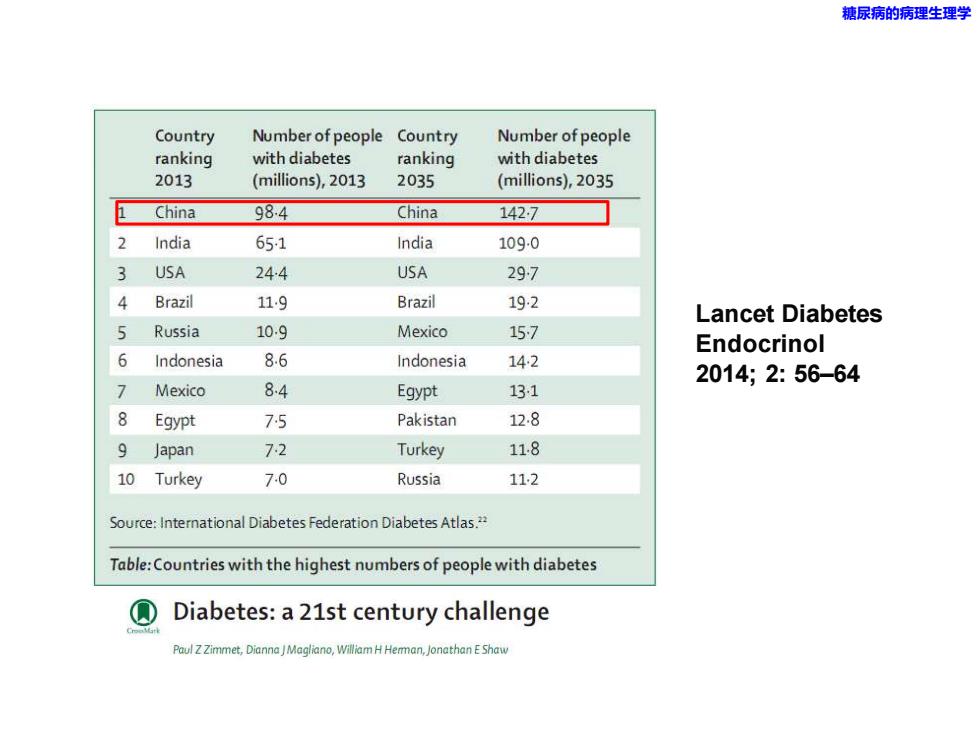
糖尿病的病理生理学 Country Number of people Country Number of people ranking with diabetes ranking with diabetes 2013 (millions),2013 2035 (millions),2035 China 984 China 1427 2 India 651 India 1090 3 USA 244 USA 297 4 Brazil 11.9 Brazil 192 Lancet Diabetes 5 Russia 10.9 Mexico 157 Endocrinol 6 Indonesia 8.6 Indonesia 142 2014;2:56-64 7 Mexico 84 Egypt 131 8 Egypt 75 Pakistan 12.8 9 Japan 72 Turkey 118 10 Turkey 7.0 Russia 11,2 Source:International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. Table:Countries with the highest numbers of people with diabetes Diabetes:a 21st century challenge Paul Z Zimmet,Dianna JMagliano,William H Hemman,Jonathan E Shaw
Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2014; 2: 56–64 糖尿病的病理生理学

糖尿病的病理生理学 糖尿病的病理生理学要解决什么问题? 病因和发病条件一胰岛素为什么会缺乏? 发病机制一胰岛素缺乏为什么会导致糖尿病? (胰岛素功能是什么?) 糖尿病时机体功能代谢有什么变化 症状、体征、并发症及其机制 治疗原则 上述几个问题,你认为这节课的重点在哪里?
糖尿病的病理生理学要解决什么问题? 发病机制—胰岛素缺乏为什么会导致糖尿病? (胰岛素功能是什么?) 病因和发病条件—胰岛素为什么会缺乏? 糖尿病时机体功能代谢有什么变化 症状、体征、并发症及其机制 治疗原则 糖尿病的病理生理学 上述几个问题,你认为这节课的重点在哪里?

一、糖尿病的病因学一各种原因导致胰岛素缺乏 有糖尿病家族史 疾病和生活压力 肥胖 不良的饮食及生活习惯 缺乏体力活动 既往有妊娠的妇女 年龄因素 曾经分娩过巨大胎儿的妇女
一、糖尿病的病因学—各种原因导致胰岛素缺乏

糖尿病的病理生理学一、病因和发病学 胰岛素为什么会缺乏?-1 遗传性因素 环境因素(病毒、毒素和应激) 自身免疫反应(缺失) 破坏了胰腺β细胞,导致胰岛素生成减少 1-胰岛素绝对缺乏 ↓ 1型糖尿病(T1DM,胰岛素依赖型糖尿病,IDDM)
胰岛素为什么会缺乏?--1 遗传性因素 环境因素(病毒、毒素和应激) 自身免疫反应(缺失) 破坏了胰腺β细胞,导致胰岛素生成减少 1--胰岛素绝对缺乏 1型糖尿病(T1DM,胰岛素依赖型糖尿病,IDDM) 糖尿病的病理生理学 一、病因和发病学